Afterburn Explained: You Burn Extra Calories After Workouts
Afterburn explained yes you burn extra calories after certain workouts – Afterburn explained: yes, you burn extra calories after certain workouts. Ever wondered why you feel energized and slightly warm even after finishing a tough workout? That’s the magic of afterburn, also known as EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption). This phenomenon is your body’s way of recovering and rebuilding after intense exercise, leading to an extended calorie burn even after you’ve stopped sweating.
Imagine this: you’ve just crushed a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) session. Your heart is racing, your muscles are screaming, and you’re breathing heavily. While you’re catching your breath, your body is working hard to replenish oxygen levels, repair damaged muscle fibers, and restore energy stores.
This metabolic process, driven by hormones like growth hormone and adrenaline, continues for a period after your workout, resulting in a calorie burn that extends beyond your exercise session.
Benefits of Afterburn
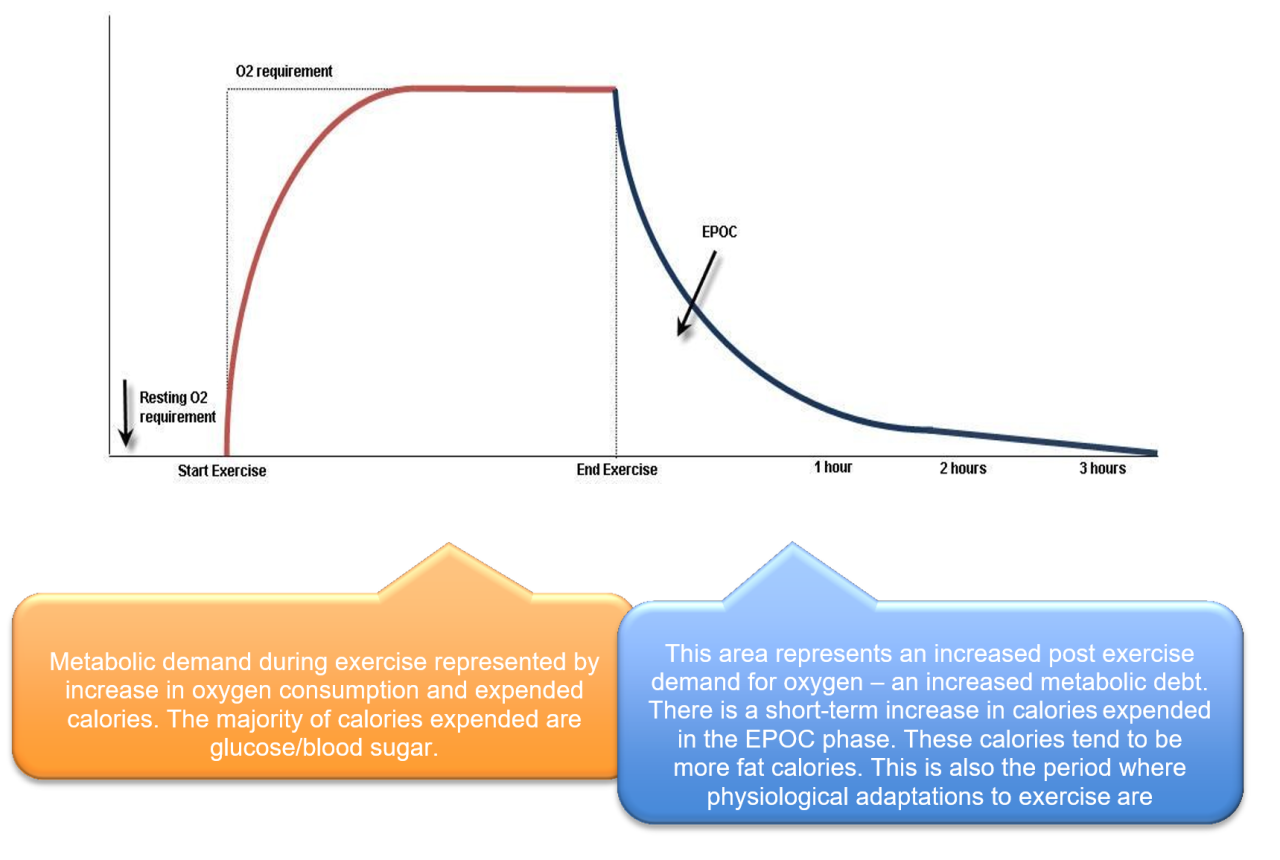
Afterburn, also known as Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC), is the increased energy expenditure your body experiences after a workout. It’s like your body continues to burn calories even after you’ve stopped exercising, and it can be a significant contributor to weight loss and overall fitness.
Weight Loss and Fat Burning
Afterburn can play a crucial role in weight loss by increasing your overall calorie expenditure. The longer you sustain a high intensity workout, the more calories you burn during and after your exercise session. This means that you can continue to burn calories even when you’re relaxing on the couch.
A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) resulted in significantly higher EPOC compared to moderate-intensity continuous training.
Afterburn, or EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption), is a real thing! It’s the extra calories you burn after a tough workout, which is awesome for boosting your metabolism. But to fuel those intense workouts and keep your energy levels high, you need to make sure you’re getting enough carbs.
If you’re looking for healthy ways to increase your carb intake, check out this article from Ask the RD: How Can I Increase Carbs With Healthy Options? With the right carb sources, you’ll be ready to crush those workouts and reap the benefits of afterburn!
Improved Fitness and Metabolic Health, Afterburn explained yes you burn extra calories after certain workouts
Afterburn is not just about burning calories; it can also contribute to improved fitness and metabolic health. Studies have shown that afterburn can lead to:
- Increased muscle mass and strength: EPOC can stimulate muscle protein synthesis, leading to increased muscle mass and strength.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Regular exercise, particularly high-intensity workouts, can improve insulin sensitivity, helping your body regulate blood sugar levels more effectively.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: By improving your metabolic health, afterburn can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
So you’ve heard about afterburn, that magical period after a workout where your body keeps burning calories even though you’re done sweating. It’s a real thing, and while it’s not a free pass to eat whatever you want, it’s definitely a motivator to push yourself! If you’re looking for some extra motivation, why not challenge yourself to some of the awesome fitness feats listed in this article: 7 feats to add to your fitness bucket list.
After conquering one of these challenges, you’ll definitely be feeling that afterburn, and that feeling of accomplishment is worth more than any extra calories burned!
Maximizing Afterburn
Here are some practical tips to maximize the benefits of afterburn:
- Engage in high-intensity workouts: High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and other high-intensity workouts have been shown to trigger a greater EPOC response.
- Train your muscles to fatigue: Push yourself to the point of muscular fatigue during your workouts. This will increase the demand on your body and lead to a greater afterburn effect.
- Focus on compound exercises: Compound exercises, such as squats, deadlifts, and push-ups, engage multiple muscle groups and result in a greater calorie burn.
- Prioritize strength training: Strength training builds muscle mass, which increases your resting metabolic rate, leading to a higher calorie burn even at rest.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can hinder your body’s ability to recover from exercise and may reduce the afterburn effect.
- Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in protein and complex carbohydrates will provide your body with the nutrients it needs to recover and rebuild muscle tissue.
Afterburn, that magical post-workout calorie burn, is a real thing! It’s a great way to maximize your fitness efforts, but don’t let the stress of achieving it overwhelm you. Take a moment to chill out and check out these 8 quick ways to reduce stress right now , then get back to your workout routine feeling refreshed and ready to conquer that afterburn!
Misconceptions About Afterburn: Afterburn Explained Yes You Burn Extra Calories After Certain Workouts
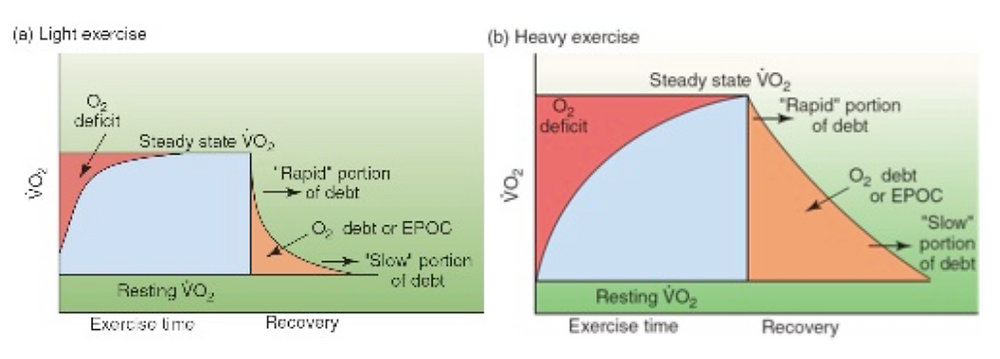
Afterburn, also known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), is a fascinating physiological phenomenon that can contribute to increased calorie expenditure after a workout. While the benefits of afterburn are often touted, it’s important to understand the limitations and debunk some common misconceptions surrounding this metabolic process.
The Significance of Afterburn
It’s a common misconception that afterburn is a significant calorie-burning mechanism that can drastically impact weight management. While afterburn does contribute to calorie expenditure, its overall impact is often overestimated. Studies have shown that the calorie burn from afterburn is typically modest, ranging from 6-15% of total calories expended during exercise.
Misleading Claims About Afterburn
- “High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) leads to a massive afterburn effect.”While HIIT workouts can lead to a greater EPOC than steady-state cardio, the difference in calorie expenditure is not as dramatic as often portrayed. Research suggests that the afterburn effect from HIIT workouts may be slightly higher than moderate-intensity exercise but is not a major contributor to weight loss.
- “Afterburn is the key to burning fat.”Afterburn plays a role in calorie expenditure, but it’s not the sole factor determining fat loss. Weight management depends on a combination of factors, including diet, exercise, and genetics. While afterburn can contribute to calorie expenditure, it’s not a magic bullet for fat loss.
- “The longer and more intense the workout, the greater the afterburn effect.”While longer and more intense workouts can lead to a slightly higher EPOC, the relationship is not linear. After a certain point, the body adapts, and the afterburn effect may plateau or even decrease.
Epilogue

So, the next time you hit the gym or push yourself in a challenging workout, remember the power of afterburn. It’s not just about the immediate calorie burn during your exercise; it’s about the extended metabolic boost that helps you reach your fitness goals faster.
While afterburn alone won’t magically melt away pounds, it’s a valuable tool in your fitness arsenal, especially when combined with a balanced diet and consistent exercise routine. Embrace the burn, and let your body work its magic even after your workout is done.