7 Pro Tips for Injury-Free Lifting
7 pro tips injury free lifting – 7 Pro Tips for Injury-Free Lifting: Want to lift heavy weights without risking injury? You’re not alone. Many people are eager to build muscle and strength but worry about getting hurt. That’s why it’s crucial to prioritize safety and learn proper techniques.
This guide will provide you with seven expert tips to ensure you lift weights effectively and safely, helping you achieve your fitness goals without compromising your well-being.
From mastering proper form to understanding the importance of progressive overload, this blog post will delve into the essential elements of injury-free weightlifting. We’ll cover everything from warm-up routines to nutrition strategies and the crucial role of sleep in maximizing your performance.
So, whether you’re a seasoned lifter or just starting, these tips will empower you to lift smarter and stronger.
Warm-up: The Foundation of Injury-Free Lifting
A proper warm-up is not just a formality; it’s a crucial step in preventing injuries and maximizing your workout potential. It prepares your body for the demands of weightlifting by gradually increasing your heart rate, blood flow, and muscle temperature.
Importance of Warming Up Muscles and Joints
A warm-up is essential for both your muscles and joints. Warming up your muscles increases blood flow to the working areas, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. This enhanced blood flow helps to improve flexibility, reduce muscle stiffness, and prepare your muscles for the strenuous activity ahead.Additionally, warming up your joints increases synovial fluid production, which lubricates the joints and reduces friction.
This lubrication helps to protect your joints from damage and allows for a greater range of motion.
Dynamic Stretching for Lifting, 7 pro tips injury free lifting
Dynamic stretching is a key component of a proper warm-up for weightlifting. Unlike static stretching, which involves holding a stretch for an extended period, dynamic stretching involves controlled movements through a range of motion. These movements mimic the actions you’ll perform during your workout, helping to activate and prepare your muscles and joints.Here are some examples of dynamic stretches that can be incorporated into your warm-up:
- Arm circles:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and extend your arms to the sides. Make small circles with your arms, gradually increasing the size of the circles. Perform 10-15 repetitions in each direction.
- Leg swings:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and hold onto a stable surface for balance. Swing one leg forward and backward, maintaining a controlled motion. Repeat with the other leg. Perform 10-15 repetitions on each side.
- Torso twists:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and place your hands on your hips. Rotate your torso from side to side, engaging your core muscles. Perform 10-15 repetitions in each direction.
- High knees:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and bring your knees up towards your chest as you run in place. Focus on keeping your core engaged and your back straight. Perform 30-60 seconds.
- Butt kicks:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and bring your heels up towards your glutes as you run in place. Focus on keeping your core engaged and your back straight. Perform 30-60 seconds.
- Walking lunges:Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and take a large step forward with one leg, lowering your body until your front knee is bent at a 90-degree angle. Push off with your front foot and step forward with the other leg.
Repeat for 10-15 repetitions on each side.
By incorporating dynamic stretching into your warm-up, you can improve your flexibility, mobility, and overall performance while reducing your risk of injury.
Proper Form: The Key to Safety and Effectiveness: 7 Pro Tips Injury Free Lifting
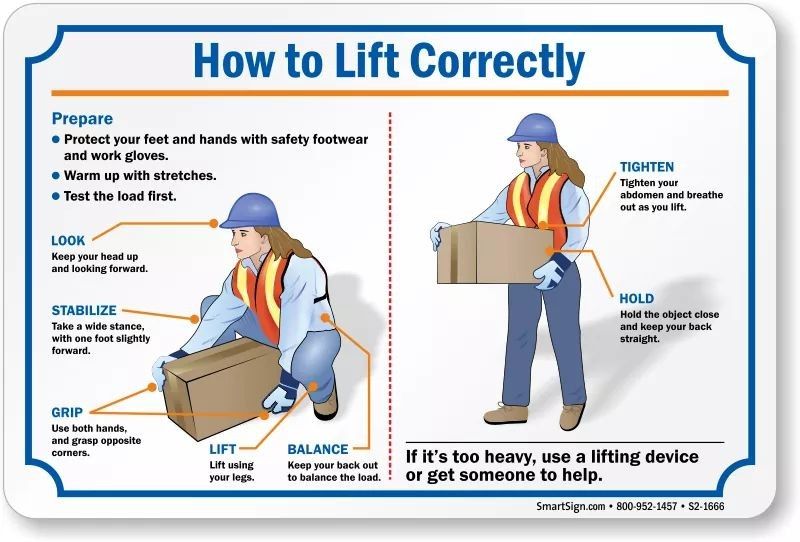
Proper form is the foundation of safe and effective weightlifting. It ensures that you are using the correct muscles to lift the weight and that you are minimizing the risk of injury. When you lift with proper form, you are able to recruit the right muscles to perform the exercise, which leads to greater strength gains and a reduced risk of injury.
Squats
Proper squat form is crucial for maximizing results and preventing injuries.
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly pointed outwards.
- Lower your hips as if you are sitting back into a chair, keeping your back straight and your core engaged.
- Descend until your thighs are parallel to the floor, or lower if you have the flexibility.
- Drive through your heels to return to the starting position.
Common mistakes to avoid:
- Rounding your back: This puts excessive stress on your spine.
- Letting your knees cave inwards: This can lead to knee pain and injury.
- Not going low enough: This reduces the effectiveness of the exercise.
Deadlifts
The deadlift is a powerful exercise that works multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Maintaining proper form is critical to prevent injuries.
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, toes pointing forward, and the barbell in front of you.
- Bend at your hips and knees, keeping your back straight and core engaged, until you can grasp the barbell with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Keep your back straight, and your core engaged throughout the lift.
- Lift the barbell by extending your hips and knees, keeping the bar close to your body.
- Lower the barbell by reversing the motion, keeping your back straight and core engaged.
Common mistakes to avoid:
- Rounding your back: This puts excessive stress on your spine.
- Lifting with your back instead of your legs: This can lead to back pain and injury.
- Not keeping the bar close to your body: This increases the risk of injury.
Bench Presses
The bench press is a fundamental exercise for building upper body strength.
Learning the 7 pro tips for injury-free lifting is a bit like mastering the essential cooking skills everyone should master – both require patience, practice, and a solid understanding of the fundamentals. Just as knowing how to properly chop an onion prevents tears, mastering proper form and technique in lifting ensures you can enjoy the benefits of a strong physique without risking injury.
- Lie on a weight bench with your feet flat on the floor and your back flat on the bench.
- Grip the barbell with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Lower the barbell to your chest, keeping your elbows slightly bent.
- Press the barbell back up to the starting position, keeping your elbows slightly bent.
Common mistakes to avoid:
- Arching your back: This puts excessive stress on your lower back.
- Letting your elbows flare out: This can lead to shoulder pain and injury.
- Not lowering the barbell all the way to your chest: This reduces the effectiveness of the exercise.
Overhead Presses
The overhead press is a great exercise for building shoulder strength.
Sticking to those 7 pro tips for injury-free lifting is key, especially if you’re following a low-carb diet. Since you’re limiting your carb intake, it’s crucial to make sure the carbs you do consume are high-quality, like those found in vegetables and whole grains, as explained in this great article on why quality of carbs matters on a low carb diet.
This way, you’re getting the energy you need for your workouts while also supporting your overall health and performance.
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand.
- Lift the dumbbells up to your shoulders, keeping your elbows slightly bent.
- Press the dumbbells overhead, keeping your elbows slightly bent.
- Lower the dumbbells back down to your shoulders, keeping your elbows slightly bent.
Common mistakes to avoid:
- Arching your back: This puts excessive stress on your lower back.
- Letting your elbows flare out: This can lead to shoulder pain and injury.
- Not keeping your core engaged: This can lead to instability and injury.
Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is a fundamental principle in weightlifting that involves gradually increasing the demands placed on your muscles over time. It’s the key to achieving consistent strength gains and building a strong, healthy physique. This principle ensures that your body adapts to the increasing workload, resulting in muscle growth and increased strength.
Progressive Overload in Practice
To implement progressive overload effectively, you need to gradually increase the weight you lift, the number of repetitions you perform, or the intensity of your workouts. This can be achieved by adding more weight to the bar, increasing the number of sets or repetitions, or reducing rest periods between sets.Here’s a sample program demonstrating how to gradually increase weight and intensity over time:
- Week 1:Start with a weight that allows you to perform 8-12 repetitions with good form for 3 sets of each exercise.
- Week 2:Increase the weight by 2.5-5 pounds (or 1-2.5 kg) for each exercise. Aim for 8-12 repetitions for 3 sets.
- Week 3:Maintain the same weight from Week 2, but increase the number of repetitions to 10-15 for 3 sets.
- Week 4:Increase the weight again by 2.5-5 pounds (or 1-2.5 kg) and perform 8-12 repetitions for 3 sets.
- Week 5:Continue increasing the weight or repetitions, or try a different exercise variation to challenge your muscles in a new way.
This is just a sample program; you should adjust it based on your individual fitness level and goals. It’s important to listen to your body and take rest days when needed.
The Importance of Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are crucial for muscle growth and injury prevention. When you lift weights, you create microscopic tears in your muscle fibers. These tears are repaired during rest, making your muscles stronger and larger.
“Rest is not laziness; it is essential for muscle growth and repair.”
It’s important to allow your body adequate time to recover between workouts. This typically involves taking 1-2 rest days per week. During rest days, you can engage in light activities like walking, stretching, or yoga.Adequate sleep is also essential for muscle recovery.
Learning those 7 pro tips for injury-free lifting can be a game-changer, but remember, it’s not just about the physical strength. A strong relationship is equally important, and that’s where the simple act of how walking together helps you stay together comes in.
It builds connection, communication, and shared experiences, which are crucial for a healthy relationship. And with a strong support system, you’ll be even more motivated to stick to those 7 pro tips and achieve your fitness goals.
Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to allow your body to repair and rebuild muscle tissue.
Listen to Your Body: Recognizing and Responding to Signals
Your body is a powerful and adaptable machine, but it also has limits. Pushing too hard without listening to its signals can lead to injuries. Recognizing and responding to your body’s cues is crucial for staying injury-free and maximizing your training gains.
Recognizing Overtraining and Injury Signals
Your body will send you signals when it’s overtrained or at risk of injury. These signals can be subtle at first, but if ignored, they can become more pronounced and lead to serious problems.
- Increased Resting Heart Rate:A consistently elevated resting heart rate can indicate that your body is not fully recovering from your workouts.
- Persistent Muscle Soreness:While some muscle soreness is normal after exercise, persistent soreness that doesn’t improve with rest can be a sign of overtraining or injury.
- Fatigue and Decreased Energy Levels:Feeling unusually tired and lacking energy, even after adequate sleep, can be a sign that your body needs more rest.
- Decreased Performance:If you notice a decline in your lifting capacity, repetitions, or overall performance, it could be a sign of overtraining or an underlying injury.
- Joint Pain:Pain in your joints, particularly if it persists or worsens with activity, can indicate a potential injury.
- Loss of Motivation:A lack of interest in training or a feeling of dread before workouts can be a sign that your body needs a break.
- Sleep Disturbances:Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep can be a symptom of overtraining or stress on your body.
- Changes in Appetite:Noticeable changes in your appetite, either a significant increase or decrease, can be a sign of overtraining or an underlying health issue.
Managing Pain and Soreness
After a lifting session, some muscle soreness is expected. It’s a sign that your muscles are adapting to the stress of exercise. However, there are strategies to manage pain and soreness and help your body recover effectively.
- Rest and Recovery:Allow your body adequate time to rest and recover between workouts. Aim for at least one to two days of rest per week.
- Active Recovery:Engage in light activities like walking, swimming, or yoga on your rest days to improve blood flow and promote recovery.
- Proper Nutrition:Consume a balanced diet rich in protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel muscle repair and recovery.
- Hydration:Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Massage:Massage can help relieve muscle tension and soreness.
- Stretching:Regular stretching can improve flexibility and range of motion, which can help prevent injuries and reduce soreness.
- Heat or Cold Therapy:Applying heat or cold therapy to sore muscles can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Nutrition and Hydration
Your body is your vehicle for lifting, and like any vehicle, it needs the right fuel to perform at its best. Nutrition and hydration are critical components of injury-free lifting, ensuring you have the energy to lift heavy weights, recover effectively, and prevent injuries.
Macronutrients for Strength and Recovery
The foundation of a weightlifting diet lies in macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays a crucial role in supporting your lifting goals.
- Carbohydratesprovide the primary source of energy for your workouts. They fuel your muscles, enabling you to lift heavier weights for longer durations. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are digested slowly, providing sustained energy. Aim for 40-50% of your daily calories from carbohydrates.
- Proteinsare essential for muscle growth and repair. After lifting weights, your muscles experience microscopic tears. Protein helps repair these tears, leading to muscle hypertrophy (growth). Aim for 0.8-1 gram of protein per pound of body weight daily. Good sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, and legumes.
- Fatsprovide energy and help your body absorb essential vitamins. Healthy fats, found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are crucial for hormone production and cell function. Aim for 20-30% of your daily calories from healthy fats.
Micronutrients for Optimal Performance
While macronutrients provide the building blocks, micronutrients, or vitamins and minerals, are essential for various bodily functions that impact your lifting performance.
- Ironis vital for red blood cell production, which carries oxygen to your muscles. Iron deficiency can lead to fatigue and reduced performance. Good sources include red meat, spinach, and fortified cereals.
- Calciumis crucial for bone health, which is essential for supporting your lifts. It also plays a role in muscle contraction. Good sources include dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods.
- Vitamin Dhelps your body absorb calcium, further contributing to bone health. It also plays a role in muscle function. Sunlight exposure is a natural source of vitamin D, and you can also find it in fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods.
Sample Meal Plan
Here’s a sample meal plan that incorporates foods that support muscle growth and recovery:
| Meal | Food | Macronutrients | Micronutrients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | Carbohydrates, protein, healthy fats | Fiber, vitamin C, antioxidants |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with quinoa and mixed greens | Protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats | Fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C |
| Dinner | Salmon with roasted vegetables | Protein, healthy fats | Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, vitamin C |
| Snack | Greek yogurt with fruit | Protein, carbohydrates | Calcium, probiotics |
Hydration: The Fuel for Your Body
Water is essential for countless bodily functions, including:
- Temperature regulation: Water helps your body maintain a stable temperature, preventing overheating during intense workouts.
- Nutrient transport: Water carries nutrients to your muscles and organs, ensuring proper function.
- Waste removal: Water helps flush out waste products from your body, preventing fatigue and muscle soreness.
- Joint lubrication: Water helps lubricate your joints, reducing friction and preventing injuries.
“Aim to drink 8-10 glasses of water daily, and more during and after intense workouts.”
Sleep
Sleep is often overlooked as a crucial component of fitness, but it’s just as important as your workout routine and nutrition plan. While you’re hitting the weights, your body is hard at work repairing and rebuilding muscle tissue. Sleep provides the ideal environment for this process to occur.
The Role of Sleep in Muscle Recovery and Performance Enhancement
Sleep is when your body repairs and rebuilds muscle tissue damaged during your workouts. During deep sleep, your body releases growth hormone, which plays a crucial role in muscle growth and repair. This process is essential for building strength and improving performance.
Getting enough sleep allows your body to fully recover, preventing overtraining and potential injuries.
Seeking Professional Guidance
While you’ve been diligently following the previous tips, there are instances where seeking professional guidance is not just recommended but crucial for maximizing your lifting journey and ensuring safety. Understanding when to consult an expert can be the difference between steady progress and potential setbacks.
When to Consult a Fitness Professional
Consulting a qualified fitness professional, such as a certified personal trainer or strength and conditioning coach, can significantly enhance your weightlifting experience and minimize the risk of injury. Here are some situations where their expertise can be invaluable:
- New to Weightlifting:Starting a new exercise program, especially weightlifting, can be daunting. A professional can guide you through proper form, teach you basic exercises, and create a personalized program tailored to your fitness goals and experience level.
- Plateauing:If you’ve been lifting for a while and find yourself stuck, unable to make further progress, a trainer can help you break through plateaus by assessing your current program, identifying areas for improvement, and suggesting new exercises or variations.
- Specific Goals:Whether you’re aiming for muscle hypertrophy, strength gains, or competitive powerlifting, a professional can provide tailored guidance and design a program that aligns with your specific objectives.
- Injury Prevention:A trainer can help you identify potential risk factors for injury and incorporate exercises and techniques that promote joint health and stability.
- Form Correction:Even experienced lifters can develop bad habits over time. A trainer can analyze your form and provide feedback to ensure you’re lifting safely and effectively.
Benefits of Working with a Personal Trainer
Beyond safety, working with a personal trainer offers a multitude of benefits for your weightlifting journey:
- Motivation and Accountability:Having a dedicated professional to guide and encourage you can significantly boost your motivation and commitment to your training regimen.
- Personalized Program Design:A trainer will create a program that aligns with your individual goals, fitness level, and limitations, ensuring that you’re working towards the right targets.
- Form and Technique Refinement:A trainer can provide real-time feedback on your form, ensuring proper technique and minimizing the risk of injury.
- Progress Tracking and Adjustments:Regularly tracking your progress allows your trainer to make adjustments to your program as needed, ensuring continuous improvement and avoiding plateaus.
- Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation:A trainer can help you identify potential risk factors for injury and incorporate exercises that promote joint health and stability. They can also provide guidance on injury rehabilitation if needed.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
While a fitness professional can provide guidance on exercise and form, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or physical therapist, if you experience any persistent pain or injury.
- Persistent Pain:If you experience pain that doesn’t subside within a few days or worsens with exercise, it’s essential to seek medical attention. This could indicate an underlying injury that requires professional evaluation and treatment.
- Sudden Injury:If you experience a sudden injury, such as a sharp pain or a popping sensation, it’s important to see a doctor immediately to rule out any serious conditions.
- Rehabilitation:After an injury, a healthcare professional can guide you through a rehabilitation program to help you regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Conclusive Thoughts

By incorporating these seven pro tips into your weightlifting routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of injury and unlock your full potential. Remember, consistency is key. Always prioritize proper form, listen to your body, and fuel your workouts with adequate nutrition and rest.
Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional when needed. With dedication and a focus on safety, you can enjoy a fulfilling and injury-free journey in the world of weightlifting.