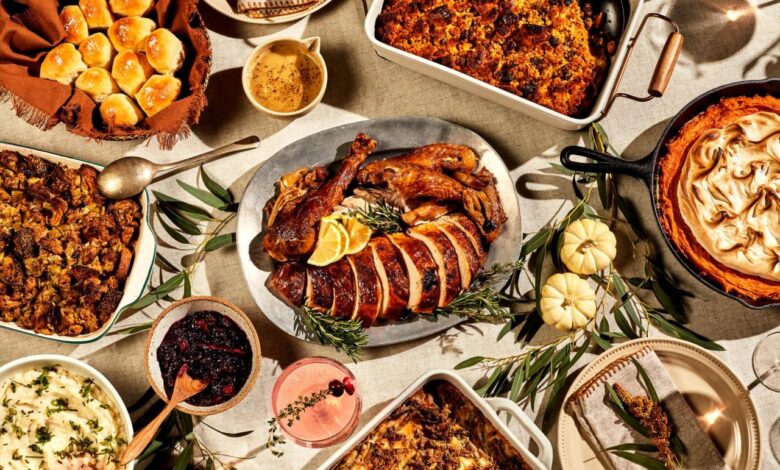
9 Thanksgiving Dishes & Their Sports Nutrition Benefit
9 thanksgiving dishes and their sports nutrition benefit – Thanksgiving, a time for family, feasting, and gratitude, is often associated with a delicious spread of traditional dishes. But beyond the culinary delight, these dishes can also offer valuable sports nutrition benefits for athletes. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your fitness journey, understanding the nutritional value of Thanksgiving favorites can help you fuel your body for peak performance.
From the protein-packed turkey to the carbohydrate-rich stuffing, Thanksgiving offers a variety of foods that can support your training and recovery. Let’s dive into the nutritional secrets of these popular dishes and explore how they can enhance your athletic performance.
Green Bean Casserole
Green bean casserole is a Thanksgiving staple, but it’s often loaded with unhealthy ingredients like cream of mushroom soup and fried onions. However, with a few simple swaps, you can make this classic dish a healthier option without sacrificing flavor.
From the protein-packed turkey to the complex carbs in mashed potatoes, Thanksgiving dishes can actually be a great source of sports nutrition! But if you’re worried about the calorie count, remember that boosting your metabolism is key. Check out this article on your secret to burning more calories at rest , and you can enjoy your Thanksgiving feast with a little less guilt! After all, a little bit of healthy indulgence is part of a balanced lifestyle, especially when it comes to those delicious cranberry sauce recipes!
Nutritional Benefits of Green Beans
Green beans are a nutrient-rich vegetable that provides a good source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as fiber and antioxidants. These vitamins and minerals are essential for various bodily functions, including immune system support, bone health, and vision.
Thanksgiving is a time for delicious food, but did you know that many traditional dishes offer surprising sports nutrition benefits? From the protein-packed turkey to the fiber-rich stuffing, there’s something for everyone. But what about calcium? While milk is a classic source, you can find it in other foods too! If you’re looking for calcium-rich alternatives to milk, check out 12 calcium rich alternatives to milk.
By incorporating these alternatives into your Thanksgiving feast, you can ensure your body gets the nutrients it needs to recover and rebuild after a big meal.
Impact of Casserole Ingredients on Nutritional Value
The nutritional value of green bean casserole can vary significantly depending on the ingredients used. The addition of cream of mushroom soup, fried onions, and other processed ingredients can increase the dish’s calorie, fat, and sodium content.
Tips for Creating a Healthier Green Bean Casserole
- Use fresh green beans: Fresh green beans have a higher nutrient content than canned green beans.
- Make your own creamy sauce: Instead of using canned cream of mushroom soup, you can make your own creamy sauce with low-fat milk, cornstarch, and fresh mushrooms.
- Use whole-wheat breadcrumbs: Instead of using traditional breadcrumbs, you can use whole-wheat breadcrumbs for added fiber.
- Bake instead of fry: Bake the onions instead of frying them to reduce the fat content.
- Add other vegetables: You can add other vegetables to your green bean casserole, such as carrots, mushrooms, or bell peppers, for added nutrients and flavor.
Pumpkin Pie
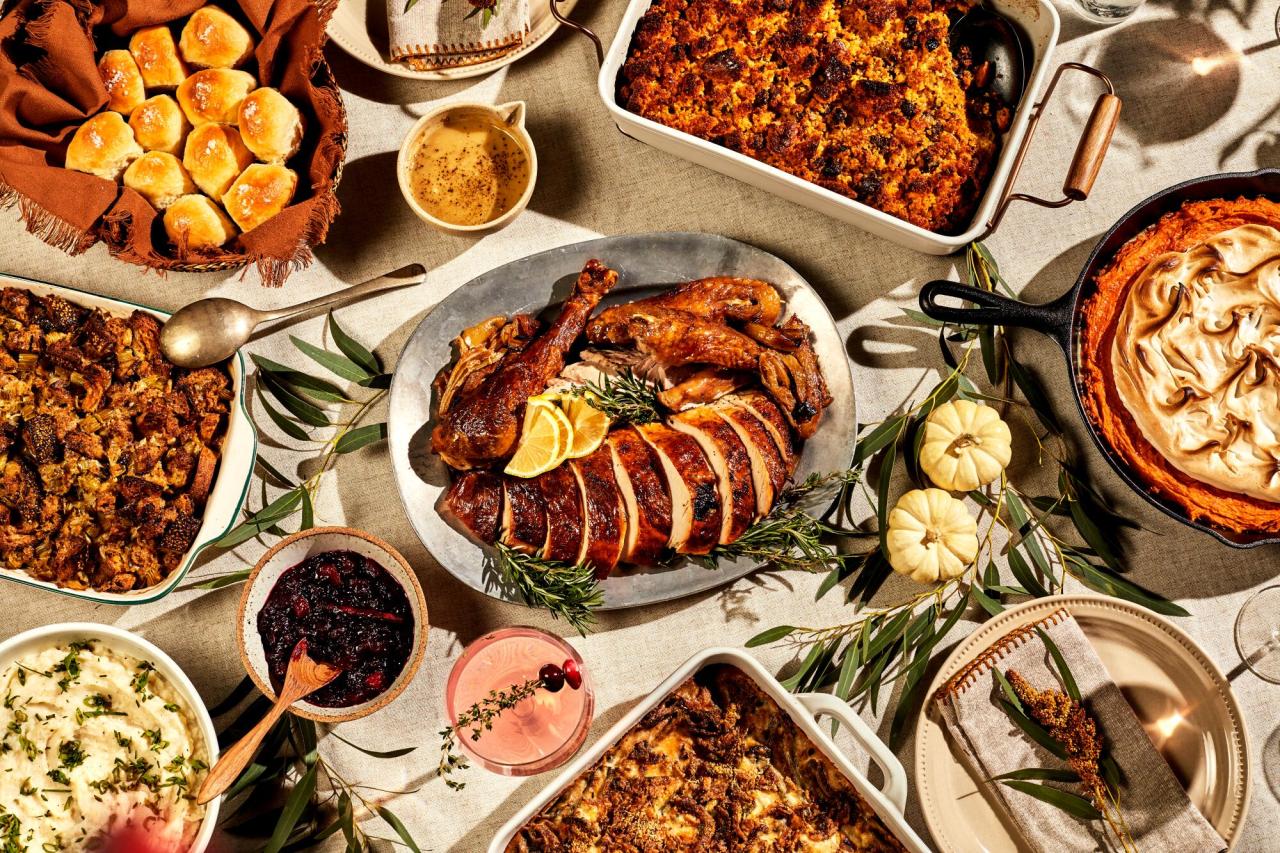

Pumpkin pie is a beloved Thanksgiving tradition, but it’s also a surprisingly nutritious choice. The star ingredient, pumpkin, is packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Nutritional Benefits of Pumpkin
Pumpkin is a powerhouse of nutrients, offering a range of health benefits. It’s an excellent source of vitamin A, which is crucial for healthy vision, skin, and immune function. Pumpkin is also rich in fiber, which aids digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Additionally, it contains potassium, which supports healthy blood pressure, and vitamin C, an antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
Impact of Pie Crust and Filling, 9 thanksgiving dishes and their sports nutrition benefit
The nutritional value of pumpkin pie can vary depending on the ingredients used. A traditional pie crust is typically made with refined flour, butter, and sugar, which can increase the calorie and fat content. However, opting for a whole wheat crust and using less sugar can significantly reduce the overall impact on your health.
Tips for a Healthier Pumpkin Pie
Creating a healthier pumpkin pie is achievable with a few simple adjustments. Consider using a whole wheat crust, which provides more fiber and nutrients than a refined flour crust. You can also reduce the amount of sugar used in the filling, relying on the natural sweetness of the pumpkin.
Additionally, incorporating spices like cinnamon and nutmeg can add flavor without adding extra calories.
Using whole wheat flour for the crust and reducing sugar in the filling can make pumpkin pie a more nutritious choice without compromising taste.
Ending Remarks: 9 Thanksgiving Dishes And Their Sports Nutrition Benefit
As we gather around the Thanksgiving table, let’s appreciate not only the culinary delights but also the nutritional benefits that these dishes offer. By understanding the sports nutrition value of our Thanksgiving favorites, we can enjoy a satisfying and fulfilling meal that supports our athletic goals.
So, let’s raise a glass to a healthy and happy Thanksgiving, filled with delicious food and the joy of being surrounded by loved ones.
From the protein-packed turkey to the carb-rich stuffing, Thanksgiving dishes offer a surprising amount of sports nutrition benefits. Of course, moderation is key, but you can find plenty of fuel for your workouts in these traditional favorites. But let’s be honest, even dietitians need a vacation from counting macros, and that’s where dietitians eat vacation comes in! So, enjoy your Thanksgiving feast, and then consider a trip where you can relax and recharge, ready to tackle those New Year’s resolutions with renewed energy.