Carb Cycling: Does It Really Help You Lose Weight?
What is carb cycling and does it promote weight loss? It’s a diet strategy that involves cycling your carbohydrate intake throughout the week, often alternating between high-carb and low-carb days. This fluctuating approach aims to manipulate your body’s hormonal response and metabolism, potentially boosting weight loss and athletic performance.
But does it really work? Let’s dive into the details and explore the science behind this popular diet trend.
Carb cycling works by manipulating your body’s insulin and glycogen levels. When you consume carbohydrates, your body releases insulin, which helps shuttle glucose into your cells for energy. If you consistently eat a high-carb diet, your body can become insulin-resistant, making it harder to burn fat.
However, by cycling your carbohydrate intake, you can potentially improve insulin sensitivity and promote fat burning. This approach can also help regulate your energy levels, prevent plateaus in your weight loss journey, and even enhance your athletic performance.
What is Carb Cycling?
Carb cycling is a dietary strategy that involves manipulating carbohydrate intake throughout the week or a specific period. This approach aims to optimize energy levels, improve athletic performance, and potentially promote weight loss by strategically altering carbohydrate consumption.
Different Phases of Carb Cycling
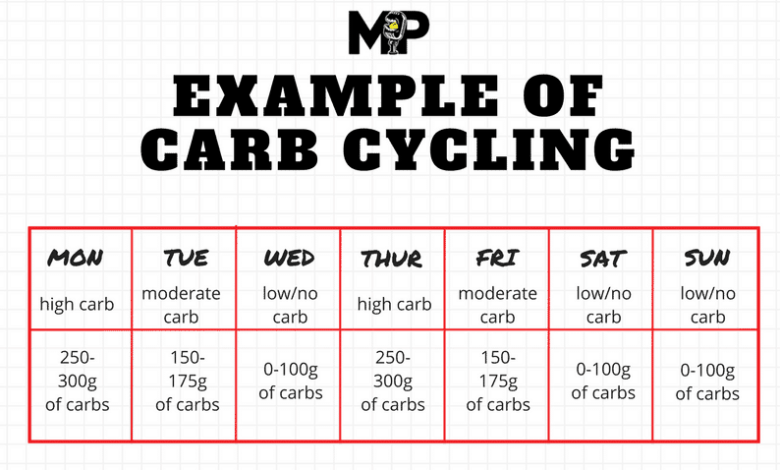
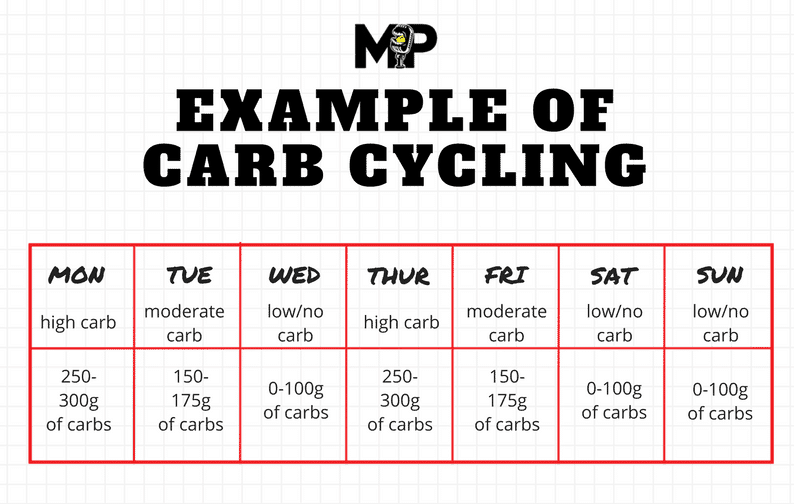
Carb cycling typically involves three distinct phases: high-carb, moderate-carb, and low-carb days.
- High-carb daysare characterized by increased carbohydrate intake, usually consumed before or after intense workouts. This phase helps replenish glycogen stores, optimize energy levels for training, and support muscle recovery.
- Moderate-carb daysinvolve a moderate carbohydrate intake, balancing energy needs with weight management goals. This phase provides a sustainable level of energy for daily activities without excessive calorie intake.
- Low-carb daysfeature a reduced carbohydrate intake, typically implemented on rest days or during periods of lower activity. This phase promotes fat burning and potentially supports weight loss by reducing overall calorie consumption.
Carb Cycling Meal Plans
Here are examples of carb cycling meal plans for different phases:
High-Carb Day Meal Plan
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and nuts (40g carbs)
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast with quinoa and vegetables (60g carbs)
- Dinner: Salmon with brown rice and steamed broccoli (70g carbs)
- Snack: Greek yogurt with fruit (20g carbs)
Moderate-Carb Day Meal Plan
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with whole-wheat toast (30g carbs)
- Lunch: Tuna salad sandwich on whole-grain bread (40g carbs)
- Dinner: Chicken stir-fry with vegetables and brown rice (50g carbs)
- Snack: Cottage cheese with fruit (15g carbs)
Low-Carb Day Meal Plan
- Breakfast: Eggs with spinach and avocado (10g carbs)
- Lunch: Chicken salad with mixed greens (20g carbs)
- Dinner: Salmon with asparagus and cauliflower rice (30g carbs)
- Snack: Nuts and seeds (5g carbs)
Potential Benefits of Carb Cycling
Carb cycling may offer several potential benefits, including:
- Improved Athletic Performance: By strategically increasing carbohydrate intake on training days, carb cycling helps replenish glycogen stores, providing the energy needed for intense workouts and supporting muscle recovery.
- Enhanced Body Composition: Carb cycling can potentially aid in fat loss by promoting periods of calorie restriction and fat burning during low-carb days, while still supporting muscle growth and maintenance through high-carb days.
How Carb Cycling Works for Weight Loss: What Is Carb Cycling And Does It Promote Weight Loss
Carb cycling, a popular weight loss strategy, involves strategically altering your carbohydrate intake throughout the week to manipulate your body’s metabolic response. This approach aims to boost metabolism, promote fat burning, and prevent plateaus.
Carb Cycling and Its Impact on Metabolism and Weight Loss
Carb cycling works by influencing insulin levels and glycogen storage in the body. When you consume carbohydrates, your body releases insulin, a hormone that helps shuttle glucose into your cells for energy. Excess glucose is stored as glycogen in your liver and muscles.
During periods of lower carb intake, your body depletes glycogen stores, leading to increased fat burning.
Carb cycling is a dietary strategy that involves alternating between high and low carbohydrate intake days. It’s often touted as a way to boost metabolism and promote weight loss, but the science is still somewhat mixed. If you’re interested in pushing your physical limits, you might want to check out everything you need to know about ultra walking , which involves walking for extended distances and durations.
While ultra walking requires a lot of energy, it’s important to remember that a well-rounded diet and proper hydration are key for both athletic performance and overall health, including whether or not carb cycling works for you.
The Role of Insulin and Glycogen in Weight Loss
Insulin is a key player in carb cycling. When insulin levels are high, your body is more likely to store fat. Conversely, when insulin levels are low, your body is more likely to burn fat for energy. Carb cycling manipulates insulin levels by alternating between high and low carb days.
- High-carb days:These days provide your body with adequate carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores and support muscle recovery, particularly after intense workouts. They also help boost your metabolism and prevent muscle loss.
- Low-carb days:These days help lower insulin levels, promote fat burning, and potentially improve insulin sensitivity.
Comparison with Other Weight Loss Strategies
Carb cycling shares similarities with other weight loss strategies, but it also has its own unique aspects.
- Calorie restriction:This involves reducing your overall calorie intake to create a calorie deficit, which is essential for weight loss. Carb cycling can be incorporated into a calorie-restricted diet by strategically adjusting carb intake on different days.
- Ketogenic diets:These diets are very low in carbohydrates and high in fat, forcing your body to enter a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for energy. Carb cycling differs from ketogenic diets by allowing for higher carbohydrate intake on specific days.
Real-World Examples of Successful Carb Cycling
Several individuals have reported success with carb cycling for weight loss. For instance, a study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that carb cycling was effective in reducing body weight and improving body composition in overweight and obese individuals.
Potential Benefits of Carb Cycling
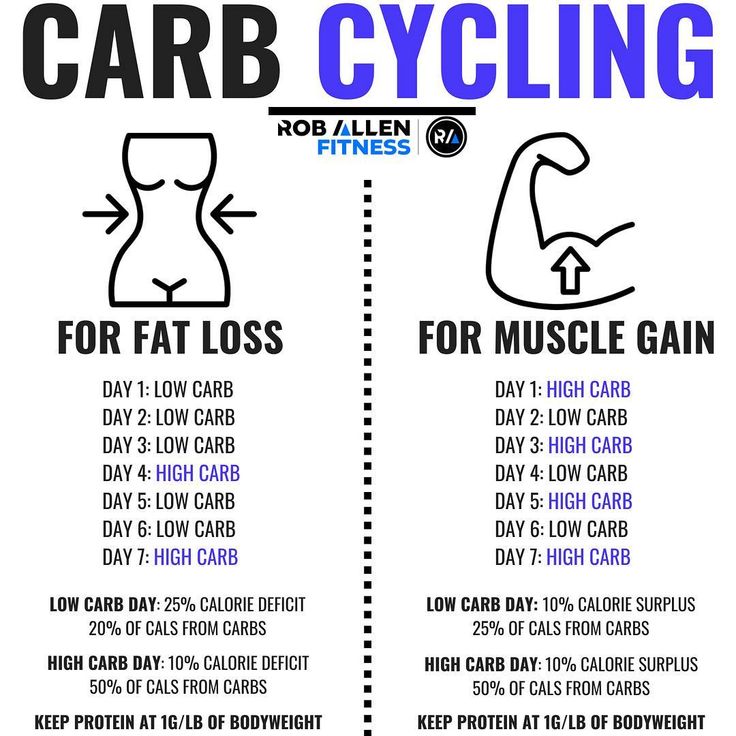
Carb cycling can offer a range of potential benefits beyond weight loss, impacting various aspects of your health and well-being. This strategy involves strategically manipulating your carbohydrate intake throughout the week, aiming to optimize your body’s response to fuel and maximize performance.
Carb Cycling and Athletic Performance
Carb cycling can potentially enhance athletic performance by optimizing energy levels and endurance. When you consume a higher amount of carbohydrates on training days, your body has ample glycogen stores, the primary energy source for muscles during exercise. This can lead to increased energy, reduced fatigue, and improved endurance, enabling you to push harder during workouts.
Carb Cycling and Body Composition
Carb cycling can potentially contribute to favorable body composition changes, promoting muscle growth and fat loss. During high-carb days, your body is better equipped to build muscle due to increased protein synthesis and glycogen replenishment. On low-carb days, your body relies more on fat for energy, potentially leading to fat loss.
This cyclical approach can help optimize your body’s response to macronutrients, supporting both muscle growth and fat reduction.
Carb Cycling and Blood Sugar Management
Carb cycling can potentially help manage blood sugar levels by minimizing fluctuations and promoting insulin sensitivity. By consuming a higher amount of carbohydrates on training days, you can better regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. On low-carb days, your body adapts to using fat as a primary energy source, potentially reducing insulin resistance.
This cyclical approach can help maintain blood sugar balance and improve overall metabolic health.
Carb Cycling and Mental Clarity
Carb cycling can potentially enhance mental clarity and mood by optimizing brain function. When you consume a higher amount of carbohydrates on training days, your brain has access to ample glucose, its primary energy source. This can lead to improved cognitive function, focus, and mood.
Carb cycling, where you manipulate your carbohydrate intake throughout the week, can be a trendy approach to weight loss. While it can lead to short-term weight fluctuations, focusing on sustainable, long-term strategies is key. For a more holistic approach, I recommend exploring an RD-approved approach to eating for fullness and satisfaction , which prioritizes balanced nutrition and mindful eating habits.
This approach will help you build a healthy relationship with food, promoting sustainable weight management and overall well-being, which are ultimately more important than quick fixes like carb cycling.
On low-carb days, your body may experience an increase in ketone production, which can also provide an alternative energy source for the brain, potentially leading to enhanced mental clarity and focus.
Potential Risks and Drawbacks of Carb Cycling
While carb cycling can be an effective weight loss strategy for some, it’s crucial to understand its potential downsides and risks. Like any diet plan, carb cycling can have unintended consequences if not implemented correctly or if you’re not a suitable candidate.
Nutrient Deficiencies and Hormonal Imbalances
Carb cycling can potentially lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly if you drastically restrict your carbohydrate intake on low-carb days. This can affect your energy levels, mood, and overall health. For example, reducing your carbohydrate intake can lower your intake of essential vitamins and minerals found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Additionally, drastic fluctuations in carbohydrate intake can disrupt hormonal balance, impacting insulin sensitivity and thyroid function. This can further affect your metabolism and weight management goals.
Impact on Energy Levels and Mood
The fluctuating carbohydrate intake associated with carb cycling can significantly impact your energy levels and mood. On low-carb days, you might experience fatigue, brain fog, and irritability due to reduced glucose availability for brain function. On high-carb days, you may experience energy spikes followed by crashes, leading to mood swings and difficulty concentrating.
Difficulty Maintaining Long-Term Adherence, What is carb cycling and does it promote weight loss
Carb cycling requires meticulous planning and discipline, making it challenging to maintain long-term adherence. The constant switching between high-carb and low-carb days can be mentally taxing, leading to cravings, feelings of deprivation, and potential for binge eating.
Potential Risks for Individuals with Certain Health Conditions
Carb cycling can pose risks for individuals with certain health conditions, such as diabetes. For example, fluctuating blood sugar levels due to carb cycling can be challenging to manage for individuals with diabetes, potentially leading to complications. Individuals with diabetes should consult their healthcare provider before embarking on carb cycling.
Who is Carb Cycling Suitable For?
Carb cycling can be a beneficial dietary approach for certain individuals, particularly those aiming to optimize their athletic performance or improve their body composition. However, it’s crucial to understand that carb cycling isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution and might not be suitable for everyone.
Suitability for Individuals with Specific Health Conditions
It’s essential to consider the potential impact of carb cycling on individuals with specific health conditions. For example, individuals with diabetes should consult with their healthcare provider before implementing carb cycling, as it can significantly affect blood sugar levels. Similarly, individuals with kidney disease or other metabolic disorders may need to adjust their carb intake based on their individual needs.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before embarking on any new dietary regimen, including carb cycling, it’s highly recommended to consult with a healthcare professional. A qualified healthcare provider can assess your individual needs, health history, and potential risks associated with carb cycling. They can also provide personalized guidance and support to ensure you’re following a safe and effective approach.
Finding a Qualified Nutritionist or Dietitian
If you’re considering carb cycling, seeking advice from a qualified nutritionist or dietitian can be invaluable. A registered dietitian can help you create a customized carb cycling plan tailored to your specific goals and health conditions. They can also provide ongoing support and guidance to ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs and achieving your desired outcomes.
To find a qualified nutritionist or dietitian in your area, you can consult with your primary care physician, search online directories, or contact professional organizations such as the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Designing a Carb Cycling Plan
Creating a carb cycling plan involves a structured approach to manipulate carbohydrate intake across different days or weeks to achieve specific goals. The plan should be tailored to individual needs, considering factors like activity levels, body composition goals, and personal preferences.
Carb cycling, a popular weight loss strategy, involves manipulating your carbohydrate intake throughout the week. While it can be an effective tool for some, it’s important to remember that sustainable weight loss comes from a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Speaking of balance, have you seen the beautiful spread of colors you can achieve on your Thanksgiving table? Check out these 5 ways to fill your Thanksgiving table with color for a truly festive and vibrant feast. Remember, incorporating a variety of colorful foods, both on Thanksgiving and throughout the year, is a great way to ensure you’re getting a diverse range of nutrients, which is crucial for both weight management and overall health.
So, while carb cycling might be a temporary strategy, a balanced diet rich in color is a lifestyle choice that will benefit you long-term.
Steps to Designing a Carb Cycling Plan
Designing a carb cycling plan requires a systematic approach to ensure it aligns with your goals and lifestyle. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Determine your goals:Define what you hope to achieve with carb cycling. This could be weight loss, muscle gain, improved athletic performance, or better blood sugar control. Understanding your goals will help you structure your plan accordingly.
- Calculate your daily calorie needs:This is crucial for determining the appropriate carbohydrate intake for each day. You can use online calculators or consult with a registered dietitian to estimate your daily calorie requirements based on your age, sex, activity level, and body composition.
- Establish your carb cycling pattern:This involves deciding how many days per week you’ll have high-carb days, moderate-carb days, and low-carb days. Common patterns include 3 high-carb days, 2 moderate-carb days, and 2 low-carb days, or a more flexible approach based on your specific needs and preferences.
- Set specific carb ranges for each day:Once you’ve established your carb cycling pattern, define the carbohydrate intake for each day. This should be based on your calorie needs and your goals. For instance, a high-carb day might be 40-50% of your total calories from carbohydrates, a moderate-carb day 25-35%, and a low-carb day 10-20%.
- Choose your macronutrient ratios:In addition to carbohydrates, determine your protein and fat intake for each day. Aim for a balanced macronutrient distribution to ensure you’re getting enough of all essential nutrients.
- Plan your meals:Based on your chosen carb ranges, create a meal plan for each day of the week. Include a variety of nutrient-rich foods from different food groups to ensure a balanced diet.
- Monitor your progress:Track your weight, body composition, energy levels, and overall well-being. This will help you determine if your carb cycling plan is working for you and make adjustments as needed.
Examples of Carb Cycling Plans
Carb cycling plans can be customized to suit individual needs and goals. Here are examples of different plans for various purposes:
Weight Loss Carb Cycling Plan
- High-carb days:40-50% of calories from carbohydrates, focusing on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Moderate-carb days:25-35% of calories from carbohydrates, with a focus on lean protein and healthy fats.
- Low-carb days:10-20% of calories from carbohydrates, prioritizing protein and healthy fats, with limited intake of refined carbohydrates.
Muscle Gain Carb Cycling Plan
- High-carb days:50-60% of calories from carbohydrates, with an emphasis on complex carbohydrates to fuel intense workouts.
- Moderate-carb days:30-40% of calories from carbohydrates, focusing on protein and healthy fats for muscle recovery.
- Low-carb days:15-25% of calories from carbohydrates, prioritizing protein and healthy fats to promote fat loss and muscle definition.
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
Regularly monitoring your progress is crucial to ensure your carb cycling plan is effective. Track your weight, body composition, energy levels, and overall well-being. If you’re not seeing the desired results or experiencing any negative side effects, consider making adjustments to your plan.
- Increase or decrease carb intake:If you’re not losing weight, try decreasing your carbohydrate intake on low-carb days or increasing it on high-carb days. If you’re experiencing excessive fatigue or muscle loss, consider increasing your carbohydrate intake overall.
- Adjust macronutrient ratios:If you’re not seeing desired results in terms of weight loss or muscle gain, experiment with different macronutrient ratios. For example, increase your protein intake on low-carb days or decrease it on high-carb days.
- Change the frequency of carb cycling:If you’re finding the current carb cycling pattern too restrictive or too challenging, consider adjusting the frequency. You could try cycling your carbs less frequently, such as once or twice a week, or more frequently, such as every other day.
Maintaining Consistency and Long-Term Adherence
Consistency is key to success with carb cycling. Here are tips for maintaining long-term adherence:
- Find a plan that works for you:Choose a carb cycling pattern that aligns with your goals, lifestyle, and preferences. Experiment with different plans to find one that you can stick with long-term.
- Make gradual changes:Don’t drastically change your diet overnight. Gradually adjust your carbohydrate intake and meal plans to give your body time to adapt.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods:Prioritize nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This will help you stay full and satisfied while fueling your body effectively.
- Listen to your body:Pay attention to how your body feels on different carb days. If you’re feeling excessively tired or sluggish, adjust your carbohydrate intake accordingly.
- Be patient and persistent:Carb cycling takes time and consistency to see results. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see immediate changes. Stick with your plan and make adjustments as needed.
Carb Cycling vs. Other Diets
Carb cycling is a popular weight loss strategy that involves manipulating carbohydrate intake throughout the week. But how does it stack up against other popular diets like ketogenic diets, intermittent fasting, and calorie restriction? Let’s dive into a comparison of these approaches and their potential benefits and drawbacks.
Comparison of Carb Cycling with Other Diets
Carb cycling, ketogenic diets, intermittent fasting, and calorie restriction are all popular weight loss strategies, each with its own unique mechanisms and potential benefits. Here’s a breakdown of their key features, pros, and cons:
| Diet | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carb Cycling | Alternating high-carb and low-carb days to manipulate insulin levels and boost metabolism. |
|
|
| Ketogenic Diet | High-fat, very low-carb diet that forces the body to enter ketosis, burning fat for energy. |
|
|
| Intermittent Fasting | Restricting calorie intake for specific periods, such as daily time-restricted feeding or alternate-day fasting. |
|
|
| Calorie Restriction | Reducing overall calorie intake to create a calorie deficit for weight loss. |
|
|
Effectiveness of Different Diets for Weight Loss
The effectiveness of different diets for weight loss can vary depending on individual factors like metabolism, genetics, and lifestyle. However, research suggests that all of these approaches can be effective for weight loss when followed consistently.
“A systematic review of 12 studies found that carb cycling was associated with significant weight loss and improved body composition compared to a control group.”
(Source
[Insert credible source here])
“A meta-analysis of 13 randomized controlled trials found that ketogenic diets resulted in greater weight loss than low-fat diets over a period of 6-12 months.”
(Source
[Insert credible source here])
“Intermittent fasting has been shown to be effective for weight loss, with studies demonstrating an average weight loss of 3-8% over 3-24 weeks.”
(Source
[Insert credible source here])
“Calorie restriction is a well-established strategy for weight loss, with studies consistently showing that reducing calorie intake leads to weight loss.”
(Source
[Insert credible source here])
Choosing the Right Diet for You
The best diet for you will depend on your individual needs, preferences, and goals. Consider the following factors:
- Your health goals:What are you hoping to achieve with your diet? Weight loss, improved blood sugar control, increased energy levels, or other health benefits?
- Your lifestyle:How much time and effort are you willing to invest in your diet? Do you prefer flexibility or strict adherence?
- Your preferences:What foods do you enjoy? Are you comfortable with certain dietary restrictions, such as avoiding carbohydrates or specific food groups?
- Your health status:Do you have any medical conditions that might affect your diet choices? It’s always advisable to consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting any new diet.
Final Review
Carb cycling can be a useful tool for those seeking to optimize their weight loss journey, but it’s not a magic bullet. It’s important to understand that this approach requires careful planning and can have potential risks if not implemented correctly.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new diet, and be sure to listen to your body. If you’re considering carb cycling, it’s best to do so under the guidance of a qualified nutritionist or dietitian.