Can Ice Cream Be Healthy? Exploring the Sweet Truth
Can ice cream be healthy? It’s a question that sparks debate among health enthusiasts and ice cream lovers alike. While often perceived as a sugary indulgence, ice cream can actually offer some surprising nutritional benefits. From mood-boosting effects to potential bone-strengthening properties, exploring the potential health benefits of ice cream can challenge our preconceived notions about this beloved treat.
The key lies in understanding the nutritional content of ice cream, the potential health risks associated with excessive consumption, and how to make healthier choices. By exploring the different types of ice cream, the impact of various ingredients, and practical tips for moderation, we can navigate the world of ice cream with a newfound appreciation for its potential to fit into a balanced diet.
The Nutritional Content of Ice Cream: Can Ice Cream Be Healthy
Ice cream is a beloved treat enjoyed by people of all ages. While it’s often considered a guilty pleasure, it’s important to understand the nutritional content of ice cream to make informed choices about its consumption.
Macronutrient Composition
Ice cream is primarily composed of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The specific macronutrient composition can vary depending on the type of ice cream, but generally, it contains a significant amount of sugar and fat.
- Sugar:Sugar is the primary source of carbohydrates in ice cream, contributing to its sweetness and creamy texture. The sugar content can vary widely, with some ice creams containing as much as 20 grams of sugar per serving.
- Fat:Fat provides richness and flavor to ice cream. It can be derived from milkfat, cream, or other sources. Full-fat ice cream typically contains a higher percentage of fat compared to low-fat or fat-free varieties.
- Protein:Ice cream contains a moderate amount of protein, primarily from milk and egg yolks. The protein content is relatively low compared to other dairy products, but it still contributes to the overall nutritional value.
Vitamins and Minerals
While ice cream is not a primary source of vitamins and minerals, it does contain some essential nutrients.
- Calcium:Ice cream is a good source of calcium, which is essential for strong bones and teeth.
- Vitamin A:Some ice creams contain vitamin A, which is important for vision, skin health, and immune function.
- Riboflavin:Ice cream also contains riboflavin, a B vitamin that plays a role in energy production.
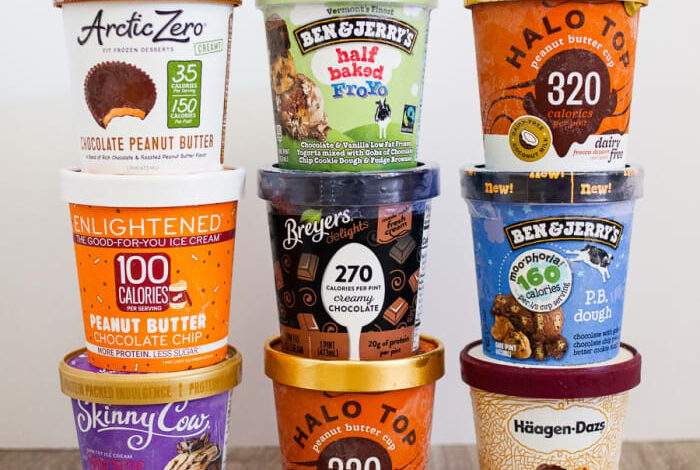
Nutritional Value of Different Types of Ice Cream
The nutritional value of ice cream can vary significantly depending on the type.
- Full-Fat Ice Cream:Full-fat ice cream is typically higher in calories, fat, and sugar. However, it also contains more vitamins and minerals, including calcium, vitamin A, and riboflavin.
- Low-Fat Ice Cream:Low-fat ice cream contains less fat and calories than full-fat varieties. However, it may also contain added sugars and artificial ingredients to compensate for the reduced fat content.
- No-Sugar-Added Ice Cream:No-sugar-added ice cream is typically sweetened with natural sweeteners like stevia or erythritol. These varieties can be a healthier option for those watching their sugar intake.
Health Benefits of Ice Cream
While often considered a treat, moderate ice cream consumption can offer some surprising health benefits. These benefits stem from the ingredients found in ice cream, including calcium, vitamin D, antioxidants, and probiotics, which can contribute to overall well-being.
Mood Enhancement and Stress Reduction, Can ice cream be healthy
Ice cream can act as a mood booster and stress reliever. The simple act of indulging in a sweet treat can trigger the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Additionally, the creamy texture and cold temperature of ice cream can have a calming effect on the nervous system.
Bone Health
Ice cream, especially varieties enriched with calcium and vitamin D, can play a role in maintaining strong bones. Calcium is essential for bone formation and density, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium effectively.
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that individuals with higher calcium intake had a lower risk of fractures.
Antioxidant Benefits
Some ice cream varieties contain antioxidants, which protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. These antioxidants can be found in ingredients like cocoa, berries, and nuts.
Can ice cream be healthy? It’s a question that sparks debate, but it’s all about moderation and making smart choices. If you’re looking to feel fuller for longer, check out this awesome guide to High Fiber Meals for Weight Loss: A Guide to Feeling Full and Slim for some tips on making healthier choices that don’t leave you craving a sweet treat.
While ice cream might not be the most nutritious choice, there are definitely ways to enjoy it in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, which is linked to chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Probiotic Benefits
Ice cream containing probiotics can contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support digestive health and immune function.
Probiotic-rich ice cream can help balance the gut bacteria, promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption.
Potential Health Risks of Ice Cream
While ice cream can be a delicious treat, excessive consumption can lead to various health concerns. It’s important to be mindful of the potential risks associated with indulging in this sweet delight too often.
Can ice cream be healthy? It’s a question that sparks debate, but the answer might surprise you. Ultimately, it comes down to moderation and understanding how your body works. Factors like portion control, frequency, and the ingredients themselves all play a role.
To shed light on the connection between food choices and weight management, it’s helpful to understand the three key hormones involved in the process, as outlined in this insightful article: 3 Hormones to Keep in Mind for Weight Loss.
By making informed choices and paying attention to these hormones, you can find a balance that allows you to enjoy your favorite treats, like ice cream, without compromising your health goals.
Weight Gain
Ice cream is typically high in calories, fat, and sugar, making it a significant contributor to weight gain if consumed in excess. A single serving of ice cream can contain anywhere from 200 to 500 calories, depending on the size and ingredients.
Regularly exceeding your daily calorie needs through ice cream consumption can lead to an accumulation of excess weight over time.
Tooth Decay
The high sugar content in ice cream can promote tooth decay. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities. The sticky nature of ice cream can also trap sugar particles on teeth, increasing the risk of decay.
Blood Sugar Spikes
The rapid absorption of sugar from ice cream can cause sudden spikes in blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance. This can lead to complications such as fatigue, headaches, and increased thirst.
Cardiovascular Health
Ice cream often contains high amounts of saturated fat and added sugars, both of which can negatively impact cardiovascular health. Saturated fat can raise LDL cholesterol levels, contributing to plaque buildup in arteries and increasing the risk of heart disease.
Excessive sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and inflammation, all of which are associated with cardiovascular problems.
Allergies and Sensitivities
Some ice cream varieties contain artificial colors and flavors, which can trigger allergies or sensitivities in certain individuals. These ingredients can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, swelling, and digestive issues. Additionally, some ice creams contain dairy products, which can be problematic for individuals with lactose intolerance.
Making Ice Cream Healthier
Ice cream is a beloved treat enjoyed by people of all ages, but its high sugar and fat content can raise concerns about its healthfulness. Fortunately, there are ways to make ice cream healthier without sacrificing flavor. By making a few adjustments to your recipe and incorporating nutritious ingredients, you can enjoy a guilt-free dessert that satisfies your sweet tooth and nourishes your body.
Can ice cream be healthy? It’s a question that sparks debate, but the truth is, moderation is key. If you’re aiming for a healthier lifestyle, it’s wise to consider making small, sustainable changes, like those outlined in 10 Simple Changes That Lead to Weight Loss.
These changes can help you enjoy your favorite treats, like ice cream, in a way that aligns with your overall health goals.
Using Natural Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners, such as honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar, can be used to reduce the sugar content of ice cream. These sweeteners are less processed and contain nutrients that can benefit your health. However, it’s important to note that they are still sugars and should be consumed in moderation.
Reducing Sugar Content
Reducing the amount of sugar in your ice cream recipe is a simple way to make it healthier. You can start by gradually reducing the sugar content by 10% to 25% and adjust to your taste preference.
Incorporating Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables can add natural sweetness, fiber, and vitamins to your ice cream. You can blend them into your ice cream base or use them as toppings. For example, you can add bananas, berries, or spinach for a boost of nutrients and flavor.
Using Alternative Ingredients
Using alternative ingredients can make your ice cream healthier and more flavorful. Here are some popular options:
- Greek yogurt:Greek yogurt adds creaminess and protein to your ice cream, while also reducing the fat content.
- Nut butters:Nut butters, such as almond butter and peanut butter, add a rich flavor and healthy fats to your ice cream.
- Avocado:Avocado is a creamy fruit that adds a unique flavor and healthy fats to your ice cream. It also provides fiber and antioxidants.
Healthy Ice Cream Recipe
Here is a recipe for a healthy ice cream variation that incorporates many of the tips mentioned above:
Strawberry-Avocado Ice Cream
Ingredients:
- 1 cup frozen strawberries
- 1 ripe avocado, pitted and peeled
- 1/2 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1/4 cup honey or maple syrup (adjust to taste)
- 1/4 teaspoon vanilla extract
- Pinch of salt
Instructions:
- Combine all ingredients in a blender and blend until smooth.
- Pour the mixture into a freezer-safe container and freeze for at least 4 hours, stirring every hour to prevent ice crystals from forming.
- Enjoy your healthy and delicious ice cream!
Nutritional Profile:This recipe provides a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium, and folate. It is also relatively low in calories and fat compared to traditional ice cream. Taste:This ice cream has a creamy texture and a sweet and slightly tangy flavor from the strawberries and avocado.
The honey or maple syrup adds a touch of sweetness, while the vanilla extract enhances the overall flavor.
Moderation and Balance

The key to enjoying ice cream without jeopardizing your health lies in moderation and balance. It’s not about completely eliminating this delicious treat but rather integrating it into a healthy lifestyle that prioritizes overall well-being.
The Importance of Moderation
Moderation means consuming ice cream in reasonable quantities. While it’s tempting to indulge in large portions, it’s crucial to recognize that ice cream is high in calories, sugar, and fat. Overconsumption can contribute to weight gain, increased risk of chronic diseases, and nutritional imbalances.
Comparing Ice Cream to Other Sweet Treats
Ice cream is not inherently worse than other sweet treats like cookies, cakes, or candy. The key difference lies in the nutritional content and how these treats are consumed. For example, a small cup of ice cream might contain fewer calories and less sugar than a slice of chocolate cake.
However, both can contribute to an unhealthy diet if consumed excessively.
Tips for Incorporating Ice Cream into a Balanced Diet
- Choose Smaller Portions:Opt for a smaller size or share a larger portion with someone else. This reduces the overall calorie and sugar intake.
- Limit Frequency:Instead of indulging in ice cream daily, reserve it for special occasions or treat yourself once or twice a week.
- Pair it with Nutritious Foods:Combine your ice cream with fruit, nuts, or yogurt to create a more balanced dessert. This adds fiber, protein, and vitamins to your treat.
- Make Healthy Substitutions:Consider homemade ice cream with natural sweeteners, low-fat milk, and fresh fruit. You can also explore frozen yogurt or sorbet as healthier alternatives.
Summary

Ultimately, the answer to whether ice cream can be healthy depends on individual dietary needs, preferences, and moderation. While excessive consumption can lead to health concerns, enjoying ice cream in moderation as part of a balanced diet can be a delicious way to indulge in a sweet treat without compromising overall health.
By making informed choices and embracing a balanced approach, we can savor the joy of ice cream while prioritizing our well-being.