Primer: Active vs. Passive Stretching – Unlock Your Flexibility
Primer active passive stretching – Primer: Active vs. Passive Stretching – Unlock Your Flexibility. Ever wondered about the difference between active and passive stretching? Both are important for flexibility and mobility, but they work in distinct ways. Active stretching involves using your own muscles to move a limb through a range of motion, while passive stretching relies on external forces like gravity or a partner to help you stretch.
This guide explores both techniques, their benefits, and how to incorporate them into your fitness routine.
We’ll dive into the techniques, benefits, and risks of each type of stretching. You’ll learn how to choose the right approach based on your fitness goals and individual needs. We’ll also provide a sample stretching routine and address common concerns about stretching, such as whether it’s necessary to stretch every day.
Primer on Passive Stretching
Passive stretching is a form of stretching where an external force is used to move a joint beyond its normal range of motion. This force can be applied by a partner, a therapist, or even a piece of equipment. The goal of passive stretching is to increase flexibility and range of motion by lengthening muscles and tendons.
Techniques of Passive Stretching
Passive stretching techniques involve using external forces to lengthen muscles and increase range of motion. The most common techniques include:
- Partner-Assisted Stretching:Involves a partner applying gentle pressure to the muscle being stretched, allowing the individual to relax and lengthen the muscle further than they could on their own. This technique is often used in physical therapy settings.
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF):This technique involves a combination of isometric contractions and passive stretching. It is often used by physical therapists to increase muscle length and flexibility.
- Gravity-Assisted Stretching:Utilizes gravity to help lengthen muscles. This technique involves hanging from a bar or using a weight to apply a force to the muscle being stretched.
- Equipment-Assisted Stretching:Uses tools like foam rollers, resistance bands, or stretch straps to provide support and leverage for stretching. This technique allows individuals to stretch more effectively and safely.
Examples of Passive Stretching Exercises, Primer active passive stretching
Passive stretching exercises can be performed for various muscle groups. Here are some examples:
- Hamstring Stretch:While lying on your back, have a partner gently pull your leg towards your chest until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh.
- Calf Stretch:While standing facing a wall, place one leg slightly behind the other and lean forward until you feel a stretch in your calf.
- Quadriceps Stretch:While standing, grab your foot with one hand and gently pull your heel towards your buttocks until you feel a stretch in the front of your thigh.
- Pectoral Stretch:While standing in a doorway, place your hands on the doorframe at shoulder height and gently lean forward until you feel a stretch in your chest.
- Shoulder Stretch:While sitting with your arms relaxed at your sides, have a partner gently pull your arm across your body until you feel a stretch in your shoulder.
Benefits of Passive Stretching
Passive stretching offers several benefits, including:
- Increased Muscle Length:By applying external force, passive stretching can lengthen muscles beyond their normal range of motion, improving flexibility and range of motion.
- Improved Posture:Increased muscle length and flexibility can help improve posture by allowing muscles to support the body more effectively.
- Reduced Muscle Tension and Pain:Stretching can help release muscle tension and reduce pain by improving blood flow and reducing muscle stiffness.
- Enhanced Performance:Improved flexibility and range of motion can enhance athletic performance by allowing for greater freedom of movement.
- Relaxation:Passive stretching can promote relaxation and reduce stress by decreasing muscle tension and promoting a sense of well-being.
Comparing Active and Passive Stretching
Stretching is an essential part of any fitness routine, helping to improve flexibility, range of motion, and overall performance. There are two main types of stretching: active and passive. Both have their benefits and drawbacks, and understanding the differences can help you choose the best stretching methods for your needs.
Techniques and Benefits
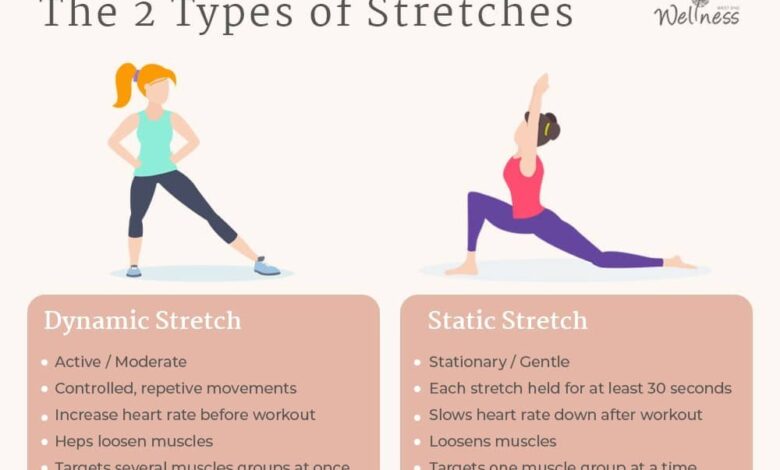
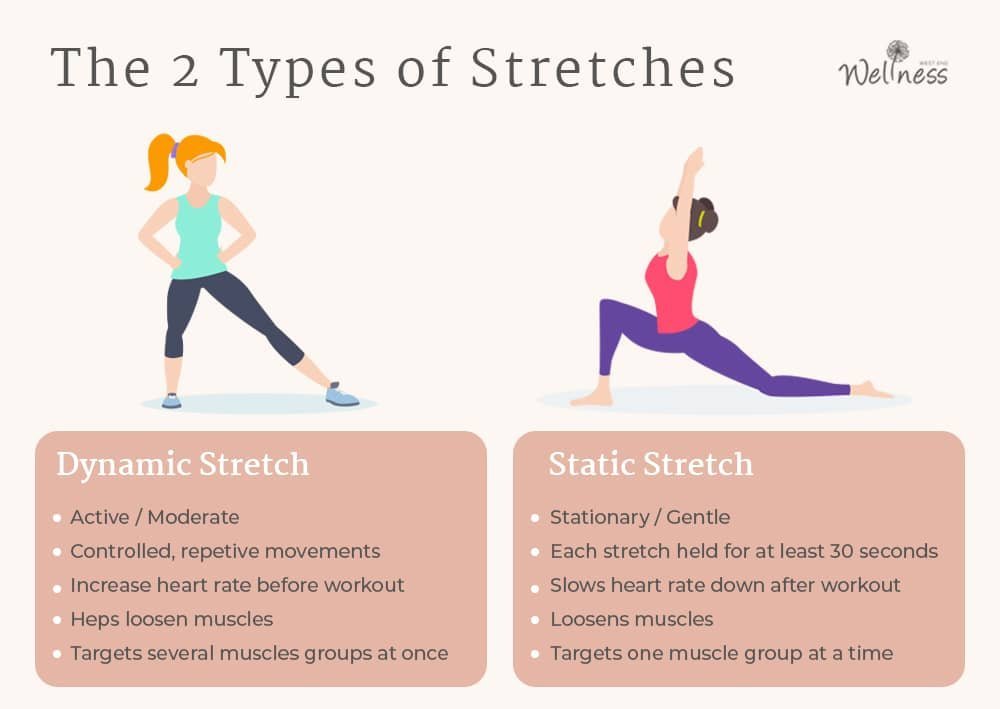
Active stretching involves using your own muscles to move your body into a stretch position and hold it. This type of stretching often involves dynamic movements and is often used as a warm-up before exercise.
Primer active and passive stretching are essential for preparing your body for long distances, especially when it comes to ultra walking. If you’re thinking about taking on this challenge, be sure to check out everything you need to know about ultra walking to learn about the specific training and preparation involved.
Once you’ve got the basics down, incorporating a good stretching routine will help you avoid injuries and maximize your performance.
- Active stretching uses your own muscle strength to move your body into a stretch position.
- It is often used as a warm-up before exercise and can help to improve flexibility, range of motion, and blood flow.
- Examples of active stretches include arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists.
Passive stretching involves using external force, such as gravity or a partner, to move your body into a stretch position and hold it. This type of stretching is often used for relaxation and can help to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
- Passive stretching involves using external force, such as gravity or a partner, to move your body into a stretch position.
- It is often used for relaxation and can help to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
- Examples of passive stretches include holding a hamstring stretch with a towel or having a partner gently pull your leg into a hip flexor stretch.
Potential Risks and Limitations
While both active and passive stretching can be beneficial, there are also potential risks and limitations to consider.Active stretching can be more challenging and may increase the risk of injury if done incorrectly. It is important to use proper form and avoid pushing yourself too far.
- Active stretching can be more challenging and may increase the risk of injury if done incorrectly.
- It is important to use proper form and avoid pushing yourself too far.
Passive stretching can be less effective if not held for a long enough period of time. Additionally, it can be difficult to control the amount of force being applied, which could lead to injury.
- Passive stretching can be less effective if not held for a long enough period of time.
- It can be difficult to control the amount of force being applied, which could lead to injury.
Stretching Methods for Different Fitness Goals and Levels
The best type of stretching for you will depend on your fitness goals and level.For those new to stretching, passive stretching may be a good starting point. It is generally safer and easier to control. As you become more flexible, you can gradually incorporate active stretching into your routine.
Primer, active, and passive stretching all play important roles in preparing your body for exercise. While active stretching helps warm up muscles, and passive stretching increases flexibility, the easiest exercise you can do to lose weight is often overlooked: walking.
Check out this article to learn more about the benefits of walking for weight loss. Remember, even a simple 30-minute walk can significantly improve your health and well-being, making it a great complement to your stretching routine.
- For those new to stretching, passive stretching may be a good starting point.
- As you become more flexible, you can gradually incorporate active stretching into your routine.
Active stretching is often preferred for athletes and those who want to improve their performance. It can help to increase range of motion, improve muscle activation, and reduce the risk of injury.
- Active stretching is often preferred for athletes and those who want to improve their performance.
- It can help to increase range of motion, improve muscle activation, and reduce the risk of injury.
It is important to listen to your body and stop if you feel any pain. If you are unsure about the best stretching methods for you, consult with a qualified fitness professional.
- It is important to listen to your body and stop if you feel any pain.
- If you are unsure about the best stretching methods for you, consult with a qualified fitness professional.
Integrating Stretching into a Workout Routine

Stretching is an important component of any fitness program. It can help improve flexibility, range of motion, and overall performance. Stretching can also help reduce the risk of injuries and improve recovery time.There are two main types of stretching: active and passive.
Active stretching involves using your own muscles to move your body into a stretched position. Passive stretching involves using external forces, such as gravity or a partner, to move your body into a stretched position.
Incorporating Active and Passive Stretching into a Fitness Program
The frequency and duration of stretching will vary depending on your individual goals and fitness level. However, in general, it is recommended to stretch at least 2-3 times per week. Each stretching session should last for 10-15 minutes.It is important to warm up your muscles before stretching.
A light warm-up, such as a brisk walk or light cardio, can help increase blood flow and prepare your muscles for stretching.You can incorporate active and passive stretching into your fitness program by following these guidelines:
- Warm up before stretching.A light warm-up, such as a brisk walk or light cardio, can help increase blood flow and prepare your muscles for stretching.
- Stretch after your workout.This will help to improve flexibility and range of motion.
- Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds.This will allow your muscles to relax and lengthen.
- Breathe deeply while stretching.This will help to relax your muscles and improve blood flow.
- Don’t bounce.This can increase your risk of injury.
- Listen to your body.If you feel any pain, stop the stretch immediately.
Sample Stretching Routine
Here is a sample stretching routine that includes both active and passive exercises:
- Warm-up:5 minutes of light cardio, such as jogging in place or jumping jacks.
- Active stretches:
- Arm circles:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Extend your arms out to the sides, and then make small circles with your arms. Gradually increase the size of the circles. Repeat 10 times in each direction.
- Leg swings:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Swing one leg forward and back, keeping your leg straight. Repeat 10 times on each leg.
- Torso twists:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Place your hands on your hips, and then twist your torso to the right and left. Repeat 10 times in each direction.
- Passive stretches:
- Hamstring stretch:Sit on the floor with your legs extended in front of you. Reach down towards your toes, keeping your back straight. Hold for 30 seconds.
- Quadriceps stretch:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Bend one knee and grab your foot with your hand. Pull your heel towards your buttock. Hold for 30 seconds.
- Calf stretch:Stand facing a wall with your feet shoulder-width apart. Lean forward, keeping your back straight, until you feel a stretch in your calves. Hold for 30 seconds.
- Chest stretch:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Interlace your fingers behind your back and lift your arms up as high as possible. Hold for 30 seconds.
- Cool-down:5 minutes of light cardio, such as walking.
Importance of Proper Warm-up and Cool-down Stretches
Warm-up stretches help to prepare your muscles for activity. They increase blood flow to the muscles, which helps to improve flexibility and range of motion.
Primer, active, and passive stretching are all essential components of a well-rounded fitness routine, but tracking your progress can help you tailor your stretches for optimal results. Understanding how your body responds to different types of stretching can be a game changer.
You can use tracked data to make informed decisions about how long to hold each stretch, how often to stretch, and which stretches are most effective for your individual needs. Check out this article on 3 ways to use tracked data to meet your goals for some great tips on how to use data to reach your fitness goals.
By tracking your progress, you can ensure you’re getting the most out of your stretching routine and achieving the flexibility you desire.
Warm-up stretches should be dynamic, meaning they involve movement.
Cool-down stretches help to prevent muscle soreness and stiffness. They also help to promote relaxation and recovery.
Cool-down stretches should be static, meaning they involve holding a stretch for a period of time.
Considerations for Different Populations

Stretching is a crucial aspect of maintaining physical well-being, but its approach should be tailored to the specific needs and limitations of different individuals. This section will delve into considerations for stretching in various populations, including athletes, seniors, and individuals with injuries, offering tailored recommendations and emphasizing the importance of personalized guidance.
Athletes
Athletes require a specific type of stretching to optimize their performance and minimize the risk of injury. They can benefit from both active and passive stretching techniques, depending on their training goals and the type of sport they participate in.
- Dynamic stretching: Warming up with dynamic stretches, such as leg swings, arm circles, and torso twists, improves flexibility and prepares the muscles for physical activity.
- Static stretching: Static stretching, holding a stretch for a longer duration, is often incorporated after training to improve range of motion and reduce muscle soreness.
- Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching: This technique involves contracting and relaxing the muscles in a controlled manner to increase flexibility. PNF stretching can be particularly beneficial for athletes seeking to enhance their range of motion and recover from strenuous activity.
Seniors
Seniors often experience age-related changes in their bodies, including reduced flexibility and increased risk of falls. Tailoring stretching routines to their specific needs is essential for maintaining mobility and independence.
- Gentle stretches: Focusing on gentle, controlled movements is crucial for seniors. Avoid pushing too hard, as this can increase the risk of injury.
- Chair-based stretches: Many stretches can be performed while seated, making them accessible for individuals with limited mobility.
- Balance exercises: Incorporating balance exercises alongside stretching can help improve stability and reduce the risk of falls.
Individuals with Injuries
Stretching can be beneficial for individuals recovering from injuries, but it’s crucial to proceed with caution and seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
- Pain-free stretches: Only perform stretches that do not cause pain. If you experience any discomfort, stop the stretch immediately.
- Specific stretches: Your healthcare provider can recommend stretches tailored to your specific injury and recovery stage.
- Gradual progression: Gradually increase the intensity and duration of stretches as your injury heals.
Ending Remarks: Primer Active Passive Stretching
Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your fitness journey, understanding the difference between active and passive stretching is crucial. By incorporating both techniques into your routine, you can unlock greater flexibility, reduce injury risk, and improve overall well-being.
Remember, consistency is key. Don’t forget to listen to your body, and always consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or injuries.






