Is Food Combining Helpful for Weight Loss?
Is food combining helpful for weight loss? This intriguing question has sparked countless debates and dietary trends, leaving many wondering if the principles behind this approach can truly contribute to shedding pounds. The idea of food combining revolves around the belief that consuming certain food groups together can optimize digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, and ultimately lead to weight loss.
Food combining proponents argue that by pairing compatible foods, you can prevent digestive distress, reduce bloating, and promote efficient metabolism. They often suggest avoiding combinations like protein and carbohydrates, claiming they slow down digestion and lead to weight gain.
However, scientific evidence supporting these claims remains limited, and many experts caution against overly restrictive dietary practices.
What is Food Combining?: Is Food Combining Helpful For Weight Loss
Food combining, also known as the “food combining diet,” is a dietary approach that emphasizes consuming certain food groups together and avoiding others. It’s based on the idea that different foods digest at different rates and combining incompatible foods can lead to digestive issues, weight gain, and other health problems.
Fundamental Principles, Is food combining helpful for weight loss
Food combining advocates believe that the body can digest and absorb nutrients more efficiently when certain food groups are eaten separately. This is because different foods require different enzymes and digestive processes. For example, proteins are broken down in an acidic environment, while carbohydrates are best digested in an alkaline environment.
According to this theory, combining proteins and carbohydrates in the same meal can lead to indigestion, bloating, and slow digestion.
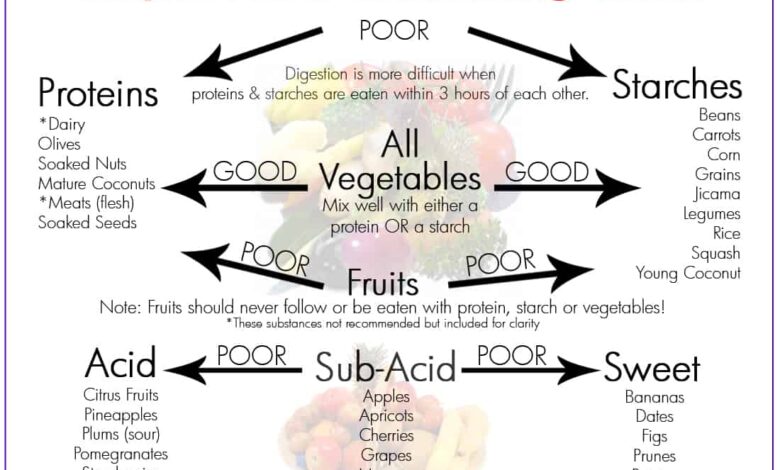
Food Groups and Combinations
Food combining typically divides foods into four main groups:
- Proteins: These include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
- Carbohydrates: These include grains, fruits, starchy vegetables, and sugars.
- Fats: These include oils, butter, avocados, and nuts.
- Fruits: Fruits are generally considered to be best eaten alone or in combination with other fruits.
Beneficial and Non-Beneficial Food Combinations
Beneficial Combinations
- Protein with Vegetables: This combination is considered beneficial because proteins and vegetables digest at similar rates. Examples include grilled chicken with broccoli, salmon with asparagus, or lentil soup with carrots.
- Fruits with Other Fruits: Fruits digest quickly, so combining different fruits is generally acceptable. Examples include a fruit salad, a smoothie made with various fruits, or a banana with berries.
Non-Beneficial Combinations
- Proteins with Carbohydrates: This combination is discouraged because it is believed to slow digestion and lead to digestive issues. Examples include a hamburger with fries, pasta with meatballs, or chicken with rice.
- Fruits with Proteins or Carbohydrates: Fruits are believed to digest too quickly when combined with proteins or carbohydrates, leading to fermentation and gas. Examples include a banana with yogurt, a piece of fruit with a slice of bread, or a fruit salad with granola.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Food Combining for Weight Loss
Food combining, also known as the “separation diet,” is a dietary approach that claims to promote weight loss by restricting the combination of certain food groups. While proponents argue that it aids digestion and reduces calorie intake, scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness for weight loss is limited and inconclusive.
Food combining is a popular diet trend, but it’s important to remember that healthy eating is about finding a sustainable approach that you can enjoy. If you’re struggling to embrace healthy foods, exploring ways to learn to love or like eating healthy might be a better starting point.
Ultimately, sustainable healthy habits are more likely to lead to long-term weight management than restrictive diets.
Studies Supporting Food Combining
There is a lack of robust scientific evidence to support the claim that food combining aids in weight loss. Most studies investigating food combining have methodological limitations, such as small sample sizes, short durations, and lack of control groups.
However, a few studies have suggested potential benefits.
A small study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition in 2003 found that a food combining diet resulted in significant weight loss compared to a conventional diet.
This study, however, was conducted on a small group of participants and lacked a control group, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions.
So, you’re wondering if food combining is the key to weight loss? While it’s true that some combinations might be easier to digest, the real magic happens when you understand the quality of carbs you’re consuming. A low-carb diet can be incredibly effective, but it’s essential to choose the right carbs.
Read more about why quality of carbs matters on a low carb diet to make informed choices. Ultimately, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and managing your overall calorie intake will be far more impactful for sustainable weight loss than strict food combining rules.
Studies Refuting Food Combining
Several studies have failed to find evidence that food combining promotes weight loss. A review article published in the journal Nutrition Reviews in 2014 concluded that there is no scientific basis for food combining.
The review article stated that “the idea that combining certain foods can lead to weight loss is not supported by scientific evidence.”
Another study published in the journal Obesity in 2015 found that a food combining diet did not result in significant weight loss compared to a control diet.
Potential Benefits of Food Combining
While the evidence for weight loss is limited, some studies have suggested that food combining may have other potential benefits, such as improved digestion and reduced bloating.
While food combining might be a popular weight loss strategy, I find it’s more about enjoying delicious, nutrient-packed meals that keep me feeling full and satisfied. And chickpeas are a fantastic ingredient for that! Check out these delicious ways to use chickpeas under 360 calories – they’re packed with protein and fiber, which are both key for keeping hunger at bay.
So, instead of focusing solely on combining foods, I prefer to prioritize healthy, satisfying meals, and chickpeas are a perfect fit for that!
A small study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine in 2008 found that a food combining diet improved digestive symptoms in individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
It is important to note that these studies were conducted on small groups of participants and further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Potential Drawbacks of Food Combining
Food combining can have potential drawbacks, such as:
- Nutrient deficiencies:Restricting certain food groups can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients. For example, eliminating grains can limit intake of fiber and B vitamins.
- Social isolation:Food combining can be restrictive and make it difficult to eat with friends and family.
- Increased risk of disordered eating:The focus on food rules and restrictions can contribute to disordered eating patterns.
Mechanisms of Action
The proposed mechanisms by which food combining might influence weight loss are based on the idea that specific food combinations can affect digestion, nutrient absorption, and metabolic processes, potentially leading to weight loss. While there is no conclusive scientific evidence to support these claims, proponents of food combining suggest that it can enhance digestion, reduce bloating, and promote a feeling of fullness, ultimately contributing to weight management.
Impact on Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
The proponents of food combining argue that combining certain food types can disrupt digestion and nutrient absorption, leading to weight loss. They suggest that mixing protein with carbohydrates, for example, can slow down digestion and lead to fermentation in the gut, potentially causing bloating and discomfort.
They also claim that combining different food groups can increase the time it takes for food to be broken down and absorbed, reducing the overall caloric intake.
- Protein and Carbohydrates:Combining protein with carbohydrates, according to food combining proponents, can slow down digestion and lead to fermentation in the gut, potentially causing bloating and discomfort. This is because protein digestion requires a different set of enzymes than carbohydrate digestion.
When combined, these enzymes may compete for resources, leading to incomplete digestion and potentially increased fermentation.
- Fats and Carbohydrates:Food combining proponents also argue that combining fats with carbohydrates can lead to a similar effect, as fats slow down the digestion of carbohydrates. This can lead to a prolonged feeling of fullness and potentially reduce overall caloric intake.
- Fruits and Other Foods:Food combining proponents often suggest that fruits should be consumed separately from other foods, as they are believed to digest quickly. This is because fruits contain high amounts of fructose, which can be absorbed quickly, potentially leading to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels.
Consuming fruits with other foods, they argue, can slow down this process and lead to fermentation.
Influence on Metabolism
Food combining proponents suggest that specific food combinations can influence metabolism, leading to increased energy expenditure and potentially weight loss. They argue that combining protein with carbohydrates can increase insulin production, which can lead to fat storage. By separating these food groups, they believe that insulin spikes can be minimized, promoting fat burning instead of fat storage.
However, it is important to note that there is no scientific evidence to support this claim.
“Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When you eat carbohydrates, your body releases insulin to help transport glucose (sugar) from your bloodstream into your cells for energy. Insulin also promotes fat storage. “
Impact on Satiety and Appetite
Food combining proponents believe that specific food combinations can influence satiety and appetite, leading to reduced food intake and potentially weight loss. They suggest that combining protein with carbohydrates can increase satiety, as protein takes longer to digest and absorb than carbohydrates.
This can lead to a prolonged feeling of fullness and potentially reduce overall caloric intake. They also argue that consuming fruits separately from other foods can enhance the feeling of fullness due to their high fiber content and quick absorption.
Alternative Weight Loss Strategies
Food combining is one approach to weight loss, but it’s not the only one. Several other strategies are popular and have varying degrees of scientific support. Understanding the pros and cons of different approaches can help you choose the best strategy for your individual needs and preferences.
Comparison of Weight Loss Strategies
Here’s a comparison of food combining with other popular weight loss strategies:
Calorie Restriction
Calorie restriction involves consuming fewer calories than your body burns, creating a calorie deficit that leads to weight loss.
- Pros:
- Proven effective for weight loss.
- Simple to understand and implement.
- Widely supported by scientific research.
- Cons:
- Can be difficult to maintain long-term.
- May lead to nutrient deficiencies if not planned carefully.
- Can slow down metabolism if done too aggressively.
Exercise
Regular physical activity burns calories and helps build muscle mass, contributing to weight loss and overall health.
- Pros:
- Improves cardiovascular health.
- Boosts mood and energy levels.
- Increases metabolism.
- Helps maintain muscle mass during weight loss.
- Cons:
- Can be time-consuming and require effort.
- May not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain health conditions.
- Can be challenging to stick to consistently.
Summary Table of Weight Loss Methods
| Method | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Combining | Focuses on the order and combination of foods consumed. | May improve digestion and nutrient absorption. | Limited scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness for weight loss. |
| Calorie Restriction | Reducing calorie intake below daily expenditure. | Proven effective for weight loss. | Can be difficult to maintain long-term, may lead to nutrient deficiencies. |
| Exercise | Regular physical activity, including cardio and strength training. | Improves overall health, boosts metabolism, helps maintain muscle mass. | Can be time-consuming and challenging to stick to consistently. |
Last Recap
Ultimately, while food combining might offer some potential benefits, it’s crucial to approach it with a balanced perspective. There’s no magic bullet for weight loss, and relying solely on food combining without addressing other lifestyle factors like calorie intake and physical activity is unlikely to yield significant results.
If you’re considering adopting food combining, consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to ensure it aligns with your individual needs and health goals.






