Can Dieting Damage Your Metabolism?
Can dieting damage your metabolism? It’s a question that often pops up in the world of weight loss, and the answer isn’t always straightforward. While dieting can be a valuable tool for achieving a healthy weight, some approaches can have unintended consequences on our metabolic rate.
This can lead to a slower metabolism, making weight loss more challenging and potentially impacting overall health.
Understanding how dieting impacts metabolism is crucial for making informed choices about our health and wellness. We’ll explore the intricacies of metabolism, the potential downsides of restrictive diets, and strategies for maintaining a healthy metabolic rate.
Understanding Metabolism
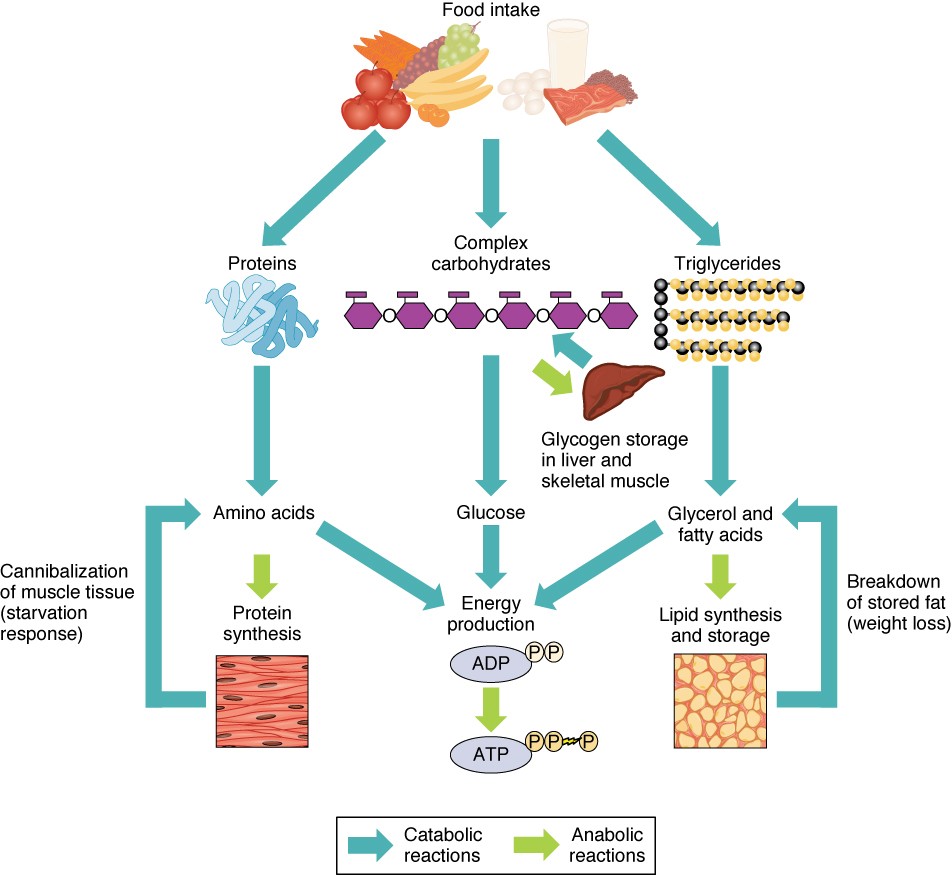
Metabolism is a complex process that encompasses all the chemical reactions occurring within your body to maintain life. It involves breaking down food into energy and using that energy to perform vital functions, such as breathing, circulating blood, and maintaining body temperature.
You know how they say “dieting can damage your metabolism”? Well, it’s true, but there’s another sneaky culprit that can wreak havoc on your body’s ability to burn calories: lack of sleep. Chronic sleep deprivation, or insomnia, can actually trigger hormonal changes that make you more prone to weight gain, and that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
Read more about the undeniable reason you need to deal with insomnia to see how it can affect your overall health and well-being. So, if you’re struggling to shed those extra pounds, consider addressing your sleep habits first. You might be surprised by how much of an impact it has on your metabolism.
Understanding metabolism is crucial for weight management, as it plays a significant role in determining how many calories you burn at rest and during physical activity.
You might be surprised to learn that restrictive dieting can actually slow down your metabolism, making it harder to lose weight in the long run. Instead of depriving yourself, focus on fueling your body with nutrient-rich foods that keep you feeling full and satisfied.
Check out this list of 12 healthy foods that fill you up best to get some inspiration for your next meal. By prioritizing healthy eating habits, you can support a healthy metabolism and achieve sustainable weight management goals.
Basal Metabolic Rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) refers to the number of calories your body burns at rest, simply to maintain basic bodily functions. It accounts for the majority of your daily energy expenditure. Several factors influence BMR, including:
- Age: BMR naturally declines with age due to a decrease in muscle mass and an increase in fat mass.
- Sex: Men generally have a higher BMR than women due to their larger muscle mass.
- Body Composition: Individuals with more muscle mass have a higher BMR than those with more fat mass, as muscle tissue burns more calories at rest.
- Genetics: Your genes play a role in determining your BMR, with some individuals naturally having a faster metabolism than others.
- Hormones: Hormones such as thyroid hormones influence BMR, with an underactive thyroid leading to a slower metabolism.
Thermic Effect of Food, Can dieting damage your metabolism
The thermic effect of food (TEF) refers to the calories your body burns to digest, absorb, and process food. TEF accounts for a smaller portion of your daily energy expenditure compared to BMR, but it still plays a role in weight management.
You might be surprised to learn that restrictive dieting can actually backfire and slow down your metabolism. It’s like your body is trying to conserve energy in a time of perceived scarcity. Instead of focusing solely on calories, consider shifting your mindset to thinking outside the lox – embracing a balanced approach that prioritizes nutrient-rich foods and mindful eating habits.
This can help you achieve sustainable weight loss without compromising your metabolic health.
Different types of food have varying TEF values, with protein having the highest TEF followed by carbohydrates and then fats.
Physical Activity
The energy expenditure associated with physical activity is directly proportional to the intensity and duration of the activity. Engaging in regular exercise, even at moderate intensity, can significantly boost your metabolism and contribute to weight loss.
Other Factors Influencing Metabolism
Several other factors can influence your metabolism, including:
- Sleep: Inadequate sleep can disrupt hormone balance and slow down your metabolism.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger the release of cortisol, a hormone that can increase appetite and promote fat storage.
- Environmental Temperature: Your body burns more calories to maintain a stable internal temperature in cold environments.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants and beta-blockers, can slow down your metabolism.
Healthy Approaches to Weight Management

Dieting can be detrimental to your metabolism, but that doesn’t mean you should abandon weight management altogether. Instead, focus on sustainable, healthy approaches that support your metabolism and promote long-term well-being.
Designing a Balanced Diet Plan
A balanced diet plan plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy metabolism. This means consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups in appropriate proportions.
- Prioritize Whole Foods:Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. These foods are packed with essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that support metabolic function.
- Control Portion Sizes:While consuming a variety of foods is important, portion control is equally crucial. Pay attention to the recommended serving sizes and avoid overeating.
- Hydrate Adequately:Water is essential for numerous bodily functions, including metabolism. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Limit Processed Foods:Processed foods are often high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and sodium, which can negatively impact your metabolism. Limit your intake of these foods.
- Reduce Sugar Intake:Excess sugar consumption can lead to insulin resistance and other metabolic issues. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, desserts, and processed foods.
Maintaining a Healthy Metabolism Over Time
Maintaining a healthy metabolism is an ongoing process that requires consistent effort. Here are some tips:
- Eat Regularly:Skipping meals can disrupt your metabolic rate. Aim to eat regular, balanced meals throughout the day to keep your metabolism functioning optimally.
- Get Enough Sleep:Sleep deprivation can negatively impact your metabolism. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Manage Stress:Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect your metabolism. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Stay Active:Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy metabolism. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is not only essential for weight management but also has a profound impact on your metabolism.
- Increased Muscle Mass:Exercise, particularly strength training, helps build muscle mass. Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue, boosting your metabolism.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity:Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to use glucose more effectively and reducing the risk of insulin resistance.
- Enhanced Fat Burning:Exercise, especially cardio, helps burn calories and fat, contributing to weight loss and a healthier metabolism.
- Improved Hormonal Balance:Exercise can help regulate hormone levels, including those involved in metabolism, such as thyroid hormones and growth hormone.
Last Point: Can Dieting Damage Your Metabolism

Navigating the world of dieting and metabolism can be complex, but by understanding the science behind it, we can make healthier choices. Remember, a balanced approach that focuses on sustainable lifestyle changes is key. If you’re concerned about your metabolism, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
By prioritizing a healthy lifestyle, we can support a healthy metabolism and achieve our weight management goals in a way that benefits our overall well-being.