Ask the RD: Should You Choose Sugar or Splenda?
Ask the rd should you choose sugar or splenda – Ask the RD: Should You Choose Sugar or Splenda? sets the stage for a captivating exploration of the sweet world of sweeteners. We’ll delve into the nutritional profiles of sugar and Splenda, comparing their calorie content, carbohydrate makeup, and glycemic index.
We’ll also examine the potential health implications of each sweetener, considering both the benefits and risks associated with their consumption. This journey will guide you towards a better understanding of these common sweeteners and help you make informed choices for your health and well-being.
From the impact of these sweeteners on your blood sugar levels to their role in a balanced diet, we’ll uncover the science behind their effects on your body. We’ll explore the common uses of sugar and Splenda in various food and beverages, and we’ll discuss the potential alternatives available to satisfy your sweet cravings.
This exploration will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the world of sweeteners with confidence and make choices that align with your individual needs and preferences.
Sugar vs. Splenda
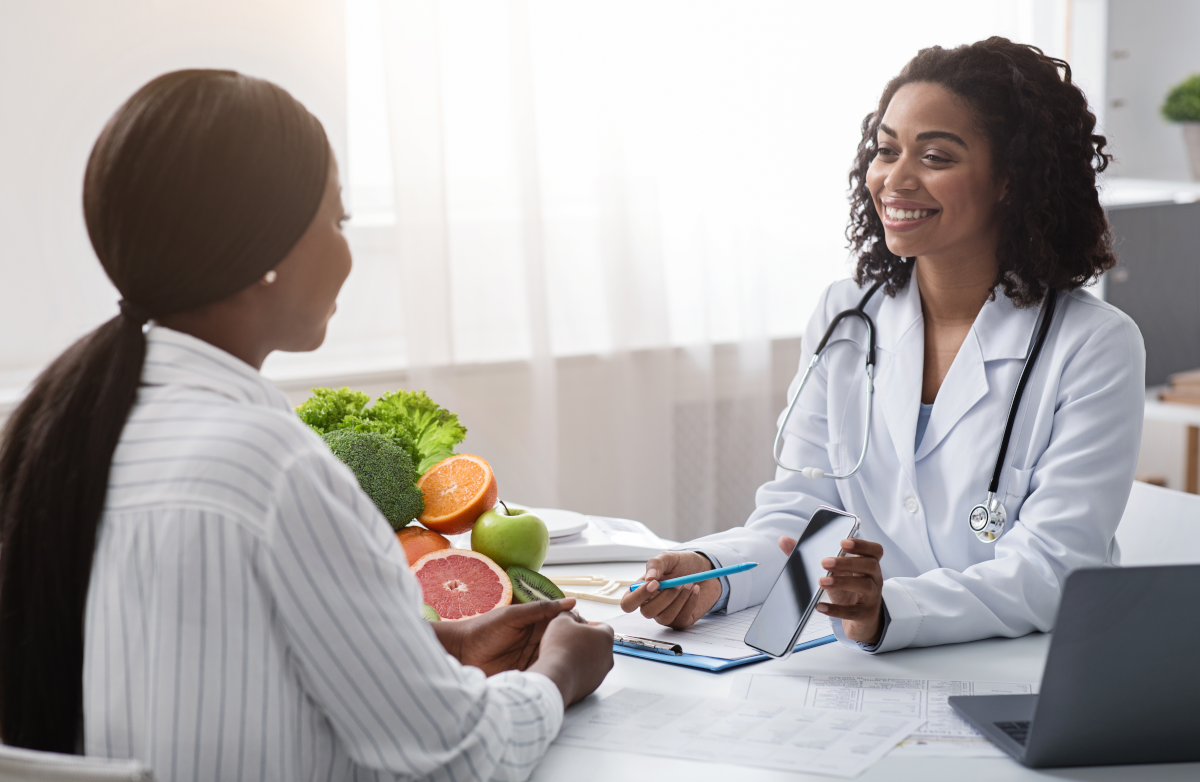

Making informed choices about sweeteners can be challenging, especially when considering the popular options of sugar and Splenda. Understanding their nutritional profiles and potential health effects is crucial for making informed decisions. This article will delve into a comparative analysis of sugar and Splenda, highlighting their key differences and potential implications for your health.
Nutritional Comparison
Sugar and Splenda differ significantly in their nutritional profiles. Sugar, a natural sweetener derived from sugarcane or sugar beets, is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose. Splenda, on the other hand, is an artificial sweetener made from sucralose, a chlorinated sugar derivative.
- Calories and Carbohydrates:Sugar provides 4 calories per gram and is a source of carbohydrates. Splenda, being an artificial sweetener, contains negligible calories and carbohydrates.
- Glycemic Index (GI):Sugar has a high glycemic index (GI), meaning it can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels after consumption. Splenda, with no carbohydrates, does not affect blood sugar levels and has a GI of 0.
- Other Nutrients:Sugar provides no other nutrients, while Splenda offers no nutritional value either.
Potential Health Effects, Ask the rd should you choose sugar or splenda
The potential health effects of sugar and Splenda have been extensively studied. Sugar consumption has been linked to several health concerns, including:
- Weight Gain and Obesity:Excessive sugar intake contributes to weight gain and obesity due to its high calorie content and potential to stimulate appetite.
- Type 2 Diabetes:Sugar’s high GI can lead to insulin resistance and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Disease:High sugar intake can elevate triglyceride levels and contribute to the development of heart disease.
- Dental Cavities:Sugar provides a food source for bacteria in the mouth, leading to tooth decay.
Splenda, as an artificial sweetener, does not contribute to calorie intake or blood sugar fluctuations. However, some studies have raised concerns about potential health effects, including:
- Gut Health:Some research suggests that Splenda may alter gut microbiota composition, potentially impacting digestion and overall health.
- Long-Term Effects:Long-term effects of Splenda consumption are still being investigated, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential implications.
Sweeteners in the Diet
Sweeteners, whether natural or artificial, play a significant role in our daily lives, adding sweetness to our food and beverages. Understanding the impact of sweeteners on our health is crucial for making informed choices about our dietary habits.
Artificial Sweeteners: Health Implications
Artificial sweeteners have gained popularity as sugar alternatives, often touted as a way to reduce calorie intake and manage weight. However, their long-term effects on health are still being investigated.
- Gut Microbiota:Some studies suggest that artificial sweeteners may disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, potentially leading to changes in metabolism and increased risk of metabolic disorders.
- Metabolic Processes:Artificial sweeteners can interfere with the body’s natural response to sweetness, potentially impacting insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation.
- Long-Term Health Outcomes:While some studies have linked artificial sweeteners to an increased risk of conditions like type 2 diabetes, obesity, and heart disease, further research is needed to establish definitive cause-and-effect relationships.
Moderation and Alternative Sweeteners
A balanced diet emphasizes moderation in all aspects, including sugar consumption. While some individuals may benefit from using artificial sweeteners in moderation, it’s important to consider the potential risks and to explore alternative options.
- Natural Sweeteners:Stevia, honey, and maple syrup offer natural sweetness without the same level of processing as artificial sweeteners. These options may have a lower glycemic index and provide additional nutrients.
- Fruit:Incorporating whole fruits into your diet can provide natural sweetness and fiber, contributing to overall health and satiety.
- Spices and Herbs:Many spices and herbs can add flavor and sweetness to dishes without relying on added sugars. Cinnamon, ginger, and vanilla extract are examples of natural sweeteners that can enhance the taste of food and beverages.
Sugar and Splenda in Food and Beverages
Sugar and Splenda are widely used sweeteners in food and beverages, each contributing to the taste and texture of various products. Understanding their applications and impact is crucial for making informed choices about our consumption habits.
Common Uses of Sugar and Splenda
Sugar and Splenda are incorporated into a wide range of food and beverage products, each with unique properties that affect their use.
Choosing between sugar and Splenda can be a tough call, especially if you’re trying to manage your weight. While Splenda is calorie-free, it’s important to consider the overall impact on your health. Remember, making small changes to your diet can have a big impact on your weight loss journey.
Check out these 10 Simple Changes That Lead to Weight Loss for inspiration. Ultimately, the best choice for you depends on your individual goals and preferences. So, ask your registered dietitian for personalized guidance and together, you can find the sweet spot for your health and weight management.
- Sugar:A naturally occurring carbohydrate, sugar is found in various forms, including granulated sugar, brown sugar, and honey. It is commonly used in baked goods, candies, desserts, beverages, and processed foods to provide sweetness and enhance flavor. Sugar also plays a role in the texture of products, contributing to browning and caramelization during baking.
- Splenda:A synthetic, non-caloric sweetener, Splenda is about 600 times sweeter than sugar. It is often used in diet foods, beverages, and desserts to provide sweetness without adding calories or carbohydrates. Splenda is also commonly found in sugar-free versions of popular products, such as yogurt, jams, and candies.
Impact of Sweeteners on Food and Beverages
Sugar and Splenda significantly influence the taste, texture, and overall quality of food and beverages.
- Sugar:Sugar’s sweetness and browning properties are essential for creating desirable flavors and textures in baked goods and desserts. For example, the caramelization of sugar during baking contributes to the golden-brown crust of bread and the rich flavor of cookies.
Sugar also influences the texture of jams and jellies, providing a smooth and spreadable consistency.
- Splenda:Splenda offers a sugar-free alternative for those seeking to reduce their sugar intake. It provides sweetness without contributing to calorie intake or blood sugar fluctuations. However, Splenda can sometimes have a slightly bitter aftertaste, which may not be as appealing as sugar’s natural sweetness.
Additionally, Splenda does not contribute to browning or caramelization, which may affect the texture and appearance of certain baked goods.
Alternatives to Sugar and Splenda
While sugar and Splenda are widely used, several alternatives offer natural sweetness and sugar-free options.
- Natural Sweeteners:These include honey, maple syrup, agave nectar, and stevia. These sweeteners provide a natural source of sweetness and often have additional nutritional benefits, such as antioxidants and minerals. However, it’s important to note that these natural sweeteners still contain calories and carbohydrates, so they should be consumed in moderation.
- Sugar-Free Options:These include artificial sweeteners such as sucralose (Splenda), aspartame, and saccharin. These sweeteners provide sweetness without adding calories or carbohydrates, making them suitable for those following a low-calorie diet. However, concerns have been raised about the potential health effects of artificial sweeteners, and some people may experience side effects, such as headaches or digestive issues.
Understanding the Science Behind Sweeteners
To make informed decisions about our dietary choices, it’s crucial to understand the science behind the sweeteners we consume. This section delves into the chemical makeup, taste mechanisms, and scientific evidence regarding the safety and potential health effects of sugar and Splenda.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Sugar, or sucrose, is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose. It has the chemical formula C 12H 22O 11. Splenda, on the other hand, is a synthetic sweetener that is a chlorinated derivative of sucrose. It is chemically known as sucralose and has the formula C 12H 19Cl 3O 8.The key difference between sugar and Splenda lies in their chemical structures.
While both contain glucose and fructose, Splenda has three chlorine atoms replacing three hydroxyl groups in the sucrose molecule. This structural modification makes Splenda much sweeter than sugar, and it is not metabolized by the body in the same way.
So, you’re wondering whether to reach for sugar or Splenda? It’s a common question, and the answer depends on your goals. If you’re looking to manage your weight, you might want to check out this article on High Fiber Meals for Weight Loss: A Guide to Feeling Full and Slim which can help you feel satisfied and make healthier choices.
High-fiber foods can be a great way to keep your blood sugar levels stable, which is important when considering sugar substitutes.
Mechanisms of Sweetness Perception
Both sugar and Splenda stimulate the sweetness receptors on the tongue, known as T1R2/T1R3 receptors. These receptors are located on the taste buds and send signals to the brain, triggering the perception of sweetness. However, the mechanisms by which these sweeteners activate the receptors differ slightly.Sugar binds to the T1R2/T1R3 receptors through hydrogen bonding and other interactions.
This binding triggers a cascade of events that ultimately lead to the perception of sweetness. Splenda, due to its chlorine atoms, interacts with the receptors in a different way. It is thought to activate the receptors through a more complex mechanism, potentially involving a different binding site or interaction.
Scientific Evidence on Safety and Health Effects
The safety and health effects of consuming sugar and Splenda have been extensively studied. While sugar is a natural component of many foods, its consumption in excess has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and tooth decay.
Sugar
Short-term Effects
- Increased blood sugar levels:Consuming sugar leads to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, which can be detrimental for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Energy spikes and crashes:The rapid surge in blood sugar levels from sugar consumption is often followed by a sharp decline, leading to feelings of fatigue and low energy.
- Inflammation:High sugar intake has been linked to increased inflammation in the body, which can contribute to various chronic diseases.
Long-term Effects
- Obesity:Excess sugar consumption contributes to weight gain and obesity, as it provides empty calories without essential nutrients.
- Type 2 Diabetes:Chronic high sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance and ultimately type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Disease:Sugar consumption has been linked to increased risk of heart disease, particularly due to its contribution to high triglyceride levels and low HDL cholesterol.
- Tooth Decay:Sugar feeds bacteria in the mouth, producing acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities.
Splenda
Short-term Effects
- No significant impact on blood sugar levels:Splenda does not raise blood sugar levels as it is not metabolized by the body.
- No immediate energy spikes or crashes:As Splenda does not affect blood sugar, it does not cause the energy fluctuations associated with sugar consumption.
Long-term Effects
- Limited evidence of negative health effects:Numerous studies have investigated the safety of Splenda, and there is limited evidence to suggest significant negative health effects.
- Potential for gut microbiome disruption:Some studies have indicated that Splenda may alter the composition of gut bacteria, but further research is needed to understand the implications for human health.
- Possible impact on gut health:Although research is ongoing, some studies suggest that Splenda may affect gut health, potentially leading to digestive issues or inflammation.
It’s important to note that these are general observations, and individual responses to sugar and Splenda may vary. The optimal intake of sweeteners will depend on individual health conditions, dietary needs, and lifestyle factors.
So, you’re wondering whether sugar or Splenda is the better choice, huh? It’s a tough call, but maybe a little pizza inspiration could help you decide. If you’re looking for healthier pizza options, check out this list of 11 healthy pizzas under 400 calories.
Maybe a slice of something delicious will help you make that sugar vs. Splenda decision a little easier!
Choosing the Right Sweetener for You
The world of sweeteners can be overwhelming, with numerous options available. Making the right choice depends on your individual needs and preferences. This guide will help you navigate the complexities and select the sweetener that aligns with your health goals, dietary restrictions, and taste buds.
Factors to Consider
Understanding your unique needs is crucial for selecting the most appropriate sweetener. Consider the following factors:
- Health Goals:Are you aiming to manage blood sugar levels, lose weight, or simply reduce your sugar intake? Different sweeteners have varying impacts on these aspects.
- Dietary Restrictions:Do you follow a specific diet, such as ketogenic, vegan, or gluten-free? Some sweeteners are not compatible with certain dietary restrictions.
- Taste Preferences:Do you prefer a sweet taste that is similar to sugar or something less intense? Different sweeteners have distinct sweetness profiles.
- Health Conditions:Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, obesity, or metabolic syndrome, may require specific considerations when choosing sweeteners.
Personalized Recommendations
Based on your individual circumstances, here are some personalized recommendations:
Individuals with Diabetes
- Sugar Alcohols:Options like erythritol, xylitol, and maltitol can provide sweetness without significantly affecting blood sugar levels. However, excessive consumption can lead to digestive discomfort.
- Artificial Sweeteners:Aspartame, sucralose, and stevia are sugar-free alternatives that can be helpful for managing blood sugar levels. However, some individuals may experience side effects like headaches or digestive issues.
Individuals with Obesity
- Sugar Alcohols:Erythritol and xylitol can contribute to a lower calorie intake compared to sugar. However, they may still contain calories, and moderation is key.
- Artificial Sweeteners:Aspartame, sucralose, and stevia can help reduce calorie intake, but they do not necessarily promote weight loss. Focus on a balanced diet and regular exercise for weight management.
Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
- Sugar Alcohols:Erythritol and xylitol can help reduce sugar intake and potentially improve insulin sensitivity. However, further research is needed to confirm their long-term effects on metabolic syndrome.
- Artificial Sweeteners:Aspartame, sucralose, and stevia may contribute to reducing calorie intake, but their impact on metabolic syndrome requires further investigation.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or physician, for personalized advice on sweetener choices. They can consider your individual health history, medications, and potential interactions to provide tailored recommendations.
Closing Summary: Ask The Rd Should You Choose Sugar Or Splenda
Ultimately, the decision of whether to choose sugar or Splenda depends on your individual health goals, dietary restrictions, and preferences. By understanding the nuances of each sweetener, you can make informed choices that support your overall health and well-being. Remember, moderation is key, and seeking guidance from a healthcare professional can provide personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.