Everything You Need to Know About Muscle Fiber Types
Ever wondered why some people excel at endurance sports while others dominate in explosive power events? The answer lies within the fascinating world of muscle fiber types. Everything you need to know about muscle fiber types reveals the intricate tapestry of these tiny powerhouses that fuel our movements, revealing how they influence our athletic potential and even our overall health.
Our muscles are made up of different types of fibers, each with its unique characteristics. These fibers are like specialized athletes, each excelling in a specific type of activity. Understanding these muscle fiber types unlocks a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay between our bodies and the activities we engage in.
It’s like peering into the engine room of our bodies, revealing the secrets behind our strength, speed, and endurance.
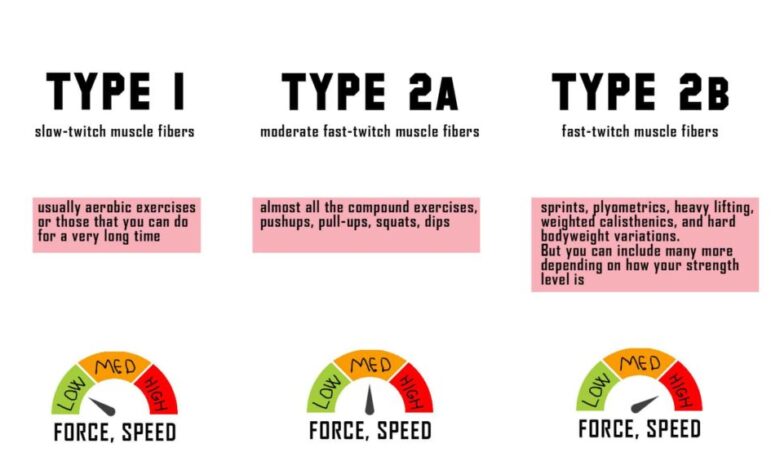
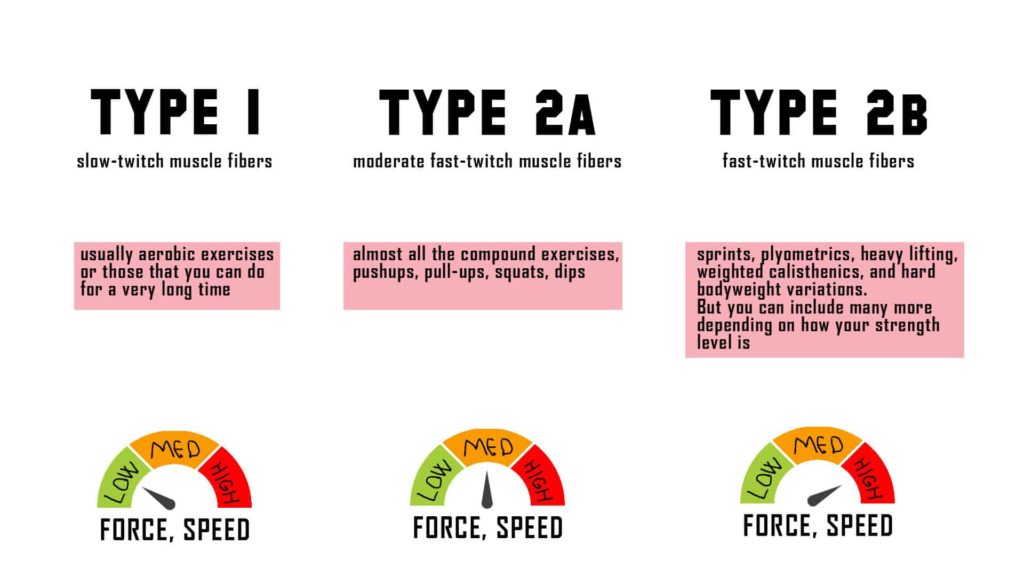
Type IIa (Fast-Twitch Oxidative) Muscle Fibers
Type IIa muscle fibers are a fascinating blend of speed and endurance, making them incredibly versatile for a wide range of activities. These fibers are known for their fast contraction speed, which allows for powerful movements, but also possess a moderate oxidative capacity, giving them a decent level of fatigue resistance.
Understanding muscle fiber types is key to optimizing your workouts and recovery. Knowing which fibers are dominant in your muscles can help you tailor your training to maximize gains and prevent injuries. And, just as important as pushing your limits is giving your body the rest it needs to rebuild and recover.
Check out this great article on this is your body on a recovery day to learn how to support your body’s natural repair processes. By combining targeted training with proper recovery, you can unlock your full potential and achieve your fitness goals.
Let’s delve deeper into the unique characteristics of Type IIa fibers and explore how they contribute to both power and endurance activities.
Characteristics of Type IIa Fibers
Type IIa fibers exhibit a unique combination of characteristics that make them stand out:
- Fast Contraction Speed:Type IIa fibers are known for their fast contraction speed, which enables them to generate powerful movements quickly. This is due to their high myosin ATPase activity, which allows them to break down ATP rapidly, providing energy for muscle contractions.
Understanding muscle fiber types is crucial for optimizing your workouts, but it’s also important to fuel your body with the right nutrients. Think about incorporating superfoods to use in holiday dishes that can help you recover and build muscle.
After all, a healthy diet is just as important as a good exercise routine when it comes to maximizing your fitness potential.
- Moderate Oxidative Capacity:Unlike Type IIb fibers, which rely primarily on anaerobic metabolism, Type IIa fibers possess a moderate oxidative capacity. This means they can utilize oxygen more efficiently, allowing them to sustain activity for longer periods. They have a higher density of mitochondria, the powerhouses of cells, and a rich capillary network, facilitating oxygen delivery.
Understanding muscle fiber types is crucial for optimizing your workout routine. Whether you’re aiming for explosive power or endurance, knowing the different types of fibers helps you tailor your training to achieve your goals. This knowledge can also help you navigate the often-confusing world of weight loss, as a well-structured workout plan is a key component of sustainable weight management.
If you’re looking for healthy and effective strategies to shed pounds without resorting to fad diets, check out this article on 4 sustainable ways to lose weight without fad diets. By incorporating these strategies into your lifestyle, you can achieve your weight loss goals while maintaining a healthy relationship with food and exercise.
Returning to muscle fiber types, it’s important to remember that your body is a complex system, and understanding how it works is essential for achieving your fitness goals.
- Moderate Resistance to Fatigue:Due to their moderate oxidative capacity, Type IIa fibers exhibit moderate resistance to fatigue. They can sustain moderate-intensity activities for a longer duration compared to Type IIb fibers but may eventually fatigue when subjected to high-intensity or prolonged efforts.
Role of Type IIa Fibers in Endurance and Power Activities, Everything you need to know about muscle fiber types
Type IIa fibers play a crucial role in both endurance and power activities due to their unique characteristics. They are particularly well-suited for activities that require a combination of strength and endurance:
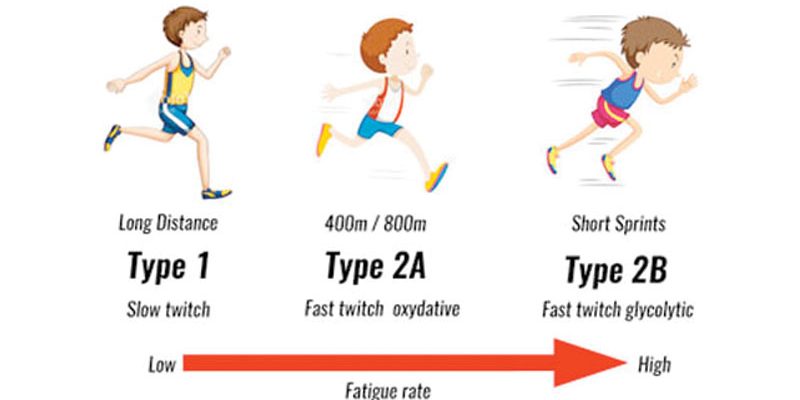
- Endurance Activities:Type IIa fibers contribute to endurance activities by sustaining moderate-intensity efforts for extended periods. Their moderate oxidative capacity allows them to utilize oxygen efficiently, delaying fatigue. Examples include middle-distance running, cycling, and swimming.
- Power Activities:Type IIa fibers also play a role in power activities, where bursts of force are required. Their fast contraction speed enables them to generate powerful movements, making them essential for activities like weightlifting, sprinting, and jumping.
Activities Utilizing Type IIa Fibers
Type IIa fibers are heavily involved in a variety of activities that demand a blend of power and endurance:
- Middle-Distance Running:Middle-distance running, typically ranging from 800 meters to 5000 meters, requires both speed and endurance. Type IIa fibers are essential for maintaining a fast pace while sustaining the effort over a significant distance.
- Weightlifting:Weightlifting exercises, such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses, demand significant muscle power. Type IIa fibers contribute to generating the force needed to lift heavy weights, while their moderate fatigue resistance allows for multiple repetitions.
- Interval Training:Interval training, which alternates between high-intensity bursts and periods of rest or low-intensity activity, heavily relies on Type IIa fibers. These fibers are crucial for producing powerful contractions during the high-intensity phases and recovering quickly for the next burst.
Muscle Fiber Type Distribution and Genetics: Everything You Need To Know About Muscle Fiber Types
The distribution of muscle fiber types within a muscle is a complex interplay of genetic predisposition and environmental factors, primarily training. Understanding the factors influencing this distribution is crucial for optimizing athletic performance and rehabilitation strategies.
Muscle Fiber Type Ratios and Athletic Performance
The ratio of different muscle fiber types within a muscle is known as the muscle fiber type distribution. This ratio is a key determinant of an individual’s athletic potential. For instance, athletes in power-based sports, such as sprinting or weightlifting, typically have a higher proportion of fast-twitch muscle fibers, which are better suited for generating explosive force.
Conversely, endurance athletes, like marathon runners, tend to have a higher percentage of slow-twitch fibers, which are more efficient at utilizing oxygen for sustained activity.
The Heritability of Muscle Fiber Type
Research indicates that muscle fiber type distribution is significantly influenced by genetics. Studies have shown that the heritability of muscle fiber type, which is the proportion of variation in a trait attributable to genetic factors, can range from 40% to 70%.
This suggests that a considerable portion of an individual’s muscle fiber type profile is predetermined by their genes.
The heritability of muscle fiber type is a complex topic, and the exact percentage can vary depending on the specific study and population being examined. However, it is generally accepted that genetics play a significant role in determining muscle fiber type distribution.
Training and Muscle Fiber Type Adaptation
While genetics play a significant role in determining muscle fiber type distribution, training can influence the expression of these fibers. While it’s not possible to change the fundamental type of a muscle fiber (e.g., converting a slow-twitch fiber into a fast-twitch fiber), training can induce adaptations within the existing fiber types.
For example, endurance training can lead to an increase in the oxidative capacity of fast-twitch type IIa fibers, making them more efficient at utilizing oxygen. Similarly, strength training can promote hypertrophy (growth) in both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, enhancing their force-generating capabilities.
- Endurance Training:Can enhance the oxidative capacity of fast-twitch type IIa fibers, making them more efficient at utilizing oxygen.
- Strength Training:Can promote hypertrophy (growth) in both slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, enhancing their force-generating capabilities.
Final Wrap-Up
The world of muscle fiber types is a captivating one, full of intricate details and fascinating insights. As we delve deeper into the workings of these tiny powerhouses, we gain a deeper understanding of our own capabilities and the potential for improvement.
Whether you’re an athlete seeking to optimize performance or simply curious about the inner workings of your body, understanding muscle fiber types provides a valuable lens for navigating the world of fitness, health, and athletic achievement.