
Ask the RD: Can Diet Reduce Arthritis Inflammation?
Ask the rd can diet reduce the inflammation that causes arthritis – Ask the RD: Can Diet Reduce Arthritis Inflammation? Arthritis, a chronic condition affecting millions, is often characterized by pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. While there’s no cure for arthritis, managing its symptoms is crucial for improving quality of life.
One approach gaining traction is dietary intervention, focusing on reducing inflammation, a key player in arthritis development and progression.
The link between diet and inflammation is becoming increasingly evident. Certain foods can trigger inflammatory responses in the body, potentially exacerbating arthritis symptoms. Conversely, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may help dampen these responses, providing relief and improving overall well-being.
Understanding Arthritis and Inflammation
Arthritis is a condition that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. It is a common condition, affecting millions of people worldwide. Inflammation plays a crucial role in the development and progression of arthritis.
Types of Arthritis, Ask the rd can diet reduce the inflammation that causes arthritis
Arthritis is an umbrella term encompassing various conditions that affect the joints. Here are some of the most common types:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):This is the most prevalent type of arthritis, often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited movement.
You’re asking if diet can help reduce inflammation that causes arthritis? It’s a great question, and the answer is complex. While some foods can definitely contribute to inflammation, managing stress is also crucial. Check out these 8 quick ways to reduce stress right now to see how stress reduction can play a role in your overall health and well-being, including managing inflammation.
Ultimately, working with a registered dietitian can help you tailor a diet plan that addresses your specific needs and may help you manage inflammation.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):This is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the tissues lining the joints, causing inflammation and damage. It can affect any joint, but commonly affects the hands, wrists, feet, and knees.
- Gout:This type of arthritis is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, resulting in sudden, severe pain, redness, and swelling. It commonly affects the big toe.
- Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA):This is an inflammatory arthritis that affects people with psoriasis, a skin condition. It can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, as well as skin lesions.
The Role of Inflammation in Arthritis
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection. It involves a complex process that brings white blood cells to the affected area to fight off the cause of inflammation. However, in arthritis, this process becomes chronic and persistent, leading to damage in the joints.
So many people ask me if diet can reduce the inflammation that causes arthritis, and it’s a complex question. One common concern is pasta, as it’s often associated with carbs and inflammation. But is that true? You might be surprised to learn that pasta can actually be healthy, especially when made with whole grains and paired with plenty of vegetables.
To learn more about how to make pasta a part of a healthy diet, check out this article on can pasta be healthy. Once you understand the basics of a healthy diet, we can talk more about how it might affect arthritis inflammation.
Inflammation and Joint Pain, Stiffness, and Swelling
The inflammation in arthritis causes the following symptoms:
- Pain:Inflammation triggers the release of chemicals that cause pain in the affected joints. The pain can be constant or intermittent, and it can worsen with activity.
- Stiffness:Inflammation can cause the joint tissues to become stiff and difficult to move. This stiffness is often worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Swelling:Inflammation causes fluid to build up in the joint, leading to swelling. This swelling can make it difficult to move the joint and can also cause pain.
The Potential of Diet in Managing Arthritis
While arthritis is a complex condition with no single cure, research suggests that diet can play a significant role in managing symptoms and potentially slowing disease progression. The connection between diet and inflammation, a key factor in arthritis, is a growing area of study.
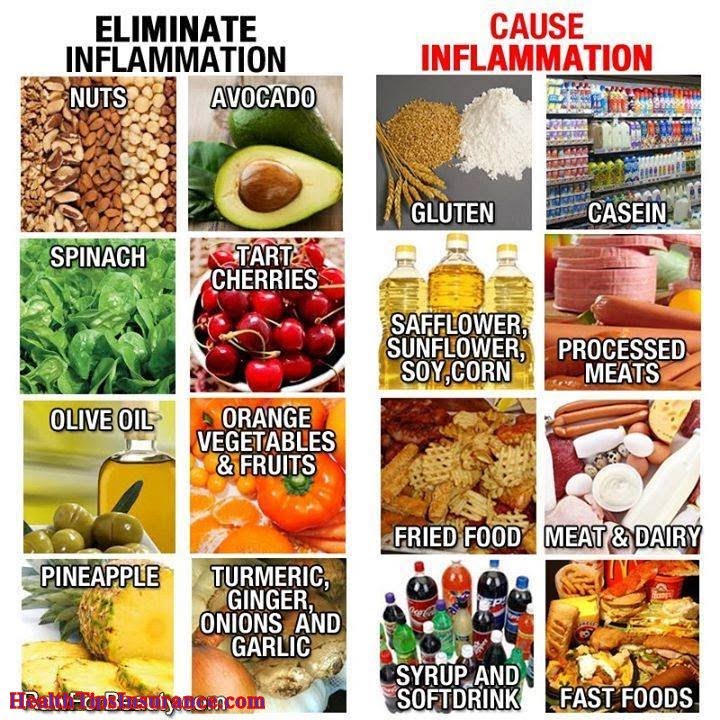
Foods that Contribute to Inflammation
Certain foods can trigger or exacerbate inflammation, potentially worsening arthritis symptoms. Understanding these dietary triggers can help individuals make informed choices to manage their condition.
So, you’re wondering if diet can really help reduce the inflammation that causes arthritis? It’s a great question, and the answer is a resounding yes! A healthy diet that emphasizes anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and berries can definitely make a difference.
For some tasty inspiration, check out these 9 hearty winter soups under 360 calories that are packed with flavor and nutrients. By incorporating these nourishing soups into your routine, you can support your overall health and well-being, potentially helping to manage the inflammation associated with arthritis.
- Processed Foods:High in saturated and trans fats, processed foods, such as packaged snacks, fried foods, and processed meats, contribute to inflammation. These foods are often high in refined carbohydrates, which can also promote inflammation.
- Sugar:Excessive sugar intake can lead to increased inflammation, potentially aggravating arthritis symptoms. This includes added sugars found in processed foods, sugary drinks, and desserts.
- Red Meat:While red meat is a source of protein, consuming excessive amounts can contribute to inflammation due to its high saturated fat content.
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids:While essential for health, excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids, found in vegetable oils like corn, soybean, and sunflower oil, can promote inflammation.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals: Ask The Rd Can Diet Reduce The Inflammation That Causes Arthritis

While a healthy diet can play a crucial role in managing arthritis symptoms, it’s essential to remember that it’s not a cure-all. Consulting with a healthcare professional is vital for personalized advice and a comprehensive approach to managing your condition.
Tailoring Dietary Recommendations
A registered dietitian or a doctor specializing in arthritis can provide personalized dietary recommendations based on your individual needs, health conditions, and medication. They can help you:
- Identify specific foods that might be triggering your arthritis symptoms.
- Create a meal plan that meets your nutritional needs and dietary restrictions.
- Address any underlying nutritional deficiencies that could be contributing to your arthritis.
- Develop strategies for managing weight, which can significantly impact joint health.
Resources and Support Groups
For individuals with arthritis, numerous resources and support groups are available to provide guidance and connect with others facing similar challenges.
- The Arthritis Foundation: This organization offers a wealth of information on arthritis, including dietary recommendations, treatment options, and support groups. They also provide resources for navigating the healthcare system and finding qualified healthcare professionals.
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH): The NIH offers comprehensive information on arthritis, including research findings, treatment options, and clinical trials. They also provide resources for individuals with arthritis and their families.
- Local Support Groups: Many communities have local support groups for individuals with arthritis. These groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, exchanging tips, and receiving emotional support from others who understand what you’re going through.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, while diet alone cannot cure arthritis, it can be a powerful tool in managing its symptoms. By understanding the inflammatory processes involved in arthritis and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, you can potentially reduce pain, stiffness, and swelling.
However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice tailored to your individual needs and health conditions. Remember, taking a proactive approach to your diet can contribute significantly to your overall health and well-being, particularly when living with arthritis.






