Science Says: Can Diet Help Manage Asthma?
Science says changing your diet could help manage asthma, and it’s a fascinating concept. Imagine, instead of relying solely on medications, you could potentially find relief through the foods you eat. This idea has sparked a lot of research, and while more studies are needed, there’s growing evidence that certain dietary choices might play a role in managing asthma symptoms.
This blog post dives into the world of diet and asthma, exploring the potential connections, identifying foods that might help or hinder your condition, and discussing the importance of a balanced diet for overall lung health. We’ll also look at how lifestyle factors like exercise and stress can interact with your asthma.
Asthma and Diet
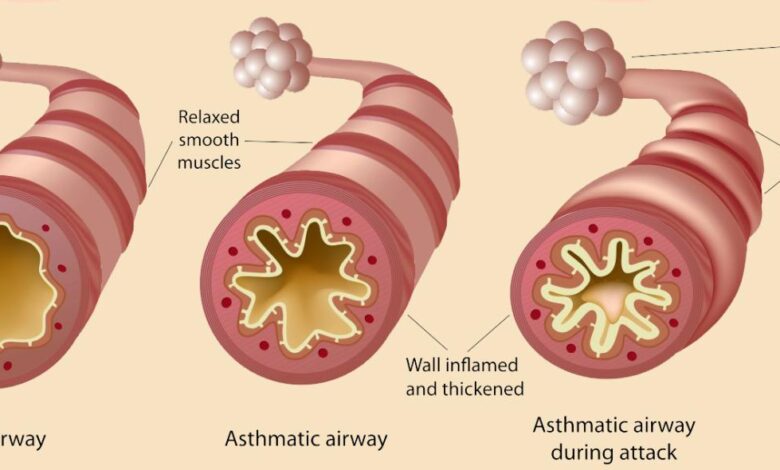
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide. While genetics play a significant role, environmental factors, including diet, can significantly influence asthma symptoms and severity. Understanding the relationship between diet and asthma can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively.
Mechanisms of Dietary Influence
Dietary components can influence asthma symptoms through various mechanisms.
- Inflammation:Certain foods can trigger inflammation in the airways, leading to bronchospasm and difficulty breathing. For example, foods high in omega-6 fatty acids, found in processed foods and vegetable oils, can promote inflammation.
- Immune Response:Diet can modulate the immune system, which plays a crucial role in asthma. Some foods, like those rich in antioxidants, may help strengthen the immune system and reduce inflammation, while others, like those containing histamine, may trigger allergic reactions.
- Airway Sensitivity:Diet can affect airway sensitivity to allergens and irritants. For instance, consuming foods rich in vitamin D may help reduce airway sensitivity and improve asthma control.
Common Dietary Triggers
While individual responses to food can vary, certain foods are commonly associated with asthma attacks.
- Histamine-rich foods:Histamine is a chemical that can trigger allergic reactions and worsen asthma symptoms. Examples include aged cheeses, fermented foods, and cured meats.
- Sulfites:Sulfites are preservatives commonly found in processed foods, dried fruits, and wines. They can trigger asthma attacks in sensitive individuals.
- Artificial food coloring:Certain artificial food colorings, such as yellow 5 and yellow 6, have been linked to asthma exacerbations in some individuals.
- High-fat foods:Foods high in saturated and trans fats can contribute to inflammation and worsen asthma symptoms.
Dietary Interventions for Asthma Management
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide. While there is no cure for asthma, there are many ways to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. One such way is through dietary interventions.
It’s fascinating how science is uncovering the connection between diet and asthma. While there’s no magic cure, making smart food choices can definitely help manage symptoms. For me, the key is feeling satisfied after meals, which helps avoid those cravings that can lead to unhealthy choices.
That’s why I’ve been following an RD approved approach to eating for fullness and satisfaction , and it’s been a game-changer in my journey to manage my asthma. With a focus on nutrient-rich foods and mindful eating, I’m feeling healthier and more in control than ever before.
Foods That May Help Manage Asthma Symptoms
Certain foods contain nutrients that may help reduce inflammation and improve lung function, potentially easing asthma symptoms. Here are some examples:
- Fruits and Vegetables:Rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, these foods can help combat inflammation and strengthen the immune system. Examples include berries, leafy greens, broccoli, and citrus fruits.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids:Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce asthma symptoms. They can also help improve lung function and reduce airway inflammation.
- Probiotics:These beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut can help regulate the gut microbiome, which plays a role in immune function and inflammation. A balanced gut microbiome may contribute to better asthma management.
- Vitamin D:This vitamin is essential for immune function and has been linked to improved asthma control. Sunlight exposure is a primary source of vitamin D, but supplements may be necessary for those with limited sun exposure.
Dietary Plans for Asthma Management
Incorporating these foods into a balanced diet can contribute to better asthma management. Here are some examples of dietary plans that focus on these beneficial foods:
- Mediterranean Diet:This diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil, all of which are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. It also includes moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy products, providing essential nutrients for asthma management.
It’s fascinating how science is revealing the power of food in managing health conditions. Research suggests that changing your diet could be a powerful tool for managing asthma, and that’s where registered dietitians come in. You might be surprised to learn just how much impact they have beyond just food choices, as explained in this article, 3 surprising takeaways about being a registered dietitian.
So, if you’re looking to manage your asthma naturally, consider how a personalized diet plan might help you breathe easier.
- DASH Diet:Designed to lower blood pressure, the DASH diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. This diet pattern can be beneficial for asthma management due to its emphasis on anti-inflammatory foods and its low sodium content, which may help reduce airway inflammation.
Foods to Avoid or Limit
While a healthy diet can support asthma management, certain foods can trigger or worsen symptoms. Identifying and limiting these foods can be crucial in improving asthma control.
Food Triggers and Asthma
Food triggers can cause various reactions in individuals with asthma, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. These reactions can be immediate or delayed, and the severity can vary depending on the individual and the food.
It’s fascinating how science is revealing the connection between our diet and chronic conditions like asthma. While it’s not a cure-all, research suggests that certain foods can help manage symptoms. And since we’re spending more time at home these days, it’s crucial to prioritize our well-being, both physically and mentally.
Check out these 10 ways to stay sane when working from home for some helpful tips. After all, a healthy mind and body are essential for managing any health condition, including asthma.
Food triggers are often related to food sensitivities or allergies, but they can also be caused by other factors, such as the presence of certain chemicals or additives in food.
Common Food Triggers
- Sulfites:These preservatives are commonly found in dried fruits, processed meats, wine, and beer. They can trigger asthma symptoms by causing bronchoconstriction, narrowing the airways.
- Salicylates:Found in fruits, vegetables, spices, and certain medications, salicylates can cause asthma symptoms in some individuals. Examples include apples, berries, grapes, tomatoes, cucumbers, and cinnamon.
- Histamine:This compound is naturally present in many foods, including aged cheese, fermented foods, and cured meats. It can trigger asthma symptoms by causing inflammation in the airways.
- Dairy:Milk and dairy products can trigger asthma symptoms in some people due to lactose intolerance or milk protein allergy.
- Eggs:Egg allergy is a common food allergy that can trigger asthma symptoms, including wheezing and coughing.
- Seafood:Seafood allergies can cause severe asthma reactions, including anaphylaxis. It’s essential to avoid all forms of seafood if you have a seafood allergy.
- Nuts and Seeds:Nut and seed allergies can trigger asthma symptoms, including wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing.
Identifying Food Triggers
Identifying food triggers can be challenging, as reactions can vary from person to person. Keeping a food diary can help track potential triggers and their associated symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare professional or allergist is recommended for accurate diagnosis and management.
Nutritional Considerations for Asthma Management: Science Says Changing Your Diet Could Help Manage Asthma

Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health, and it plays a significant role in managing asthma. A well-rounded diet provides the necessary nutrients to support lung function and reduce inflammation, which are key aspects of asthma management.
Role of Vitamins, Minerals, and Antioxidants, Science says changing your diet could help manage asthma
Vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants are essential components of a healthy diet that contribute to asthma management. These nutrients play a vital role in reducing inflammation, boosting the immune system, and protecting against oxidative stress, all of which are factors that can exacerbate asthma symptoms.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is essential for immune function and may help reduce inflammation. Studies suggest that low levels of vitamin D are associated with an increased risk of asthma and wheezing. Good sources of vitamin D include fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also supports the immune system and may reduce inflammation. Good sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, berries, and leafy green vegetables.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is involved in muscle relaxation and may help reduce airway inflammation. Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation can improve lung function in people with asthma. Good sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
- Selenium: Selenium is an essential mineral that acts as an antioxidant and supports immune function. Studies suggest that selenium may help reduce asthma symptoms and improve lung function. Good sources of selenium include Brazil nuts, tuna, and eggs.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They may help reduce airway inflammation and improve lung function in people with asthma. Good sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
Nutrient-Rich Foods for Lung Health
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide the essential nutrients for supporting lung health and managing asthma.
- Berries: Berries are packed with antioxidants, including vitamin C, which may help reduce inflammation and protect against oxidative stress. Examples include blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries.
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Leafy green vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, including vitamin C, magnesium, and folate. Examples include spinach, kale, collard greens, and romaine lettuce.
- Citrus Fruits: Citrus fruits are excellent sources of vitamin C, which can boost the immune system and reduce inflammation. Examples include oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes.
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and tuna, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and may help improve lung function.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds are good sources of magnesium, selenium, and omega-3 fatty acids, all of which can contribute to asthma management. Examples include almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains are rich in fiber, which can help regulate digestion and reduce inflammation. Examples include brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat bread.
Lifestyle Factors and Asthma
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact asthma symptoms and overall well-being. While medication is crucial for managing asthma, adopting a healthy lifestyle can complement treatment and enhance quality of life.
Physical Activity and Asthma
Regular physical activity is beneficial for overall health, but for individuals with asthma, it can be a double-edged sword. While exercise can improve lung function and cardiovascular health, it can also trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals.The impact of physical activity on asthma symptoms varies depending on the severity of the condition, individual triggers, and the type of exercise performed.
- Moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can generally be tolerated by most individuals with asthma. It can improve lung function, strengthen muscles, and reduce stress, all of which can positively impact asthma control.
- High-intensity exercise, such as running or playing sports, can trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals. This is because strenuous activity can lead to bronchospasm, a narrowing of the airways, making it difficult to breathe.
Tips for Incorporating Physical Activity
- Warm up before exercise: This helps prepare your body for physical activity and reduces the risk of triggering asthma symptoms.
- Choose activities that you enjoy: This will make it more likely that you’ll stick with an exercise routine.
- Start slowly and gradually increase intensity: This allows your body to adjust to exercise and reduces the risk of triggering asthma symptoms.
- Avoid exercising in cold, dry air: Cold air can irritate the airways and trigger asthma symptoms.
- Carry your inhaler with you: This allows you to manage asthma symptoms if they occur during exercise.
- Listen to your body: If you experience any difficulty breathing or other asthma symptoms, stop exercising and take your inhaler.
Stress and Asthma
Stress can worsen asthma symptoms. This is because stress triggers the release of hormones that can cause inflammation in the airways.
- Stress can lead to bronchospasm, which can make it difficult to breathe.
- Stress can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory infections that can trigger asthma symptoms.
Coping Mechanisms for Stress
- Practice relaxation techniques: Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and improve asthma control.
- Engage in activities that you enjoy: Spending time with loved ones, pursuing hobbies, or listening to music can help take your mind off of stress.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep deprivation can increase stress levels and worsen asthma symptoms.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol: These substances can exacerbate stress and worsen asthma symptoms.
- Seek professional help: If you’re struggling to manage stress, a therapist or counselor can provide support and guidance.
Scientific Evidence and Research
While the connection between diet and asthma is becoming increasingly clear, more research is needed to fully understand the complex interplay between food and this chronic respiratory condition.
Current Scientific Evidence
- Studies have shown that certain dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, may be associated with a lower risk of developing asthma and better asthma control.
- Research suggests that consuming omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, may have anti-inflammatory effects that could help manage asthma symptoms.
- Some evidence indicates that consuming foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, may protect against oxidative stress, which is thought to play a role in asthma development.
Ongoing Research
Researchers are actively investigating various aspects of diet and asthma, including:
- The role of specific nutrients, such as vitamin D, in asthma management.
- The impact of food allergies and intolerances on asthma severity.
- The potential benefits of personalized dietary interventions tailored to individual asthma profiles.
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals
While promising research is emerging, it’s crucial to remember that diet is just one aspect of asthma management. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on diet and other strategies to effectively manage your asthma. They can help you understand the best dietary approaches for your individual needs and medical history.
Last Point
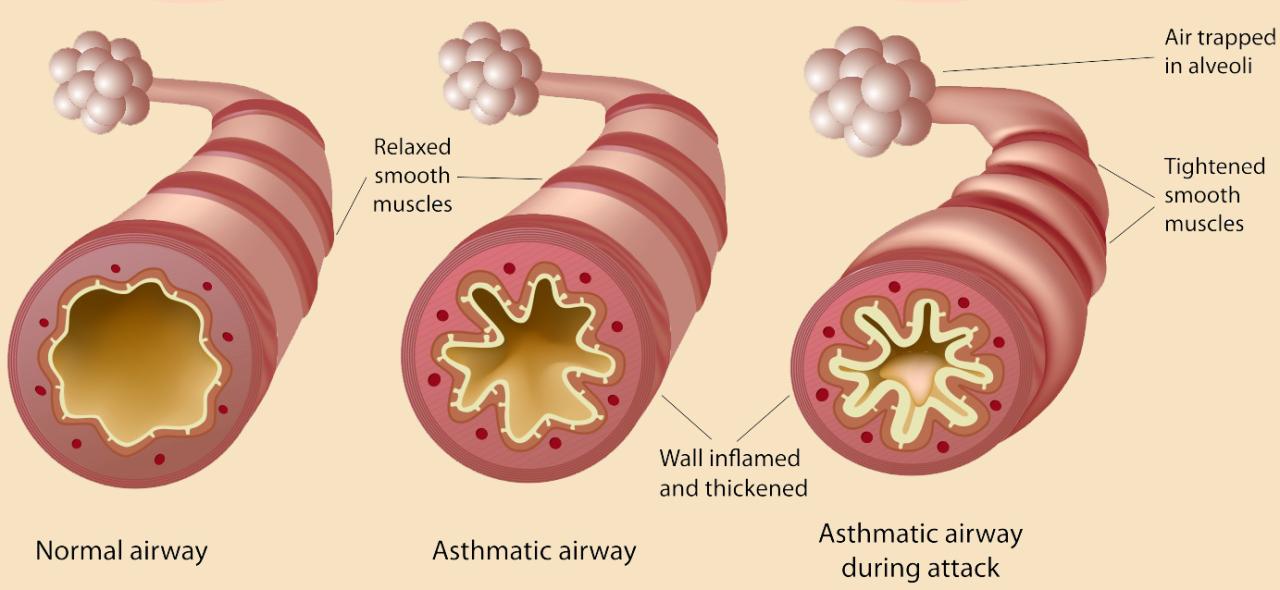
While research continues to shed light on the complex relationship between diet and asthma, it’s clear that a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing the condition. By making informed dietary choices, incorporating regular exercise, and managing stress effectively, you can take control of your asthma and improve your quality of life.
Remember, consulting with your doctor or a registered dietitian is always recommended to develop a personalized plan that’s right for you.