How Endurance Athletes Should Carb Up During Workouts
How endurance athletes should carb up during workouts is a critical aspect of maximizing performance and preventing fatigue. It’s not just about eating carbs, but about strategic timing and choosing the right types of carbohydrates to fuel your body for long and demanding activities.
This guide will explore the science behind carb loading and provide practical tips for optimizing your carb intake before, during, and after endurance events.
We’ll delve into the importance of glycogen stores, the differences in carb loading for short versus long-duration activities, and the best carb sources for endurance athletes. We’ll also cover the vital role of hydration and electrolyte balance, as well as how to tailor your carb strategy to your individual needs and goals.
Get ready to learn how to fuel your body for peak performance!
Timing Carb Intake During Workouts: How Endurance Athletes Should Carb Up During Workouts
The timing of your carbohydrate intake during workouts is crucial for optimizing performance and endurance. By strategically consuming carbs before, during, and after exercise, you can fuel your muscles effectively and delay fatigue.
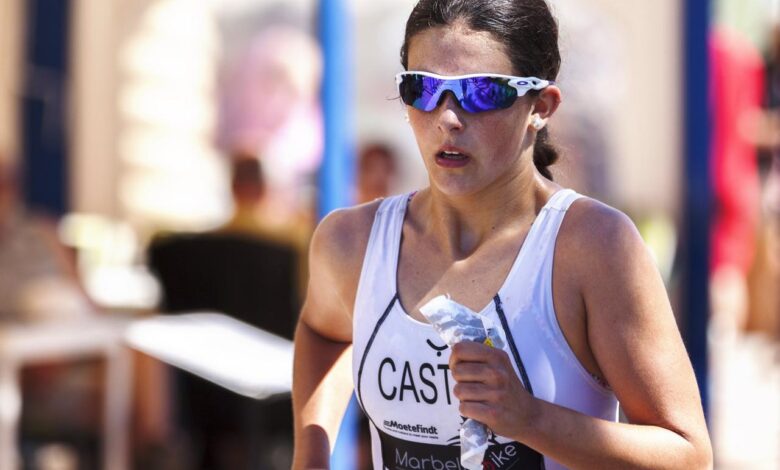
Endurance athletes need to carb up during workouts to fuel their muscles and maintain energy levels. This is especially crucial for long-distance events, as your body relies on glycogen stores for sustained performance. Understanding the connection between hormones and training performance can help you optimize your carb intake.
Hormones like cortisol and insulin play a vital role in regulating energy levels and muscle recovery, so finding the right balance of carbs can help you achieve optimal results.
Pre-Workout Carb Intake Strategies
Pre-workout carb intake is essential for providing your body with readily available energy to power your workout. Here are some key strategies:
- Timing:Aim to consume carbohydrates 2-4 hours before your workout. This allows your body to adequately digest and store the glucose as glycogen in your muscles.
- Types of Carbohydrates:Choose low-glycemic index (GI) carbohydrates, which are digested slowly and provide a sustained release of energy. Examples include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
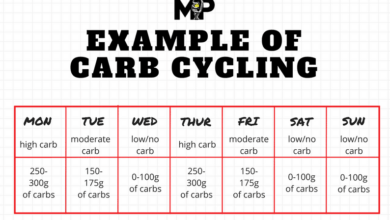
- Quantity:The amount of carbohydrates you need will depend on the duration and intensity of your workout. For moderate-intensity workouts lasting 60-90 minutes, consuming 1-2 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight is recommended. For longer or more intense workouts, you may need to increase your intake to 3-4 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Endurance athletes need to prioritize proper fueling, especially during long workouts. Carbing up before and during these intense sessions is crucial for maintaining energy levels and performance. But remember, recovery is just as important! Check out 5 great things about recovery days to learn how to optimize your rest and prepare for your next training session.
By focusing on both fueling and recovery, you can maximize your potential and achieve your endurance goals.
Adjusting Carb Intake Based on Workout Duration and Intensity, How endurance athletes should carb up during workouts
The duration and intensity of your workout significantly impact your carbohydrate needs.
- Short-Duration, Low-Intensity Workouts:For workouts lasting less than 60 minutes, your body’s glycogen stores are usually sufficient. You may not need to consume additional carbohydrates during the workout.
- Moderate-Duration, Moderate-Intensity Workouts:For workouts lasting 60-90 minutes, consuming carbohydrates during the workout can help maintain energy levels and delay fatigue. Aim for 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour.
- Long-Duration, High-Intensity Workouts:For workouts lasting over 90 minutes, it is essential to consume carbohydrates regularly throughout the workout to replenish glycogen stores. Aim for 60-90 grams of carbohydrates per hour.
Benefits of Consuming Carbohydrates During Prolonged Exercise
Consuming carbohydrates during prolonged exercise offers several benefits:
- Maintains Blood Glucose Levels:Carbohydrates provide your body with glucose, which is the primary fuel source for your muscles. By consuming carbohydrates during exercise, you can maintain stable blood glucose levels and prevent a drop in energy.
- Delays Fatigue:When your body runs out of glycogen, you experience fatigue. Consuming carbohydrates during exercise can help delay fatigue and extend your endurance.
- Improves Performance:Studies have shown that consuming carbohydrates during prolonged exercise can improve performance by reducing perceived exertion and enhancing time to exhaustion.
Examples of Suitable Carbohydrate Options
Here are some examples of suitable carbohydrate options to consume during prolonged exercise:
- Sports Drinks:Sports drinks provide a combination of carbohydrates, electrolytes, and fluids. They are a convenient option for replenishing fluids and energy during workouts.
- Energy Gels:Energy gels are concentrated sources of carbohydrates that are easy to consume during exercise. They provide a quick boost of energy and can be a good option for long runs or bike rides.
- Chewable Energy Chews:Chewable energy chews are another convenient option for consuming carbohydrates during exercise. They are typically lower in sugar than energy gels and provide a more gradual release of energy.
- Real Food:You can also consume real food during prolonged exercise, such as bananas, dried fruit, and pretzels. These foods provide a combination of carbohydrates, electrolytes, and fiber.
Carb Sources for Endurance Athletes
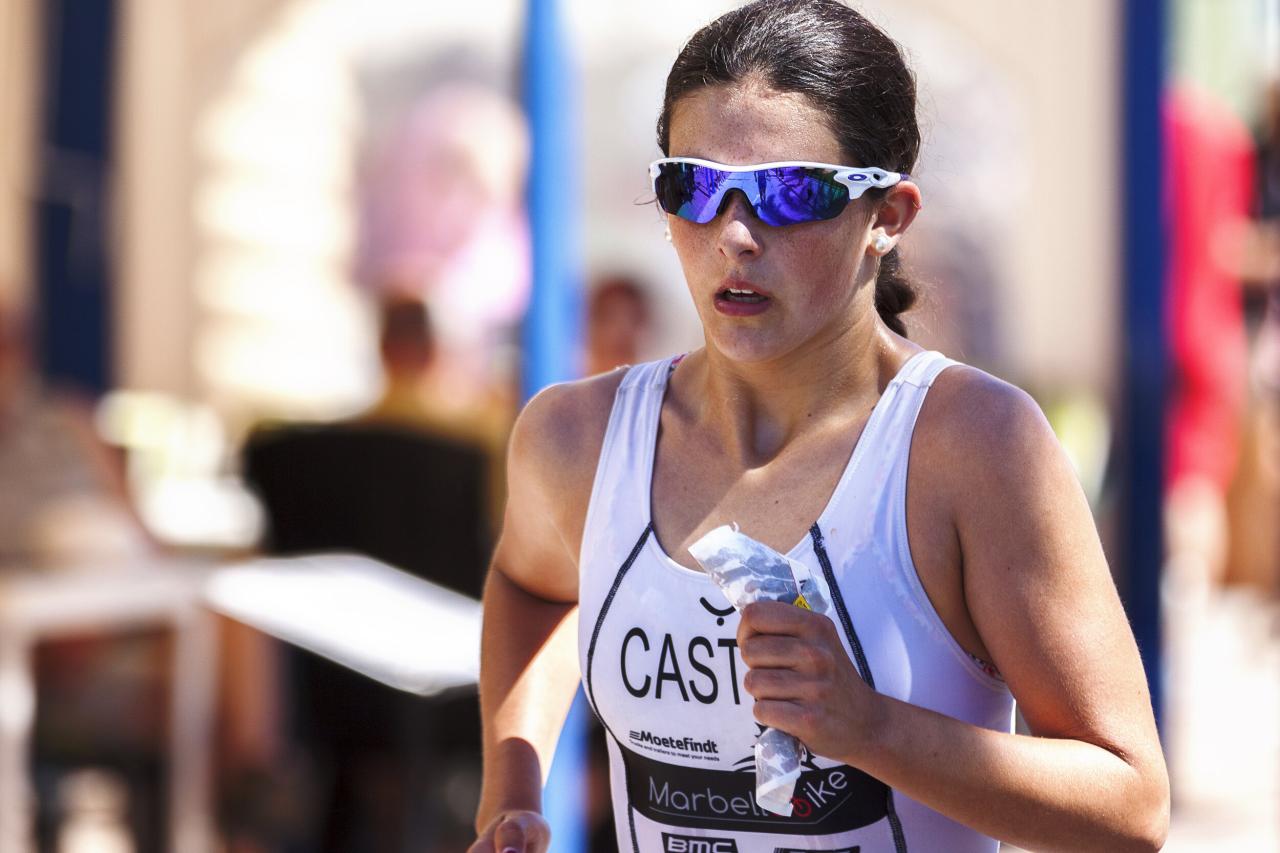

Endurance athletes require a steady supply of carbohydrates to fuel their workouts and recover effectively. These carbohydrates provide the body with glucose, the primary energy source for muscles.
Endurance athletes need to fuel their bodies with carbs during workouts to maintain energy levels and avoid hitting the wall. But even if you’re not an athlete, getting regular exercise can have a huge impact on your health. In fact, walking can help you live longer even if you’ve never exercised before , making it a great way to improve your overall well-being.
So, whether you’re training for a marathon or just looking to get more active, remember that proper fueling is key to achieving your fitness goals.
Carb Sources and Their Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) of a carbohydrate source indicates how quickly it raises blood sugar levels. High-GI foods are rapidly digested and absorbed, providing a quick burst of energy. Low-GI foods are digested and absorbed more slowly, providing a sustained release of energy.
| Carb Source | Glycemic Index | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Grains | Low to Medium | Provide sustained energy, high in fiber, and essential nutrients. | Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole-wheat bread |
| Fruits | Medium to High | Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. | Bananas, apples, oranges, berries |
| Starchy Vegetables | Medium to High | Good source of carbohydrates, fiber, and vitamins. | Potatoes, corn, peas, sweet potatoes |
| Sports Drinks | High | Provide a quick source of carbohydrates and electrolytes. | Gatorade, Powerade, Nuun |
| Energy Gels | High | Convenient and easily digestible source of carbohydrates. | Clif Shot, Gu Energy Gel, Honey Stinger |
Ideal Carb Intake Per Hour of Exercise
The ideal carb intake during exercise varies depending on the intensity and duration of the event.
| Event Type | Carb Intake Per Hour (grams) |
|---|---|
| Low-Intensity Exercise (e.g., walking, jogging) | 30-60 |
| Moderate-Intensity Exercise (e.g., cycling, running) | 60-90 |
| High-Intensity Exercise (e.g., marathon, triathlon) | 90-120+ |
Individualized Carb Strategies

No two endurance athletes are the same, and their carb needs can vary significantly. This is because several factors influence how much carbohydrates an athlete requires.
Factors Influencing Individual Carb Needs
It is crucial to consider the athlete’s training volume, intensity, and body composition when determining their carb needs. Training volume refers to the total amount of exercise an athlete undertakes, while intensity refers to the effort level during training. Body composition, on the other hand, refers to the proportion of muscle, fat, and bone in the athlete’s body.
- Training Volume:Athletes with higher training volume generally require more carbohydrates to fuel their workouts and aid in recovery. The increased energy demands of frequent and prolonged training sessions necessitate a higher carb intake to replenish glycogen stores.
- Training Intensity:High-intensity training sessions, such as interval training or races, require more carbohydrates for fuel compared to low-intensity sessions. This is because high-intensity exercises rely heavily on glucose for energy production.
- Body Composition:Athletes with a higher percentage of muscle mass need more carbohydrates to support muscle growth and repair. Muscle tissue is metabolically active, requiring more energy to maintain and grow.
Adjusting Carb Intake Based on Individual Requirements and Goals
Once you understand the factors influencing carb needs, you can adjust your intake to meet your individual requirements and goals.
- Increasing Carb Intake:Athletes with higher training volume or intensity may need to increase their carb intake to meet their energy demands. This can be done by adding carbohydrate-rich foods to their diet or consuming carb-loading supplements.
- Decreasing Carb Intake:Athletes who are trying to lose weight or maintain a specific body composition may need to decrease their carb intake. This can be achieved by choosing lower-carb options or reducing the portion sizes of carbohydrate-rich foods.
Tracking Carb Intake and Monitoring Performance
Monitoring your carb intake and performance can help you optimize your fueling strategies.
- Carb Tracking:There are various methods for tracking carb intake, including food diaries, smartphone apps, and online tools. By keeping track of your carb intake, you can ensure you are consuming enough to meet your training needs.
- Performance Monitoring:Pay attention to how you feel during your workouts and races. Are you experiencing fatigue, muscle cramps, or other signs of under-fueling? Monitoring your performance can provide valuable insights into your carb intake needs.
“The best way to determine your individual carb needs is to experiment and find what works best for you.”
Outcome Summary
By understanding the principles of carb loading and implementing a strategic carb intake plan, endurance athletes can optimize their energy levels, enhance their performance, and achieve their athletic goals. Remember, the key is to experiment and find what works best for your individual body and training needs.
With the right fueling strategy, you can conquer your next endurance challenge and reach new heights of athletic achievement.