
Body Sleep Deprivation Infographic: Understanding the Impact
Body sleep deprivation infographic – it’s a phrase that likely conjures up images of tired eyes and sluggish mornings. But the impact of sleep deprivation goes far beyond simple fatigue. It’s a silent thief, stealing away our health, happiness, and productivity, one sleepless night at a time.
This infographic delves into the alarming consequences of sleep deprivation, highlighting its effects on both our physical and mental well-being. From weakened immune systems and increased risk of chronic diseases to anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairment, the repercussions of insufficient sleep are far-reaching and often underestimated.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on the Body
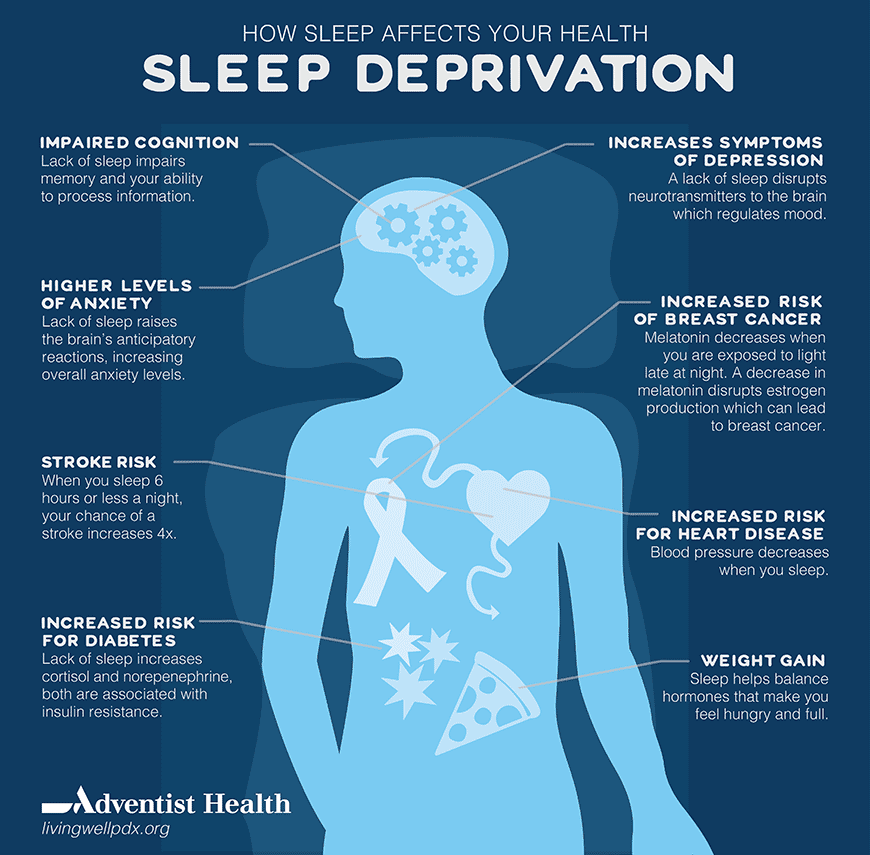
Sleep deprivation, a condition where individuals consistently get less sleep than their bodies need, can have significant and far-reaching consequences for both physical and mental well-being. The effects of sleep deprivation are multifaceted and can impact various aspects of our lives, from our physical health and mental state to our performance and overall quality of life.
That infographic about sleep deprivation really got me thinking about how much my body needs rest. I’m trying to eat healthier too, and I found this amazing recipe for a simple spaghetti squash lasagna that’s both delicious and good for you.
Maybe if I can get my sleep schedule back on track, I’ll be able to make it more often!
Impact on Physical Health
Sleep deprivation can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses. This occurs because sleep plays a crucial role in the production of immune cells and the release of cytokines, which are essential for fighting off infections.
When we are sleep-deprived, our immune system is compromised, leaving us vulnerable to various health problems.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of developing chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and obesity. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased insulin resistance, elevated blood pressure, and inflammation, all of which contribute to the development of these conditions.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Sleep deprivation can disrupt the production and regulation of various hormones, including cortisol, growth hormone, and leptin. Cortisol, the stress hormone, is typically elevated during sleep deprivation, leading to increased stress and anxiety. Growth hormone, essential for cell repair and growth, is reduced during sleep deprivation, potentially impacting muscle growth and repair.
Leptin, a hormone that regulates appetite, is also affected, leading to increased hunger and cravings for unhealthy foods.
Impact on Mental Health
Sleep deprivation can significantly impact mental health, leading to various psychological issues, including anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairment. Lack of sleep can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, affecting mood regulation and cognitive function.
- Anxiety and Depression: Sleep deprivation can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and depression. Studies have shown that individuals with insomnia are more likely to experience anxiety and depression. Lack of sleep can lead to increased stress, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, all of which contribute to mental health problems.
- Cognitive Impairment: Sleep deprivation can impair cognitive function, leading to difficulties with attention, memory, and decision-making. Lack of sleep can affect the hippocampus, a brain region crucial for memory formation and retrieval. It can also impair the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions such as planning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
That body sleep deprivation infographic really hit home. I’m definitely not getting enough sleep, and it’s starting to affect my energy levels. I need to make some changes, like prioritizing a good night’s rest and maybe even adding some extra protein to my diet.
A delicious and healthy chicken and sweet potato farro bowl might be just the ticket to help me get back on track! I’m sure a balanced meal like that would give me the energy I need to make those sleep changes.
Impact on Physical Performance
Sleep deprivation can significantly impact physical performance, leading to reduced reaction time, impaired motor skills, and an increased risk of accidents. Lack of sleep can affect muscle recovery, coordination, and overall athletic performance.
- Reduced Reaction Time: Sleep deprivation can slow down reaction time, making it more difficult to respond quickly to stimuli. This can be particularly dangerous in situations that require quick reflexes, such as driving or operating machinery. Studies have shown that sleep-deprived individuals have slower reaction times, similar to those who are intoxicated.
- Impaired Motor Skills: Sleep deprivation can impair motor skills, making it more difficult to perform complex tasks requiring coordination and precision. This can lead to increased errors and accidents, particularly in activities that require fine motor control, such as surgery or playing a musical instrument.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: Sleep deprivation can increase the risk of accidents, both at work and in everyday life. Lack of sleep can lead to fatigue, drowsiness, and impaired judgment, all of which can contribute to accidents. Studies have shown that sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to be involved in car accidents, workplace injuries, and other types of accidents.
Consequences of Chronic Sleep Deprivation

Chronic sleep deprivation is not just about feeling tired; it can have serious, long-term consequences for your physical and mental health, impacting your overall well-being. While occasional sleeplessness is normal, consistent lack of sleep can lead to a cascade of health issues and significantly affect your quality of life.
That body sleep deprivation infographic really hit home – I’m feeling the effects of a few late nights myself. To combat the fatigue, I’m craving something nourishing and comforting, like a hearty bowl of lentil sweet potato spinach stew.
The blend of protein, fiber, and vitamins will help me feel energized and ready to tackle the day, even with a bit less sleep.
Impact on Physical Health
Chronic sleep deprivation has a significant impact on your physical health, increasing the risk of developing various chronic diseases.
- Obesity:Sleep deprivation disrupts the hormones that regulate appetite, leading to increased hunger and cravings for unhealthy foods. This can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Studies have shown a correlation between sleep deprivation and an increased risk of obesity, with individuals who sleep less than 6 hours per night having a higher likelihood of becoming obese.
- Heart Disease:Sleep deprivation can raise blood pressure, increase heart rate, and contribute to inflammation, all of which are risk factors for heart disease. Research indicates that chronic sleep deprivation can lead to an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Diabetes:Sleep deprivation can impair the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Studies have found that individuals who consistently sleep less than 6 hours per night have a higher risk of developing diabetes compared to those who get sufficient sleep.
Impact on Mental Health
Sleep deprivation can significantly impact your mental health, making you more susceptible to mood disorders and other mental health issues.
- Anxiety and Depression:Chronic sleep deprivation can trigger or worsen anxiety and depression. Lack of sleep can lead to heightened stress levels, increased irritability, and difficulty concentrating, all of which contribute to anxiety and depression. Research has shown a strong link between sleep deprivation and an increased risk of developing these mental health disorders.
- Cognitive Decline:Sleep deprivation can impair cognitive function, leading to difficulty concentrating, remembering information, and making decisions. It can also affect your reaction time and overall alertness, making you more prone to errors and accidents. Long-term sleep deprivation can contribute to cognitive decline and an increased risk of dementia.
Impact on Daily Life
Chronic sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on your daily life, affecting your relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
- Relationships:Sleep deprivation can lead to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating, which can strain relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners. It can make it challenging to engage in meaningful conversations and activities, impacting the quality of your interactions.
- Work Performance:Sleep deprivation can impair your ability to focus, concentrate, and make sound decisions, affecting your work performance. It can also lead to increased errors, decreased productivity, and difficulty meeting deadlines.
- Quality of Life:Chronic sleep deprivation can negatively impact your overall quality of life, making you feel exhausted, irritable, and unable to enjoy activities you once found pleasurable. It can affect your physical and mental well-being, leading to a decrease in your overall happiness and satisfaction with life.
Tips for Improving Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene refers to the habits and practices that promote good quality sleep. By implementing effective sleep hygiene strategies, you can significantly improve your sleep quality, reduce sleep deprivation, and enhance your overall health and well-being.
Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule
A consistent sleep schedule helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, known as the circadian rhythm. This rhythm influences your body’s temperature, hormone production, and alertness levels throughout the day.
- Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to maintain a regular sleep-wake cycle.
- Avoid irregular sleep patterns, such as staying up late one night and sleeping in the next morning.
- This consistency helps signal your body when it’s time to sleep and wake up, promoting better sleep quality.
Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
A relaxing bedtime routine signals to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. This routine helps reduce stress and anxiety, making it easier to fall asleep.
- Engage in calming activities before bed, such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to soothing music.
- Avoid screen time for at least an hour before bed, as the blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Create a peaceful and quiet sleep environment by dimming the lights and minimizing distractions.
Optimizing the Sleep Environment
The sleep environment plays a crucial role in sleep quality. A comfortable and conducive environment promotes relaxation and sleep.
- Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. The ideal temperature for sleep is around 65 degrees Fahrenheit (18 degrees Celsius).
- Use blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out light. Earplugs can help minimize noise distractions.
- Ensure your bed is comfortable and supportive. Invest in a high-quality mattress, pillows, and bedding that suit your preferences.
Avoiding Caffeine and Alcohol Before Bed
Caffeine and alcohol can interfere with sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you awake, while alcohol can disrupt sleep cycles and lead to poor sleep quality.
- Avoid caffeine intake for at least 6 hours before bed. This includes coffee, tea, soda, and chocolate.
- Limit alcohol consumption, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. Alcohol can initially make you feel sleepy, but it can disrupt sleep later in the night.
- Opt for calming beverages like herbal tea or warm milk before bed.
Engaging in Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity promotes better sleep. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it can make it harder to fall asleep.
- Engage in moderate-intensity exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Aim to finish your workout at least 3 hours before bedtime to allow your body to cool down and relax.
- Avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it can stimulate your nervous system and make it harder to fall asleep.
Infographic Design
Creating a visually appealing and informative infographic about sleep deprivation is crucial to effectively convey the message and engage the audience. By combining text, graphics, and data visualizations, you can illustrate the key information in a clear and memorable way.
Visual Appeal and Structure
A well-designed infographic should be visually appealing and easy to understand. This involves choosing a color scheme, fonts, and layout that are consistent and complement the information being presented. For instance, using a dark background with bright text can create a striking contrast, while a more neutral color palette can be used for a less dramatic approach.
The layout should be well-organized, with clear headings and subheadings, and the information should flow logically. This can be achieved by using a timeline, a flowchart, or a combination of different visual elements.
Content and Visualizations, Body sleep deprivation infographic
The infographic should contain accurate and relevant information about sleep deprivation. This can include statistics, research findings, and personal anecdotes. To make the information more engaging, use a variety of visualizations such as charts, graphs, and illustrations. For example, a bar chart could be used to show the percentage of people who experience sleep deprivation, while an infographic could be used to illustrate the impact of sleep deprivation on different parts of the body.
Engagement and Impact
An engaging infographic should capture the audience’s attention and leave a lasting impression. This can be achieved by using strong visuals, compelling headlines, and a clear call to action. The infographic should be designed with a responsive layout that adapts to different screen sizes.
This ensures that the information can be accessed and understood on a variety of devices.
Examples of Visual Elements
- Icons:Use icons to represent different aspects of sleep deprivation, such as fatigue, stress, and reduced cognitive function. For example, a sleepy face icon could be used to represent fatigue, while a brain icon could be used to represent cognitive function.
- Charts and Graphs:A pie chart could be used to illustrate the different causes of sleep deprivation, such as stress, anxiety, or medical conditions. A bar chart could be used to show the percentage of people who experience sleep deprivation in different age groups.
- Illustrations:Use illustrations to depict the impact of sleep deprivation on the body, such as showing a person struggling to stay awake or experiencing a decrease in productivity.
- Infographics:Use infographics to explain complex concepts in a simple and easy-to-understand way. For example, an infographic could be used to explain the sleep cycle or the stages of sleep.
Wrap-Up: Body Sleep Deprivation Infographic
Understanding the impact of sleep deprivation is crucial for prioritizing sleep hygiene and making conscious choices that support our overall health. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, implementing sleep-enhancing strategies, and prioritizing restful nights, we can reclaim our energy, enhance our well-being, and unlock our full potential.





