Bad Gut Health Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs
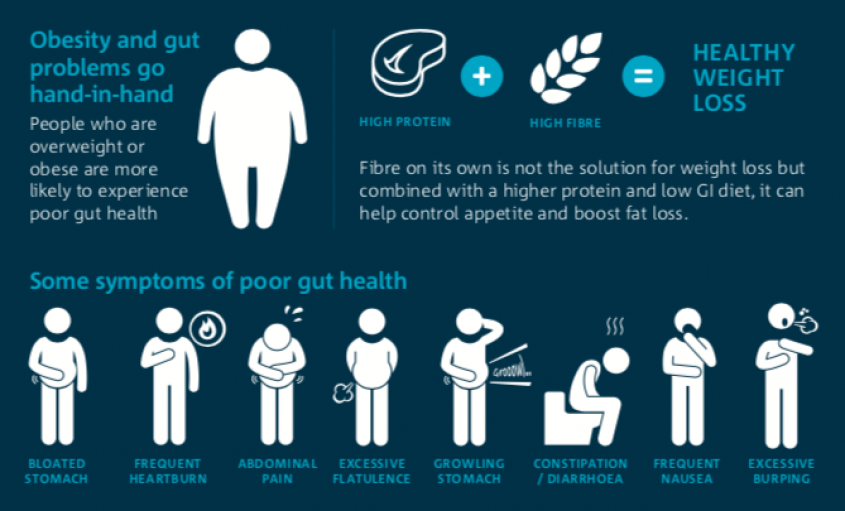
Bad gut health symptoms can be a real nuisance, impacting your daily life and overall well-being. From bloating and gas to more serious issues, a troubled gut can signal deeper problems. Understanding the common signs and their causes is crucial for taking control of your gut health and achieving a happier, healthier you.
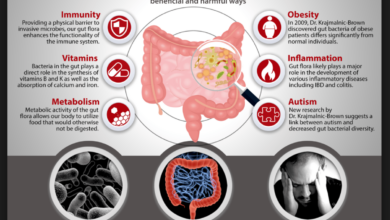
Our gut is home to trillions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiome. These tiny organisms play a vital role in digestion, immunity, and even mental health. When the balance of these bacteria is disrupted, known as dysbiosis, it can lead to a cascade of unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of Bad Gut Health
Your gut health is a complex ecosystem that plays a crucial role in overall well-being. When this delicate balance is disrupted, it can lead to a range of digestive issues and potentially impact other aspects of your health. Let’s delve into some of the common culprits behind bad gut health.
Dietary Choices
Diet plays a significant role in shaping the composition and function of your gut microbiome.
- Processed Foods:A diet high in processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria in your gut. These foods often lack the fiber and nutrients that nourish good bacteria, while contributing to inflammation and gut dysbiosis.
- Low Fiber Intake:Fiber is essential for feeding beneficial bacteria. A low-fiber diet can lead to constipation, slow down digestion, and make it difficult for beneficial bacteria to thrive.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption:Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the gut lining, increase inflammation, and disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria. This can lead to digestive issues and weaken the immune system.
- Antibiotics:While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, they can also kill off beneficial bacteria in your gut. This can disrupt the microbiome and increase the risk of gut-related problems.
Stress and Anxiety, Bad gut health symptoms
The connection between your brain and gut is undeniable. Chronic stress and anxiety can significantly impact gut health.
- Stress Hormones:When you’re stressed, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol. These hormones can alter gut motility, increase inflammation, and disrupt the balance of gut bacteria.
- Changes in Gut Microbiome:Studies have shown that chronic stress can lead to changes in the composition and function of the gut microbiome, potentially contributing to gut dysbiosis and digestive problems.
- Increased Gut Permeability:Stress can also increase gut permeability, also known as “leaky gut,” allowing harmful bacteria and toxins to enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and potentially contributing to various health issues.
Medications
Certain medications can have a negative impact on your gut health.
- Antibiotics:As mentioned earlier, antibiotics can disrupt the gut microbiome by killing off beneficial bacteria. This can lead to digestive issues and increase the risk of infections.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can irritate the stomach lining and increase the risk of ulcers, gastritis, and other digestive problems.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs):PPIs are commonly prescribed to reduce stomach acid. However, long-term use of PPIs can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and increase the risk of infections.
Infections
Infections, particularly those affecting the gastrointestinal tract, can significantly disrupt gut health.
- Gastrointestinal Infections:Viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections can damage the gut lining, cause inflammation, and disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. These infections can lead to diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and other digestive issues.
- Food Poisoning:Consuming contaminated food can lead to food poisoning, which can cause severe gastrointestinal symptoms and disrupt gut health.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to bad gut health.
- Lack of Sleep:Sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and increase inflammation. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Lack of Exercise:Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy gut. Exercise can improve gut motility, reduce inflammation, and promote a balanced gut microbiome.
- Smoking:Smoking damages the gut lining, increases inflammation, and disrupts the balance of gut bacteria. Quitting smoking is essential for improving gut health.
Last Word: Bad Gut Health Symptoms

While some gut issues may resolve on their own with simple lifestyle changes, others require professional attention. Don’t ignore persistent or severe symptoms. By understanding the signs, causes, and strategies for improving gut health, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions and take charge of your well-being.
If you’re experiencing bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort, it might be a sign of bad gut health. A balanced diet with plenty of fiber can help improve gut health, and a tasty and nutritious option is teriyaki chicken fried rice recipe.
This recipe is packed with vegetables and lean protein, making it a great choice for a healthy and satisfying meal. Of course, always consult with a doctor or registered dietitian if you have persistent gut health concerns.
Feeling bloated, sluggish, and maybe even a little irritable? These could be signs of a not-so-happy gut. Nourishing your gut with healthy, fiber-rich foods is essential for feeling your best, and a hearty bowl of chili is a great place to start! Check out these 10 easy chunky chili recipes under 360 calories for some gut-friendly inspiration.
Remember, a healthy gut is a happy gut, and a happy gut means you can enjoy all the delicious foods life has to offer!
Bloating, fatigue, and digestive discomfort are common signs of bad gut health. If you’re struggling with these issues, consider incorporating more gut-friendly foods into your diet, like those found in this delicious and nourishing chicken and sweet potato farro bowl.
This recipe is packed with prebiotics, which are essential for feeding the good bacteria in your gut, helping to promote a healthier digestive system.