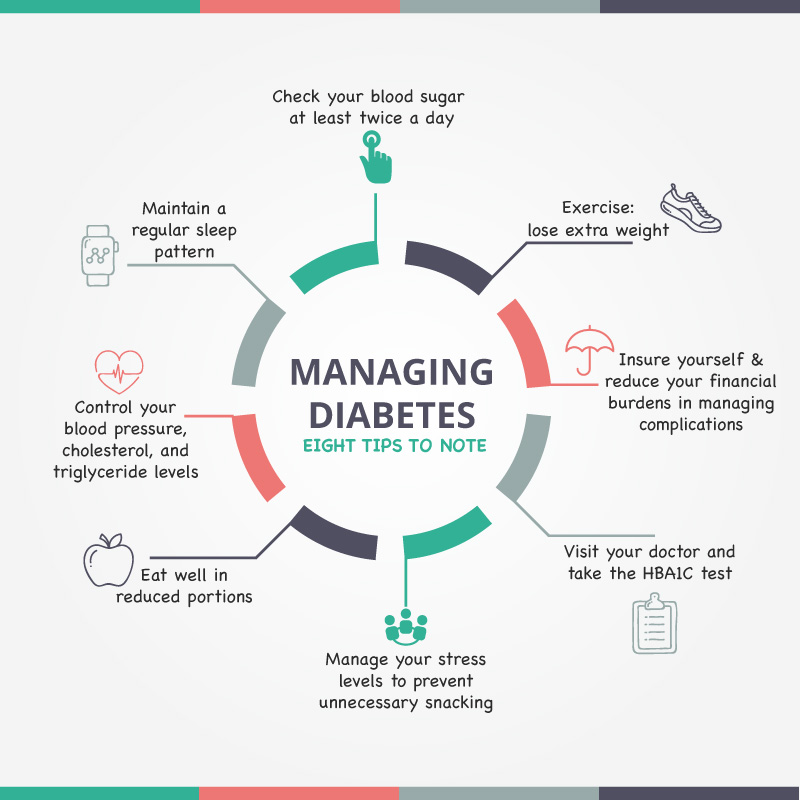
Tips to Make Living with Diabetes Easier
Tips to make living with diabetes easier are essential for managing this chronic condition and achieving a fulfilling life. Diabetes affects millions worldwide, and while there’s no cure, understanding the condition and implementing the right strategies can significantly improve quality of life.
This comprehensive guide will delve into various aspects of diabetes management, from understanding the basics to navigating the emotional challenges and harnessing the power of technology. We’ll explore how to make informed decisions about diet, exercise, medication, and emotional well-being, empowering you to take control of your health.
Diet and Nutrition for Diabetes
Diabetes management involves making healthy lifestyle choices, and a key component is a balanced diet. A well-planned diet can help control blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall health.
Living with diabetes means being mindful of your blood sugar levels, but it doesn’t have to feel restrictive. Sometimes, the biggest challenge is managing your condition when you’re away from home, like when you’re staying with friends or family.
Check out the guide to if when youre staying with friends and family for some helpful tips on navigating those situations. With a little planning and communication, you can enjoy your time with loved ones while staying on top of your diabetes management.
Designing a Balanced Meal Plan
A balanced meal plan for people with diabetes should include a variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups. This means incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats.
- Fruits and Vegetables:Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables daily. These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. Choose a variety of colors and types to ensure a diverse intake of nutrients.
- Whole Grains:Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat bread over refined grains. Whole grains are high in fiber, which helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
- Lean Protein Sources:Include lean protein sources like fish, poultry, beans, lentils, and tofu in your diet. Protein helps control blood sugar levels by slowing down the digestion process.
- Healthy Fats:Incorporate healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats can help improve cholesterol levels and promote overall heart health.
Choosing Healthy Snacks
Snacking can be a part of a healthy diet for people with diabetes. However, it’s important to choose snacks that are low in sugar and high in fiber.
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but it’s definitely manageable with the right tools and mindset. One thing that’s helped me immensely is learning to track my food intake and macronutrients. I actually stumbled upon the importance of this after reading about Kelsey’s journey in how a crash diet led kelsey to myfitnesspal and much healthier habits.
Her experience made me realize that taking control of my diet wasn’t about deprivation, but about making informed choices to fuel my body in a healthy way. And that’s what’s made a huge difference in managing my diabetes – understanding what I’m eating and how it affects my blood sugar levels.
- Fruits and Vegetables:Fresh fruits like apples, bananas, and berries are excellent choices. Vegetables like carrots, celery, and bell peppers provide a satisfying crunch and are low in calories.
- Nuts and Seeds:A handful of almonds, walnuts, or sunflower seeds can provide healthy fats and protein.
- Yogurt:Choose plain yogurt and add your own fruit or a small amount of honey for sweetness.
- Hard-Boiled Eggs:Eggs are a good source of protein and can be a convenient snack.
The Role of Portion Control and Mindful Eating
Portion control and mindful eating are essential for managing blood sugar levels.
- Portion Control:Pay attention to serving sizes and avoid overeating. Use smaller plates and bowls to help with portion control.
- Mindful Eating:Eat slowly and savor each bite. This allows your body to signal fullness and prevents overeating.
- Regular Meal Times:Eating at regular intervals can help prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes.
Medication and Insulin Therapy: Tips To Make Living With Diabetes Easier

Medication and insulin therapy are essential for managing diabetes and keeping blood sugar levels within a healthy range. Understanding the different types of medications available, their mechanisms of action, and how to manage insulin therapy is crucial for living a fulfilling life with diabetes.
Types of Diabetes Medications
Diabetes medications work by helping your body use insulin more effectively or by reducing the amount of glucose your liver produces. They are often prescribed in combination with lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise.
- Insulin:Insulin is a hormone naturally produced by the pancreas that helps glucose enter cells for energy. People with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes need insulin injections to regulate their blood sugar levels.
- Oral Medications:These medications are taken by mouth and come in various forms, including pills, tablets, and capsules.
Managing diabetes can feel like a constant balancing act, but one thing that can help is focusing on a healthy diet. The Mediterranean diet, with its emphasis on fresh fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, is a great place to start.
But if you’re looking to lower your carb intake, there are some tweaks you can make. Check out these ways to make the Mediterranean diet low carb friendly to see how you can still enjoy the delicious flavors of this diet while keeping your blood sugar levels in check.
Remember, consistency is key, so find what works for you and stick with it!
- Sulfonylureas:Stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- Meglitinides:Also stimulate insulin production, but they work faster than sulfonylureas.
- Biguanides:Reduce glucose production by the liver and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs):Increase insulin sensitivity in muscle and fat cells.
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors:Slow down the breakdown of carbohydrates in the digestive tract, reducing the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors:Increase the levels of incretin hormones, which stimulate insulin production and reduce glucagon secretion.
- Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors:Block the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion in the urine.
Adhering to Medication Regimens
Sticking to your prescribed medication regimen is essential for managing diabetes effectively. This includes taking the correct dosage at the right time and following your doctor’s instructions.
- Set Reminders:Use alarms, medication organizers, or mobile apps to remind yourself when to take your medications.
- Keep a Log:Track your medication intake, blood sugar levels, and any side effects you experience. This information can help you and your doctor monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments.
- Communicate with Your Doctor:Discuss any concerns or difficulties you have with your medications. Your doctor can provide guidance and support to help you adhere to your treatment plan.
Managing Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy requires careful attention to dosage, injection techniques, and monitoring.
- Types of Insulin:Different types of insulin have varying durations of action.
- Rapid-acting insulin:Starts working quickly and lasts for a short time.
- Short-acting insulin:Starts working within 30 minutes and lasts for 3-6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting insulin:Starts working within 1-2 hours and lasts for 12-18 hours.
- Long-acting insulin:Starts working slowly and lasts for 24 hours or more.
- Injection Techniques:Insulin is typically injected subcutaneously (under the skin).
- Rotate Injection Sites:Injecting insulin in the same spot repeatedly can lead to lipodystrophy (fat buildup or loss). Rotate injection sites regularly to avoid this.
- Use Proper Technique:Follow your doctor’s instructions for injection technique. This may involve using an insulin pen, syringe, or insulin pump.
- Dosage Adjustments:Insulin dosages may need to be adjusted based on blood sugar levels, diet, exercise, and other factors.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring:Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels to track your progress and adjust your insulin dosage as needed.
- Consult with Your Doctor:If you notice significant fluctuations in your blood sugar levels or experience any side effects from insulin therapy, consult with your doctor.
Emotional Well-being and Support
Living with diabetes can be emotionally challenging, and it’s important to acknowledge and address these feelings. It’s not just about managing blood sugar levels; it’s also about managing your mental health and well-being.
Coping with Emotional Challenges
It’s common to experience a range of emotions when you’re first diagnosed with diabetes, including shock, denial, anger, and fear. These feelings are perfectly normal and are a natural part of the adjustment process. Over time, you may also experience frustration, sadness, and anxiety.
It’s important to remember that you’re not alone. Many people with diabetes experience similar emotions, and there are ways to cope with these challenges. Here are some strategies:
- Talk to someone you trust. Sharing your feelings with a friend, family member, therapist, or support group can help you feel less alone and can provide you with a listening ear and emotional support.
- Join a support group. Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can provide a sense of community and belonging. You can learn from their experiences and share your own.
- Practice self-care. Taking care of your physical and mental health is essential for managing diabetes. This includes getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and engaging in activities you enjoy.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms. This might include mindfulness meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature. Find what works best for you.
- Challenge negative thoughts. When you find yourself thinking negative thoughts, try to challenge them. Ask yourself if they are truly accurate and if there is a more positive way to view the situation.
Resources and Support Groups
There are many resources available to help you manage diabetes and cope with the emotional challenges.
- The American Diabetes Association (ADA): This organization provides a wealth of information about diabetes, including resources for emotional support. You can find local support groups, online forums, and educational materials.
- The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF): This organization focuses on research to find a cure for type 1 diabetes. They also offer resources for people with diabetes, including support groups and educational materials.
- Your healthcare provider: Your doctor, nurse, or other healthcare professionals can provide support and guidance. They can also help you connect with other resources.
Importance of Self-Care and Stress Management, Tips to make living with diabetes easier
Self-care is crucial for managing diabetes, both physically and emotionally. Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, so it’s important to develop healthy ways to manage stress.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce stress, and improve mood.
- Get enough sleep: When you’re sleep-deprived, your body produces more stress hormones, which can affect your blood sugar levels.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet can help stabilize your blood sugar levels and provide you with the energy you need.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
Preventing Complications
Diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to various long-term complications if not managed effectively. It’s crucial to prioritize preventative measures to minimize the risk of these complications and maintain overall health. By understanding the potential risks and adopting proactive strategies, you can significantly improve your long-term well-being.
Regular Checkups and Early Detection
Regular checkups are vital for early detection and management of diabetes complications. These checkups allow healthcare providers to monitor your blood sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall health. Early detection of any potential issues allows for prompt treatment and intervention, significantly reducing the risk of serious complications.
- Eye Exams: Diabetes can affect the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can cause vision loss. Annual eye exams are essential for early detection and treatment.
- Kidney Function Tests: Diabetes can damage the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy. Regular blood and urine tests can monitor kidney function and identify early signs of damage.
- Foot Exams: Diabetes can affect blood flow to the feet, increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections. Regular foot exams, including checking for cuts, blisters, and signs of infection, are crucial.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Monitoring: High blood pressure and cholesterol levels are common in people with diabetes and can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Regular monitoring and management of these factors are essential.
Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels
High blood pressure and cholesterol levels are significant risk factors for heart disease and stroke, both of which are more common in people with diabetes. Adopting lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication can help manage these factors.
- Dietary Changes: A healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, improves blood sugar control, and promotes overall cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Medication: If lifestyle changes are not enough to control blood pressure and cholesterol levels, your doctor may prescribe medication. Following your doctor’s instructions carefully is essential for managing these conditions.
Foot Care
Diabetes can affect blood flow to the feet, making them more susceptible to injuries and infections. Proper foot care is essential for preventing complications.
- Daily Foot Inspection: Inspect your feet daily for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or any other changes. If you notice any problems, contact your doctor immediately.
- Proper Footwear: Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes that provide good support and cushioning. Avoid wearing shoes that are too tight or too loose.
- Moisturize Feet: Keep your feet moisturized, but avoid applying lotion between your toes, as this can trap moisture and increase the risk of infection.
- Trim Toenails Carefully: Trim your toenails straight across and avoid cutting them too short. If you have difficulty trimming your toenails, ask your doctor or podiatrist for assistance.
Technology and Diabetes Management

Technology has revolutionized diabetes management, offering tools that empower individuals to take control of their health and live fulfilling lives. From continuous glucose monitoring systems to insulin pumps and mobile apps, these innovations provide valuable insights and support for managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are wearable devices that track blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. These systems typically consist of a small sensor inserted under the skin, a transmitter, and a receiver. The sensor continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which is the fluid surrounding cells, and transmits the data wirelessly to the receiver.
CGM systems provide real-time data on blood sugar trends, helping individuals identify patterns and make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
- Benefits:
- Provides real-time blood sugar data, allowing for proactive adjustments to insulin doses or dietary choices.
- Offers insights into blood sugar patterns, enabling individuals to identify triggers and potential issues.
- Helps prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) by providing early warnings.
- Empowers individuals to take control of their diabetes management by providing them with greater awareness and understanding of their blood sugar levels.
- Limitations:
- CGM systems require regular calibration with finger-stick blood glucose readings.
- They can be costly and may not be covered by all insurance plans.
- Some individuals may experience discomfort or skin irritation from the sensor.
- CGM data may not always be accurate, especially during periods of rapid blood sugar fluctuations.
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps are small, portable devices that deliver insulin continuously throughout the day, mimicking the body’s natural insulin production. They typically consist of a small reservoir containing insulin, a pump that delivers the insulin through a thin catheter inserted under the skin, and a control unit that allows users to program the pump settings.
Insulin pumps offer greater flexibility and precision in insulin delivery compared to traditional injections. They allow users to adjust insulin doses based on their individual needs and blood sugar levels, making it easier to achieve tighter blood sugar control.
- Benefits:
- Provides continuous insulin delivery, mimicking the body’s natural insulin production.
- Allows for precise insulin dosing based on individual needs and blood sugar levels.
- Offers greater flexibility in insulin delivery, enabling users to adjust doses throughout the day.
- Reduces the number of daily injections, improving convenience and comfort.
- Limitations:
- Insulin pumps require careful programming and monitoring to ensure accurate insulin delivery.
- They can be expensive and may not be covered by all insurance plans.
- Pump users need to be vigilant about managing the pump and its components.
- Pump sites may become irritated or infected, requiring regular site changes.
Mobile Apps for Diabetes Management
Numerous mobile apps are available to support diabetes management, offering a wide range of features and functionalities. These apps can help individuals track blood sugar levels, log meals and medications, set reminders for insulin injections or blood glucose testing, calculate insulin doses, and connect with healthcare providers.
Mobile apps can be a valuable tool for managing diabetes, providing a convenient and user-friendly platform for organizing and accessing important information.
- Benefits:
- Provides a centralized platform for tracking blood sugar levels, meals, medications, and other important diabetes-related information.
- Offers reminders for insulin injections, blood glucose testing, and other important tasks.
- Calculates insulin doses based on blood sugar levels and other factors.
- Allows for communication with healthcare providers, facilitating better collaboration and support.
- Limitations:
- App accuracy and reliability can vary depending on the app and its features.
- Some apps may require subscriptions or in-app purchases.
- App functionality may be limited depending on the user’s device and operating system.
- Apps should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice.
Final Conclusion
Living with diabetes requires dedication and proactive effort, but it’s not about sacrificing your enjoyment of life. By embracing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can develop a personalized approach that aligns with your lifestyle and empowers you to thrive.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and with the right support and knowledge, you can navigate the challenges and live a fulfilling life.