Your Secret to Burning More Calories at Rest
Your secret to burning more calories at rest lies in understanding the intricate workings of your metabolism and harnessing the power of lifestyle choices. It’s not about grueling workouts or restrictive diets; it’s about optimizing your body’s natural calorie-burning processes.
This article will delve into the science behind calorie expenditure at rest, exploring key factors like muscle mass, hormonal balance, and even the foods you choose.
Imagine effortlessly burning calories even when you’re lounging on the couch or catching up on sleep. It’s possible, and it all starts with a deeper understanding of your body’s inner workings. Get ready to unlock the secrets to maximizing your metabolism and achieving your health and fitness goals.
Understanding Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): Your Secret To Burning More Calories At Rest
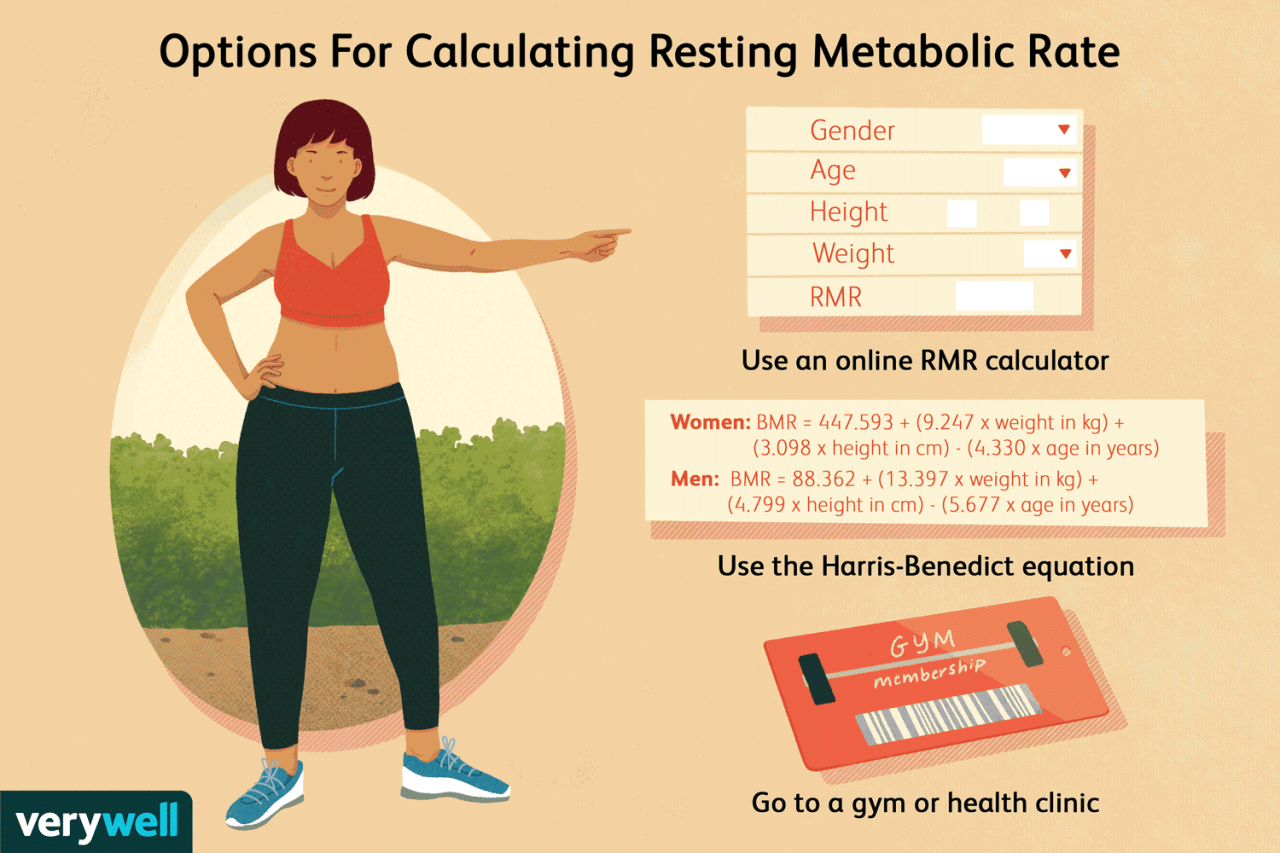
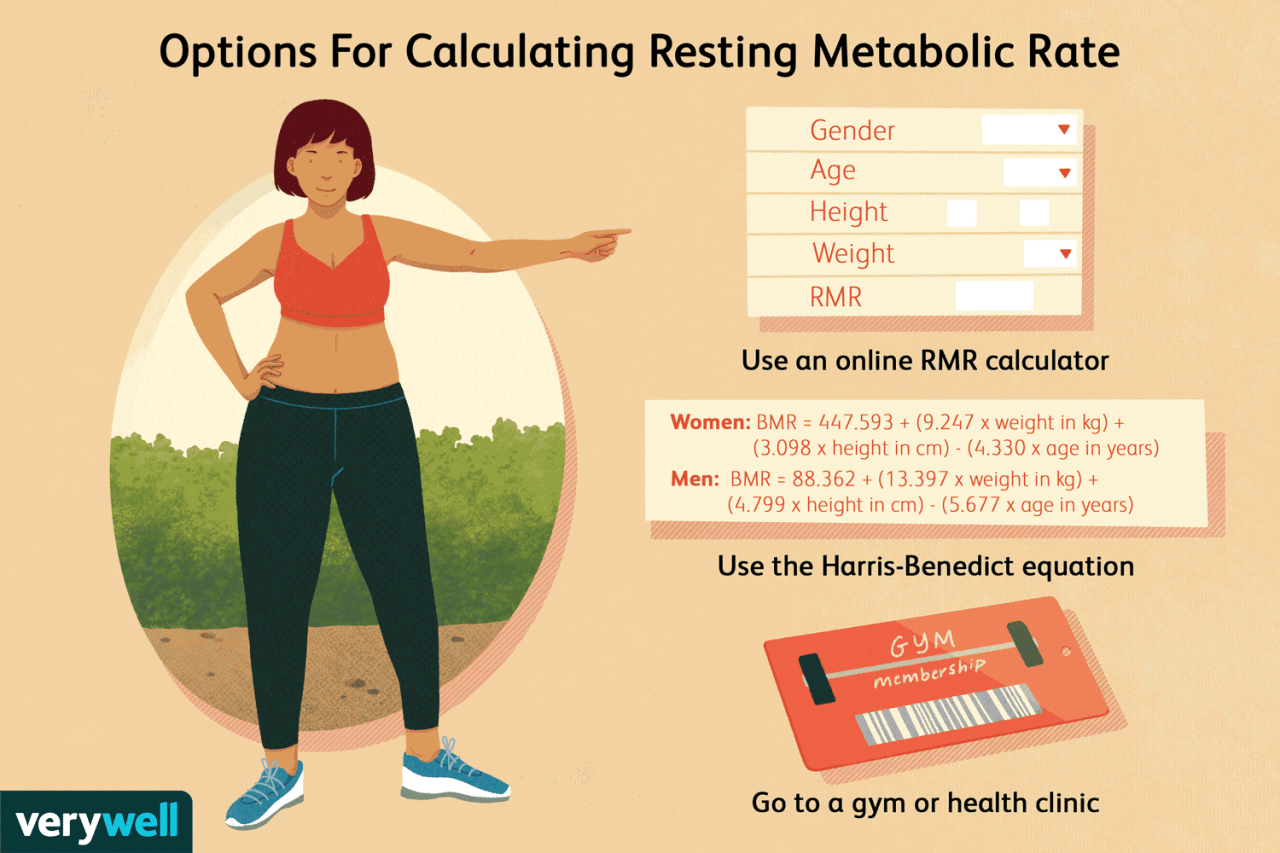
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the number of calories your body burns at rest to perform essential functions like breathing, circulation, and cell maintenance. It’s the foundation of your calorie expenditure, representing the energy your body needs to simply exist.
Understanding BMR is crucial for weight management, as it significantly influences your overall calorie needs.
Factors Influencing BMR, Your secret to burning more calories at rest
Your BMR is influenced by several factors, some of which you can control and others you can’t. Here’s a breakdown:
Age
As you age, your BMR naturally declines. This is due to a decrease in muscle mass and a slower metabolism.
My secret to burning more calories at rest? Building muscle! It’s all about increasing your metabolism. And while I’m on the topic of building a strong foundation, it’s important to remember that pregnancy brings unique challenges, and certain yoga poses can be risky.
It’s essential to avoid certain poses, like those listed in this helpful article on yoga poses to avoid during pregnancy. Once you’ve got the all-clear from your doctor, you can safely incorporate gentle yoga into your routine, which will further boost your metabolism and help you burn calories even when you’re resting.
Gender
Men typically have a higher BMR than women due to their generally larger muscle mass. Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue.
Body Composition
The ratio of muscle to fat in your body plays a significant role in BMR. More muscle mass leads to a higher BMR, while more fat mass leads to a lower BMR.
Height
Taller individuals tend to have a higher BMR because they have more surface area and require more energy to maintain their body temperature.
Genetics
Your genes can influence your BMR, with some people naturally having a higher metabolism than others.
Thyroid Function
An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can slow down your metabolism, leading to a lower BMR. Conversely, an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can increase your metabolism, resulting in a higher BMR.
Medications
Certain medications, such as stimulants and thyroid medications, can affect your BMR.
My secret to burning more calories at rest? Building muscle! It’s a game-changer, and it’s all about consistency. The key to staying motivated when starting a new habit, like hitting the gym more often, is to find ways to make it enjoyable and sustainable.
Check out this article on how to stay motivated when starting a new habit for some great tips. Once you’ve got that down, you’ll be well on your way to building muscle and burning more calories even when you’re relaxing!
Environmental Factors
Factors like temperature and altitude can also influence your BMR. For instance, your body burns more calories to maintain its temperature in a cold environment.
Significance of BMR in Weight Management
Your BMR is a crucial factor in weight management. If you know your BMR, you can estimate your daily calorie needs for weight loss, maintenance, or gain. For example, if your BMR is 1,500 calories, you’ll need to consume more than that to gain weight, consume around that amount to maintain your current weight, and consume less than that to lose weight.
To lose weight, you need to consume fewer calories than you burn.
It’s important to note that BMR is just one part of the equation. Your total daily calorie expenditure also includes calories burned through physical activity and the thermic effect of food (the energy your body uses to digest and process food).
However, understanding your BMR provides a starting point for managing your weight effectively.
Building Muscle Mass
Building muscle mass is a crucial aspect of boosting your resting calorie burn. This is because muscle tissue is metabolically active, meaning it requires more energy to maintain compared to fat tissue. In simpler terms, the more muscle you have, the more calories you burn even when you’re at rest.
You might be surprised to learn that building stronger glutes can actually help you burn more calories at rest! That’s because stronger glutes mean a more efficient metabolism. And if you’re looking for a great way to target those glutes, check out these 5 best moves for stronger glutes.
Once you start incorporating these exercises into your routine, you’ll be on your way to a more sculpted physique and a higher resting metabolic rate – the ultimate secret to burning more calories at rest!
Increasing Muscle Mass
Building muscle mass involves a two-pronged approach: exercise and nutrition.
Exercise
Strength training is the key to building muscle. This type of exercise involves lifting weights or using resistance bands to challenge your muscles. When your muscles are challenged, they break down and then rebuild themselves stronger. Here are some examples of effective strength training exercises:
- Squats
- Lunges
- Push-ups
- Pull-ups
- Deadlifts
- Bench press
- Rowing
It’s important to start with a weight that is challenging but allows you to maintain good form. As your muscles get stronger, you can gradually increase the weight.
Nutrition
To build muscle, you need to provide your body with the nutrients it needs to repair and rebuild muscle tissue. This means eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of protein. Protein is essential for muscle growth because it provides the building blocks for muscle tissue.
Aim to consume at least 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. Good sources of protein include:
- Chicken
- Fish
- Eggs
- Beans
- Lentils
- Tofu
- Greek yogurt
In addition to protein, it’s also important to consume enough carbohydrates and healthy fats. Carbohydrates provide your body with energy, and healthy fats help with hormone production and cell function.
Benefits of Strength Training
Strength training has numerous benefits beyond building muscle mass. It can also:
- Increase bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis
- Improve balance and coordination
- Reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes
- Enhance mood and cognitive function
One of the most significant benefits of strength training is its ability to increase BMR. As mentioned earlier, muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat tissue. Therefore, by building muscle mass, you can increase the number of calories your body burns at rest.
This can lead to a more efficient metabolism and help you achieve your weight management goals.
“Building muscle mass can increase your BMR by 5-10%.”
It’s important to note that building muscle takes time and effort. Be patient and consistent with your exercise and nutrition plan, and you’ll see results over time.
Lifestyle Factors
Beyond the internal workings of your body, your lifestyle choices can significantly impact your calorie burn at rest. This is because certain lifestyle factors can influence your BMR, affecting how many calories you burn even when you’re not actively moving.
Sleep
Sleep is essential for overall health and plays a crucial role in regulating your metabolism. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more of the stress hormone cortisol, which can increase your appetite and slow down your metabolism.
Studies have shown that chronic sleep deprivation can lead to a decrease in BMR, making it harder to lose weight and maintain a healthy weight.
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your BMR and overall health.
Stress
Chronic stress can also negatively impact your BMR. When you’re constantly stressed, your body releases cortisol, which can lead to increased appetite, weight gain, and a slower metabolism.
Chronic stress can lead to increased inflammation, which can further slow down your metabolism.
Managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help regulate your cortisol levels and improve your BMR.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for various bodily functions, including regulating your metabolism. Water is involved in many metabolic processes, and dehydration can slow down your metabolism.
Drinking enough water can help your body function optimally, which can boost your BMR.
Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, and avoid sugary drinks that can dehydrate you.
Summary
Mastering the art of burning more calories at rest isn’t about a quick fix; it’s about adopting sustainable lifestyle habits that support your body’s natural calorie-burning processes. From building muscle to optimizing your sleep and stress levels, every step you take contributes to a healthier, more efficient metabolism.
Remember, your body is a powerful machine, and by understanding its inner workings, you can unlock its full potential for calorie expenditure and overall well-being.






