
The Downsides of Caffeine for Athletes: What You Need to Know
The downsides of caffeine for athletes sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. We all know caffeine can give us that extra boost of energy, but for athletes, it might not be the miracle elixir they think it is.
While caffeine can provide a temporary energy surge, its long-term effects on athletic performance and recovery can be detrimental.
From dehydration and sleep disruption to anxiety and hindered muscle recovery, caffeine can present a number of challenges for athletes. This blog post delves into the potential downsides of caffeine for athletes, exploring its impact on hydration, sleep, energy levels, anxiety, muscle recovery, and interactions with other supplements.
We’ll also discuss the importance of individual variability in response to caffeine and how to make informed decisions about its consumption.
Impact on Hydration
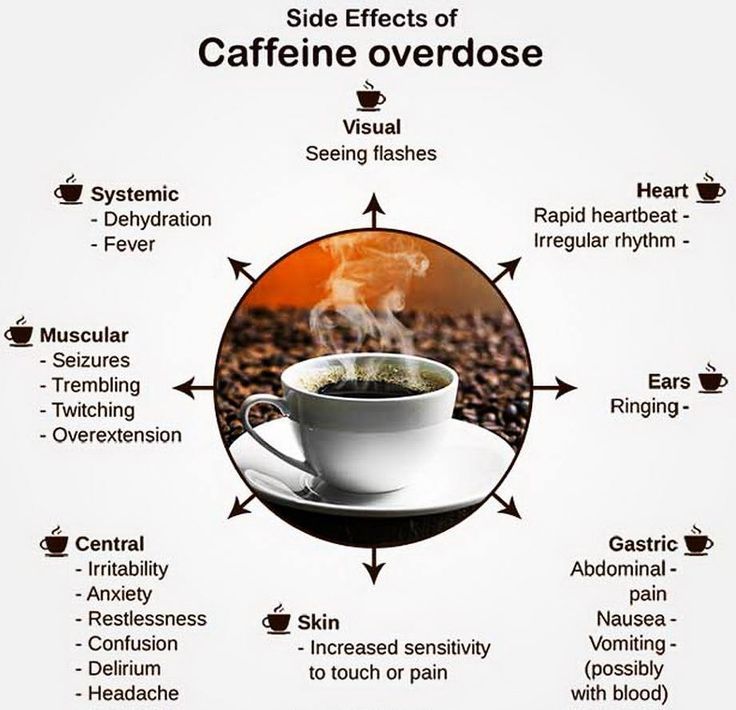
Caffeine is a diuretic, meaning it increases urine production. This can lead to dehydration, especially during intense exercise, when your body is already losing fluids through sweat. Dehydration can significantly impact athletic performance and recovery.
Importance of Proper Hydration for Athletic Performance and Recovery, The downsides of caffeine for athletes
Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for optimal athletic performance. Water plays a vital role in several bodily functions, including:* Thermoregulation:Water helps regulate body temperature during exercise, preventing overheating.
Nutrient Transport Water transports nutrients to muscles and removes waste products.
Joint Lubrication Water lubricates joints, reducing friction and improving movement.
Blood Volume Water maintains blood volume, ensuring efficient oxygen delivery to muscles.Dehydration can lead to various negative consequences, including:* Reduced Performance:Dehydration can decrease muscle strength, endurance, and reaction time.
Increased Fatigue Dehydration can contribute to fatigue and muscle cramps.
Increased Risk of Injury Dehydration can make muscles more susceptible to injury.
Delayed Recovery Dehydration can hinder the body’s ability to recover from exercise.
Recommendations for Athletes to Stay Hydrated While Consuming Caffeine
Athletes who consume caffeine should prioritize staying hydrated. Here are some recommendations:* Drink plenty of water throughout the day.Aim for 8-10 glasses of water daily.
- Drink water before, during, and after exercise.This helps replenish fluids lost through sweat.
- Consider using sports drinks.These drinks contain electrolytes, which can be lost through sweat.
- Avoid sugary drinks.Sugary drinks can contribute to dehydration.
- Listen to your body.If you feel thirsty, drink water.
“It is important to remember that caffeine is a diuretic and can lead to dehydration, especially during intense exercise. Athletes should prioritize staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day, before, during, and after exercise.”
While caffeine can provide a temporary energy boost, its long-term effects on athletes can be detrimental. It can lead to dehydration, disrupt sleep patterns, and increase anxiety. To combat these negative impacts, consider adopting a balanced diet that prioritizes whole foods and mindful eating habits, as outlined in an RD-approved approach to eating for fullness and satisfaction.
By fueling your body with nutritious foods, you’ll naturally improve your energy levels and overall well-being, ultimately enhancing your athletic performance and minimizing the downsides of caffeine consumption.
Effects on Sleep Quality
Caffeine’s stimulating effects can interfere with your sleep cycle, potentially impacting your recovery and athletic performance. While a morning cup of coffee might provide a much-needed boost, consuming caffeine too close to bedtime can disrupt your sleep patterns and leave you feeling sluggish the next day.
Caffeine’s Impact on Sleep
The impact of caffeine on sleep varies depending on individual sensitivity and the timing of consumption. However, caffeine’s effects on sleep can be summarized as follows:
- Delayed Sleep Onset:Caffeine can make it harder to fall asleep, extending the time it takes to reach a state of restful sleep. This delay can be particularly problematic for athletes who rely on adequate sleep for recovery and optimal performance.
- Reduced Sleep Duration:Caffeine can also shorten the total duration of sleep, leading to a sleep deficit. This can negatively affect energy levels, mood, and cognitive function, all of which are crucial for athletic performance.
- Disrupted Sleep Architecture:Caffeine can disrupt the different stages of sleep, including REM sleep, which is essential for memory consolidation and cognitive restoration. A reduction in REM sleep can hinder athletic performance by impairing learning, skill development, and overall recovery.
Recommended Time Frame for Caffeine Consumption
To minimize the disruptive effects of caffeine on sleep, it’s generally recommended to avoid consuming caffeine at least 6 hours before bedtime. However, individual sensitivity to caffeine can vary, so some individuals may need to avoid caffeine even earlier in the evening.
Caffeine’s Effects on Different Athletes
The effects of caffeine on sleep can vary depending on the athlete’s training schedule and competition demands. For example, athletes who train in the evening or compete at night may need to be particularly mindful of their caffeine intake to avoid sleep disruptions.
Athletes who compete in endurance events, where adequate sleep is crucial for recovery, may need to be especially cautious about caffeine consumption.
Influence on Energy Levels

Caffeine is known for its ability to provide an initial energy boost, making it a popular choice among athletes seeking to enhance their performance. However, this boost is often followed by an energy crash, which can negatively impact training and recovery.
The Energy Boost and Crash
Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, leading to increased alertness and a feeling of heightened energy. This is due to its ability to block adenosine receptors, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleepiness. This effect can be beneficial for athletes during intense training sessions or competitions, allowing them to push harder and perform better.
However, the energy boost is temporary and often followed by a crash, as the body becomes accustomed to the elevated levels of caffeine. This crash can leave athletes feeling tired, sluggish, and potentially hinder their ability to recover effectively.
Long-Term Impact on Energy Levels
The long-term use of caffeine can lead to dependence, meaning the body becomes accustomed to the presence of caffeine and requires higher doses to achieve the same effect. This dependence can lead to a cycle of caffeine use and withdrawal, impacting energy levels in the long run.
Caffeine Effects on Different Exercise Types
The impact of caffeine on energy levels can vary depending on the type of exercise.
| Exercise Type | Effects of Caffeine |
|---|---|
| Endurance Training | Caffeine can improve endurance performance by reducing perceived exertion and increasing fat oxidation. However, excessive caffeine intake can lead to dehydration and negatively impact performance. |
| Strength Training | Caffeine can enhance strength and power output, particularly in short-duration, high-intensity exercises. However, its impact on muscle growth and recovery is limited. |
| Power Training | Caffeine can improve power output and explosive strength, particularly in activities like sprinting and jumping. |
Potential for Anxiety and Jitters
Caffeine is a stimulant that can trigger the release of adrenaline, which can lead to feelings of anxiety and jitters, especially in individuals sensitive to its effects. This is particularly relevant for athletes, as their bodies are already under significant stress and their performance relies heavily on focus and composure.
Impact on Focus and Concentration
Caffeine can interfere with focus and concentration during athletic performance, especially in athletes sensitive to its effects. When caffeine levels are high, the body enters a state of heightened alertness, which can lead to feelings of restlessness and difficulty concentrating.
This can negatively impact an athlete’s ability to perform at their best, especially in activities that require fine motor skills, strategic thinking, or precise timing.
While caffeine can provide a temporary energy boost, its downsides for athletes are undeniable. It can lead to dehydration, disrupt sleep patterns, and even hinder performance in the long run. But don’t let that discourage you from fueling your workouts with healthy, delicious meals! If you’re stuck in a meal prep rut, check out these 6 proven ways to get out of a meal prep plateau.
With a little creativity and planning, you can easily create a meal prep routine that supports your athletic goals without relying on caffeine’s fleeting effects.
Managing Caffeine Intake to Minimize Anxiety and Jitters
Athletes can manage their caffeine intake to minimize the risk of experiencing anxiety and jitters. Here are some key strategies:
- Start with a Low Dose:Begin with a small amount of caffeine to assess your individual tolerance and gradually increase the dosage as needed.
- Time Your Intake:Avoid consuming caffeine close to bedtime, as it can disrupt sleep patterns and negatively impact performance the next day. Ideally, limit caffeine intake several hours before bedtime.
- Hydration:Adequate hydration is crucial for managing caffeine’s effects. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out caffeine and prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate anxiety and jitters.
- Listen to Your Body:Pay attention to your body’s response to caffeine. If you experience any adverse effects, such as anxiety, jitters, or difficulty sleeping, reduce your intake or avoid caffeine altogether.
Impact on Muscle Recovery: The Downsides Of Caffeine For Athletes
While caffeine can provide a temporary energy boost, its effects on muscle recovery are not as positive. Caffeine can interfere with the body’s natural recovery processes, potentially hindering the repair and rebuilding of muscle tissue after intense exercise.
Caffeine’s Effect on Muscle Recovery
Caffeine’s impact on muscle recovery is primarily related to its influence on inflammation and its interaction with various recovery strategies.
While caffeine can provide a temporary boost, it’s important to remember that it can also have negative effects on athletic performance. For instance, it can lead to dehydration, anxiety, and sleep disturbances, all of which can hinder your training and recovery.
If you’re feeling stressed, try incorporating some stress-reducing techniques into your routine, such as taking a few deep breaths or checking out these 8 quick ways to reduce stress right now. By managing stress and making informed choices about caffeine consumption, you can optimize your athletic performance and overall well-being.
Influence on Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response to exercise, signaling the body to initiate repair and rebuilding processes. However, caffeine can suppress the inflammatory response, potentially delaying the healing process.
Caffeine’s suppression of inflammation might seem beneficial initially, as it can reduce post-workout soreness. However, this suppression can hinder the body’s ability to effectively repair damaged muscle tissue.
Interaction with Recovery Strategies
Caffeine’s effect on muscle recovery can vary depending on the specific recovery strategies employed.
Massage
Caffeine can potentially interfere with the benefits of massage therapy. Massage helps to increase blood flow and reduce muscle tension, promoting relaxation and recovery. However, caffeine can constrict blood vessels, potentially hindering the effectiveness of massage.
Stretching
While caffeine’s impact on stretching is less clear, it’s important to note that caffeine can dehydrate the body. Dehydration can make muscles less flexible, potentially reducing the benefits of stretching.
Ice Baths
Caffeine’s effect on ice baths is complex and not fully understood. Ice baths are often used to reduce inflammation and pain, but caffeine’s potential to suppress inflammation might interfere with this process.
Interactions with Other Supplements
Athletes often use a variety of supplements to enhance their performance, and caffeine is a common addition to their routines. However, it’s crucial to understand how caffeine can interact with other supplements, as these interactions can affect both the effectiveness and safety of your supplement regimen.
Potential Interactions with Creatine
Creatine is a popular supplement that helps increase muscle mass and strength. When combined with caffeine, it can potentially enhance the benefits of both. Research suggests that caffeine may improve creatine uptake into muscle cells, leading to a more significant increase in muscle mass and strength.
Caffeine can enhance creatine uptake into muscle cells, potentially leading to increased muscle mass and strength.
However, there is also evidence suggesting that caffeine might interfere with creatine’s ability to increase muscle mass. Some studies indicate that caffeine can reduce creatine’s ability to increase muscle protein synthesis, a process essential for muscle growth.
Caffeine may interfere with creatine’s ability to increase muscle protein synthesis, which could potentially reduce muscle growth.
While the exact impact of caffeine on creatine’s effectiveness is still being studied, it’s essential to be aware of these potential interactions and adjust your supplement regimen accordingly.
Potential Interactions with Protein Powder
Protein powder is another popular supplement used by athletes to support muscle growth and repair. Caffeine can interact with protein powder in a few ways.
Caffeine can affect the absorption and utilization of protein, potentially impacting muscle growth and repair.
One potential interaction is that caffeine can increase the rate of protein breakdown, which could counteract the muscle-building effects of protein powder. On the other hand, caffeine may also enhance protein synthesis, potentially boosting muscle growth.
Caffeine may increase the rate of protein breakdown, potentially counteracting the muscle-building effects of protein powder.
More research is needed to fully understand the complex interplay between caffeine and protein powder, but athletes should be aware of these potential interactions and adjust their supplement intake accordingly.
Managing Caffeine Intake with Other Supplements
To manage caffeine intake safely and effectively alongside other supplements, consider the following:
- Start with a low dose of caffeine and gradually increase itas needed to assess your individual tolerance and avoid any adverse effects.
- Pay attention to your body’s response to caffeine, including energy levels, sleep quality, and anxiety levels. If you experience any negative effects, reduce your caffeine intake or discontinue its use.
- Consult with a healthcare professionalbefore using caffeine or any other supplements, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
- Read the labels of your supplements carefullyto understand their ingredients and potential interactions with caffeine.
- Avoid combining caffeine with other stimulants, such as ephedrine or guarana, as this can increase the risk of adverse effects.
End of Discussion
While caffeine can offer a temporary boost, its long-term effects on athletic performance and recovery can be detrimental. Ultimately, the decision to consume caffeine should be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account individual needs, training goals, and potential risks.
By understanding the potential downsides of caffeine and making informed choices, athletes can optimize their performance and ensure their long-term health and well-being.






