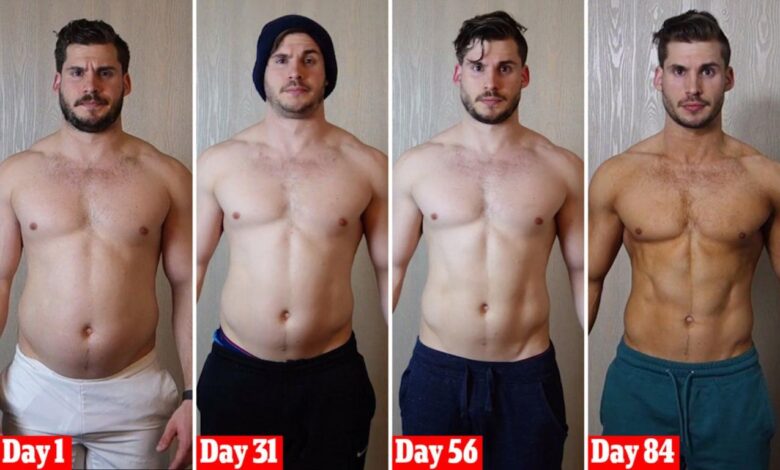
What Happens to Your Body When You Stop Exercising for a Month?
We all know exercise is good for us, but what happens when we hit the pause button? What Happens to Your Body When You Stop Exercising for a Month? is a question many of us ponder, especially when life gets busy and our workout routines fall by the wayside.
While a month-long break might seem like a minor hiccup, it can have surprising effects on your body, from your cardiovascular health to your mental wellbeing. Let’s dive into the fascinating changes that occur when you step away from your fitness routine.
From decreased cardiovascular fitness and muscle loss to potential mood swings and metabolic shifts, the impact of inactivity can be both noticeable and impactful. Understanding these changes can empower you to make informed decisions about your health and fitness journey.
Musculoskeletal System
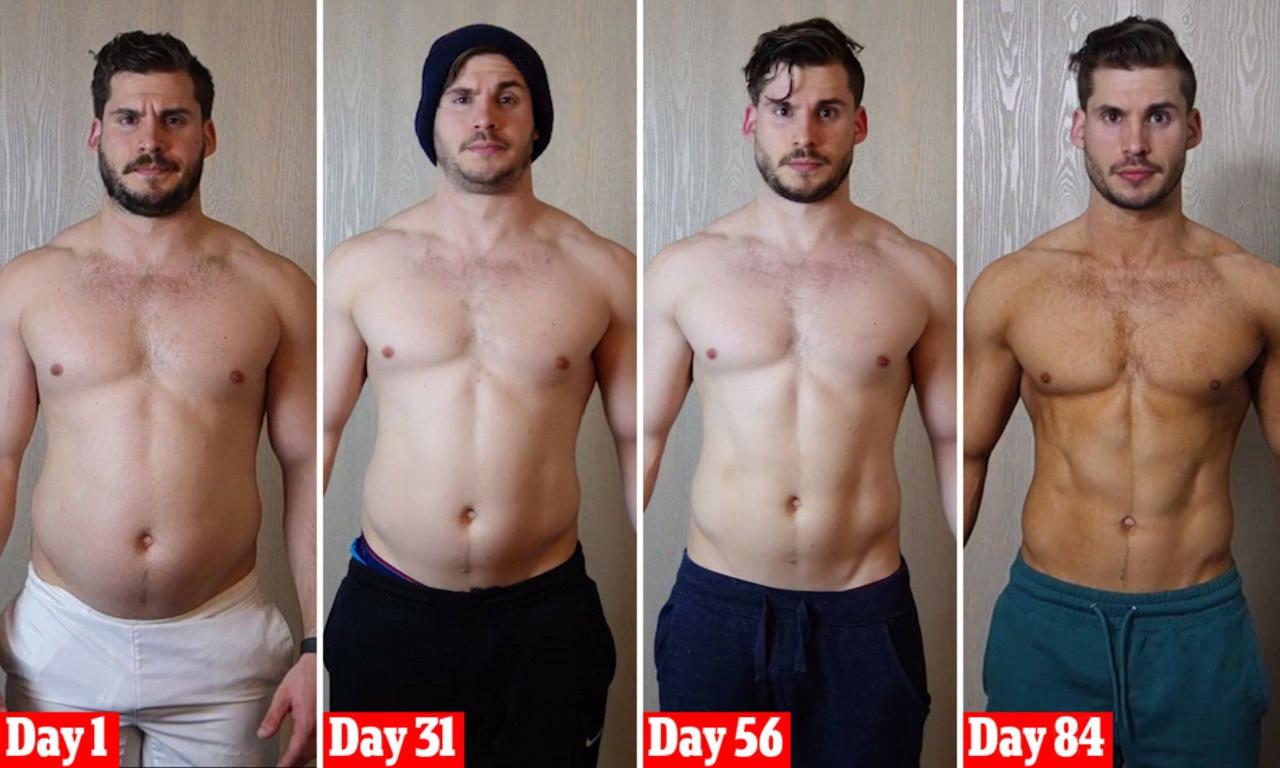

Taking a break from exercise can significantly impact your musculoskeletal system, which includes your bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. The lack of regular physical activity can lead to a decline in muscle mass and strength, affecting bone density and joint health.
Taking a month off from exercise can be tough on your body. You might notice a decrease in muscle mass, a drop in cardiovascular fitness, and even a dip in your mood. But if you’re thinking about getting back into it, you’ll need the right shoes! A quick read on walking versus running shoes whats the difference will help you choose the perfect pair to support your feet and prevent injuries as you rebuild your fitness levels.
Remember, consistency is key, so even small steps can make a big difference in getting back to your exercise goals.
Moreover, your flexibility and range of motion may be compromised.
Muscle Mass and Strength Loss
When you exercise, your muscles break down and rebuild, becoming stronger and larger. However, without the stimulus of regular exercise, your body starts to prioritize energy conservation, leading to muscle protein breakdown. This results in a gradual loss of muscle mass, known as muscle atrophy.
You might be surprised how quickly your body adapts when you stop exercising for a month. Muscle mass can decrease, and your cardiovascular system might not be as efficient. But for endurance athletes, staying fueled is crucial, even during breaks.
It’s essential to understand how endurance athletes should carb up during workouts to maintain energy levels and optimize performance. This knowledge will help you bounce back faster when you return to your training routine.
This loss of muscle mass can affect your strength and overall physical function. For instance, you may find it harder to lift heavy objects, climb stairs, or engage in other daily activities that require physical exertion.
Bone Density and Joint Health
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density. Weight-bearing exercises, such as running, jumping, and weightlifting, put stress on your bones, stimulating them to become denser and stronger. When you stop exercising, the bone-building process slows down, potentially leading to a decline in bone density, increasing your risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones.
Moreover, inactivity can negatively affect joint health. Joints are the points where two or more bones meet, and they rely on regular movement to maintain their lubrication and flexibility. Without sufficient movement, the cartilage in your joints can deteriorate, leading to stiffness, pain, and a higher risk of osteoarthritis.
Taking a month off from exercise can feel tempting, but it’s important to remember that your body adapts to your routine. You might experience a decrease in muscle mass and strength, and your cardiovascular fitness could take a hit.
To avoid these setbacks and ensure consistent progress, it’s crucial to challenge your body regularly. Check out these 6 ways to avoid workout plateaus and consistently progress for a sustainable fitness journey. Remember, even a short break can have a noticeable impact, so stay motivated and keep moving!
Flexibility and Range of Motion
Flexibility refers to the ability of your joints to move through a full range of motion. Regular stretching exercises help maintain flexibility and improve your range of motion. However, when you stop exercising, your muscles and tendons can become tight and less flexible.
This can limit your ability to move freely and may increase your risk of injuries, especially during sudden movements or strenuous activities.
Mental and Emotional Wellbeing
You might be surprised to learn that your mental and emotional well-being can also be significantly impacted by a sudden drop in physical activity. When you stop exercising, your body’s natural endorphin production decreases, which can lead to changes in your mood and energy levels.
This, in turn, can affect your overall mental well-being.
Mood and Energy Levels, What happens to your body when you stop exercising for a month
Regular exercise is known to boost mood and increase energy levels. This is because physical activity triggers the release of endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. When you stop exercising, your body’s endorphin production decreases, leading to a potential dip in your mood.
You might experience feelings of fatigue, lethargy, and even irritability. For example, a study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that individuals who stopped exercising for four weeks experienced a significant decrease in their mood and energy levels.
Increased Stress and Anxiety
Exercise is an excellent stress reliever. When you exercise, your body releases hormones that have calming effects. When you stop exercising, your body’s ability to cope with stress may be compromised, potentially leading to increased anxiety and feelings of overwhelm.
This can be especially true if you were previously relying on exercise as a coping mechanism for stress. For instance, someone who regularly used running as a way to de-stress might find themselves feeling more anxious and irritable after stopping.
Sleep Quality
Exercise can significantly improve sleep quality. Regular physical activity helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep. When you stop exercising, your sleep quality may be affected. You might find it harder to fall asleep, experience more frequent awakenings during the night, or wake up feeling unrested.
For example, research published in the journal Sleep Medicine Reviews found that regular exercise can improve sleep quality in individuals with insomnia.
Summary: What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Exercising For A Month
While a month-long break from exercise might seem insignificant, the impact on your body can be quite noticeable. From a decline in cardiovascular fitness and muscle mass to potential changes in your metabolism and mental state, it’s important to recognize the effects of inactivity.
The good news is that getting back into a regular exercise routine can reverse many of these changes. Remember, consistency is key, and even small amounts of movement can make a big difference. So, whether you’re taking a short break or facing a longer hiatus, keep in mind the impact on your body and prioritize your health by staying active whenever possible.