Inflammation Basics and the Role of Diet & Exercise
Inflammation basics and the role of diet and exercise are crucial for maintaining optimal health. Inflammation, a natural response to injury or infection, can become chronic and contribute to various health problems. Understanding the different types of inflammation, their causes, and how to manage them is essential for preventing and treating chronic diseases.
This article will delve into the intricate relationship between inflammation, diet, and exercise, providing insights into how these factors impact our overall well-being.
The role of diet in inflammation is significant. Consuming a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce chronic inflammation. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats can contribute to inflammation.
Exercise, another key component of a healthy lifestyle, can also modulate inflammation levels. Regular physical activity can reduce chronic inflammation and improve overall health.
The Role of Diet in Inflammation: Inflammation Basics And The Role Of Diet And Exercise
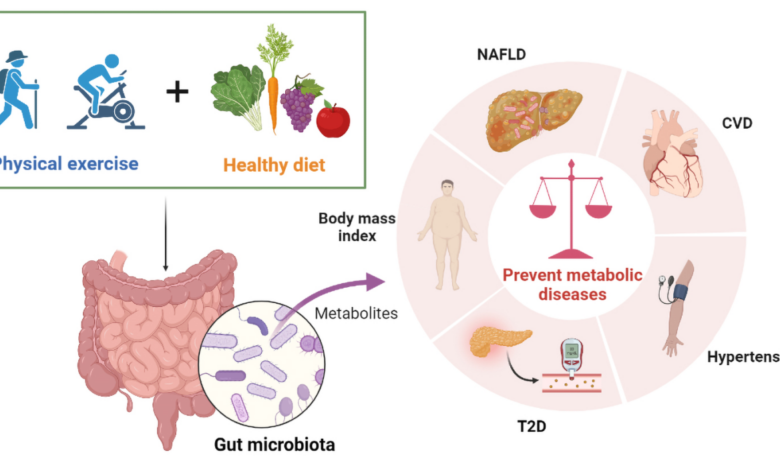
Inflammation is a natural process that helps your body heal from injuries and fight infections. However, chronic inflammation, which persists over a long period, can contribute to various health problems, including heart disease, cancer, and arthritis. While inflammation is often associated with lifestyle factors like lack of exercise and stress, your diet plays a crucial role in managing inflammation levels.
Foods That Promote Inflammation
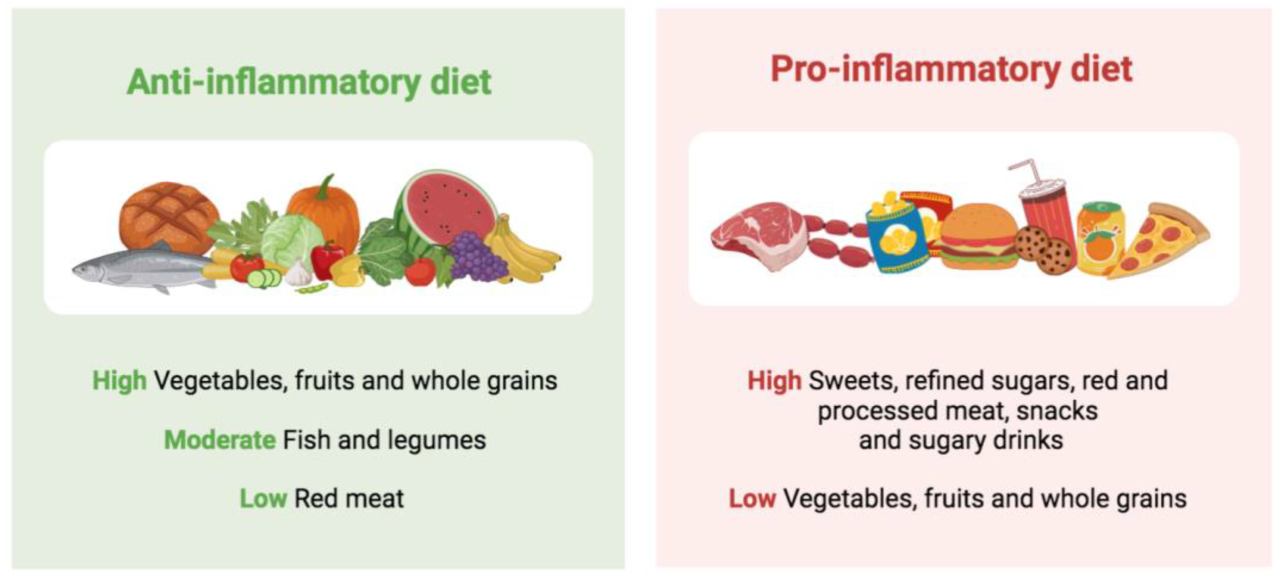
Certain dietary choices can trigger or exacerbate inflammation in the body. These pro-inflammatory foods often contain high levels of saturated and trans fats, refined sugars, and processed ingredients.
- Saturated and Trans Fats:Found in red meat, butter, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods, these fats can increase inflammation markers in the body.
- Refined Sugars:Sugary drinks, processed snacks, and baked goods can contribute to inflammation by promoting oxidative stress and insulin resistance.
- Processed Foods:These foods are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium, all of which can contribute to inflammation.
Foods That Reduce Inflammation
On the other hand, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health. These foods are packed with nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids:Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna, these healthy fats can reduce inflammation by lowering the production of inflammatory chemicals.
- Antioxidants:Found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, antioxidants help protect cells from damage caused by inflammation.
- Fiber:Found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation.
The Role of Specific Nutrients in Inflammation
Specific nutrients play a vital role in managing inflammation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids:These fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the production of inflammatory chemicals in the body.
- Antioxidants:These compounds protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which contribute to inflammation. Vitamin C, vitamin E, and carotenoids are examples of potent antioxidants found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Fiber:A diet rich in fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation. Soluble fiber, found in oats, beans, and lentils, can help lower cholesterol levels, which can also contribute to inflammation.
Sample Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan
Here’s a sample meal plan that emphasizes anti-inflammatory foods:
Breakfast
- Oatmeal with berries and walnuts
- Scrambled eggs with spinach and avocado
Lunch
- Salmon salad with mixed greens, avocado, and lemon dressing
- Lentil soup with whole-grain bread
Dinner
- Grilled chicken breast with roasted vegetables
- Tofu stir-fry with brown rice and vegetables
Snacks
- Fruits like berries, apples, and bananas
- Nuts and seeds
- Yogurt with berries
Remember, incorporating these foods into your diet is crucial for reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
Understanding inflammation basics and the role of diet and exercise is crucial for overall health. We can use tracked data to create a personalized plan for managing inflammation, like tracking food intake to identify triggers or monitoring exercise intensity to optimize recovery.
Check out these 3 ways to use tracked data to meet your goals for a more holistic approach to managing inflammation. By combining these strategies with informed lifestyle choices, you can effectively reduce inflammation and improve your overall well-being.
The Role of Exercise in Inflammation
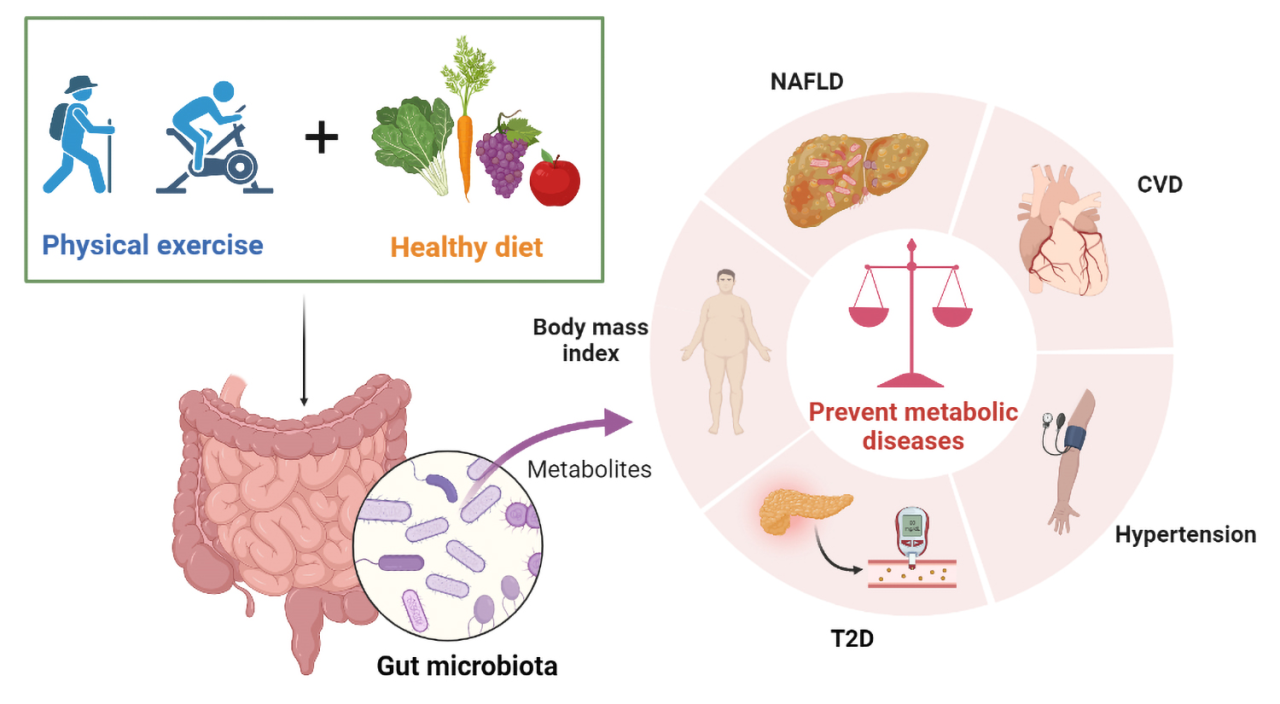
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing inflammation, and its impact goes beyond simply burning calories. When we engage in physical activity, our bodies respond in complex ways, influencing inflammation levels.
The Connection Between Exercise and Inflammation
Exercise triggers a temporary increase in inflammation, known as the “exercise-induced inflammatory response.” This is a natural process that helps repair and rebuild muscle tissue after exertion. However, regular exercise, especially moderate-intensity activities, can actually reduce chronic inflammation in the long run.
Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can contribute to various health issues. A healthy diet and regular exercise can help manage inflammation levels. However, returning to group fitness classes after a break can be a concern, especially regarding potential risks of injury or overexertion.
It’s essential to assess your current fitness level and consider the intensity of the classes before jumping back in. This article explores the risks associated with returning to group fitness, which can help you make informed decisions about your workout routine.
Remember, managing inflammation through diet and exercise is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Impact of Different Exercise Types on Inflammation, Inflammation basics and the role of diet and exercise
The type and intensity of exercise can influence inflammation levels.
Moderate-Intensity Exercise and Inflammation
Moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. This type of exercise promotes the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines, which help to reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Understanding inflammation basics and the role of diet and exercise is crucial for overall health, especially as we age. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, combined with regular physical activity, can help keep inflammation in check. Interestingly, exercise helps your memory as you age , which is likely due to its positive impact on brain health and reducing inflammation.
By managing inflammation, we can potentially improve cognitive function and overall well-being throughout our lives.
High-Intensity Exercise and Inflammation
High-intensity exercise, like interval training or sprinting, can lead to a more pronounced inflammatory response. While this may seem counterintuitive, it’s important to note that the benefits of high-intensity exercise often outweigh the temporary increase in inflammation.
Moderate-Intensity Exercise vs. High-Intensity Exercise: Inflammation Effects
Moderate-intensity exercise generally leads to a lower, more manageable inflammatory response compared to high-intensity exercise. This is because moderate-intensity exercise tends to activate a different set of signaling pathways in the body, leading to a more balanced inflammatory response.
Recommendations for Incorporating Exercise into a Lifestyle to Manage Inflammation
To effectively manage inflammation through exercise, consider the following recommendations:
- Start gradually:Begin with short sessions of moderate-intensity exercise and gradually increase the duration and intensity over time.
- Listen to your body:Pay attention to how your body feels and adjust your exercise routine accordingly. If you experience pain or discomfort, rest and consult with a healthcare professional.
- Vary your workouts:Include a mix of different exercise types, such as cardio, strength training, and flexibility exercises, to engage various muscle groups and promote overall health.
- Prioritize consistency:Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Consistency is key to reaping the long-term benefits of exercise for inflammation management.
Inflammation and Health
Inflammation is a natural and essential process that helps our bodies heal from injuries and fight infections. However, when inflammation becomes chronic and persists over a long period, it can contribute to a wide range of health problems.
The Connection Between Chronic Inflammation and Health Conditions
Chronic inflammation is linked to various health conditions, including:
- Heart disease: Inflammation plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Diabetes: Chronic inflammation can impair insulin sensitivity, leading to type 2 diabetes.
- Cancer: Inflammation can promote tumor growth and spread, increasing the risk of cancer development.
- Arthritis: Chronic inflammation is a key factor in various forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
- Alzheimer’s disease: Inflammation in the brain is associated with the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
The Long-Term Consequences of Uncontrolled Inflammation
Uncontrolled inflammation can lead to significant health complications, including:
- Accelerated aging: Chronic inflammation can contribute to premature aging and cellular damage.
- Increased risk of chronic diseases: Chronic inflammation is a significant risk factor for various chronic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and arthritis.
- Impaired organ function: Prolonged inflammation can damage organs and impair their function, leading to organ failure.
- Reduced quality of life: Chronic inflammation can cause pain, fatigue, and other symptoms that significantly affect quality of life.
Early Detection and Intervention for Inflammatory Conditions
Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing inflammatory conditions. Early detection allows for timely treatment and can help prevent the development of complications.
Closing Notes
By understanding the basics of inflammation and incorporating a balanced diet and regular exercise into our lifestyle, we can effectively manage inflammation and promote long-term health. It’s crucial to remember that chronic inflammation is a complex process, and a holistic approach involving lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and preventive measures is often necessary.
By taking proactive steps to address inflammation, we can enhance our overall well-being and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases.