
How Cooking Impacts Foods Nutrition Levels: A Guide to Healthy Eating
How cooking impacts foods nutrition levels is a question that often arises when we think about healthy eating. We all know that cooking is essential for preparing food, but did you know that different cooking methods can significantly impact the nutrient content of our meals?
From boiling to frying, baking to steaming, each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages when it comes to preserving vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This article will explore the fascinating relationship between cooking and nutrition, delving into the science behind nutrient retention, degradation, and bioavailability.
We’ll examine how various cooking methods affect different nutrients, discuss the importance of cooking temperature and time, and explore the role of ingredients and additives in influencing the nutritional value of our food. Ultimately, we’ll discover how to cook in ways that preserve nutrients, enhance their absorption, and ensure food safety while still enjoying delicious and flavorful meals.
Cooking Methods and Nutrient Retention
Cooking is an essential part of food preparation, transforming raw ingredients into palatable and digestible meals. However, the cooking process can also affect the nutritional content of foods, impacting the availability of essential vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds. Understanding how different cooking methods influence nutrient retention is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet.
Impact of Cooking Methods on Nutrient Content
The cooking method employed significantly impacts the nutrient content of food. Some methods are more effective at preserving nutrients than others.
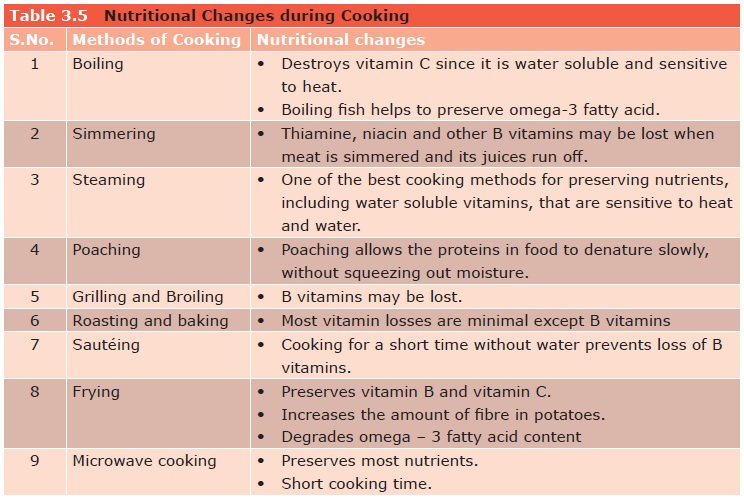
- Boiling:This method involves immersing food in boiling water, which can leach water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins into the cooking water. While some nutrients are lost, boiling can be a good method for preserving other nutrients, such as fiber.
- Frying:This method involves cooking food in hot oil, which can lead to the formation of harmful compounds, such as acrylamide, and can also cause nutrient loss through oxidation. However, frying can be a good way to preserve some nutrients, such as vitamin E.
- Baking:This method involves cooking food in a dry heat oven, which can be a good way to preserve nutrients, as it does not involve the use of water or oil. However, some nutrients, such as vitamin C, can be lost during prolonged baking times.
- Steaming:This method involves cooking food with steam, which is a gentle and effective way to preserve nutrients. Steaming helps retain water-soluble vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Comparison of Nutrient Loss Across Cooking Techniques
Different cooking techniques lead to varying degrees of nutrient loss.
| Cooking Method | Nutrient Loss |
|---|---|
| Boiling | High loss of water-soluble vitamins (vitamin C, B vitamins) |
| Frying | Moderate loss of some vitamins and minerals due to oxidation and formation of harmful compounds |
| Baking | Moderate loss of some nutrients, especially with prolonged cooking times |
| Steaming | Low nutrient loss, considered a nutrient-preserving method |
Impact of Cooking Time and Temperature on Nutrient Retention
The duration and intensity of heat exposure during cooking play a significant role in nutrient retention.
- Cooking Time:Prolonged cooking times can lead to greater nutrient loss, especially for heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C.
- Cooking Temperature:High temperatures can accelerate nutrient degradation and loss. For instance, frying at high temperatures can lead to significant vitamin E loss.
It is generally recommended to cook food at lower temperatures for shorter durations to minimize nutrient loss.
Nutrient Degradation During Cooking: How Cooking Impacts Foods Nutrition Levels
Cooking is an essential part of food preparation, transforming raw ingredients into palatable and safe meals. However, the heat and moisture involved in cooking can also lead to the degradation of certain nutrients, affecting the nutritional value of our food.
Understanding the factors that contribute to nutrient loss during cooking can help us make informed choices about our cooking methods and maximize the nutritional benefits of our meals.
Types of Nutrients Susceptible to Degradation
The heat and moisture used in cooking can significantly impact the stability of various nutrients. Vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants are particularly susceptible to degradation during cooking.
- Vitamins:Vitamins are organic compounds that play crucial roles in various bodily functions. Some vitamins are more sensitive to heat and moisture than others. For instance, water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins are more easily lost during cooking, especially when exposed to high temperatures and prolonged cooking times.
Fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A, D, E, and K are generally more stable, but they can still be affected by prolonged cooking or exposure to light.
- Minerals:Minerals are inorganic substances that are essential for various bodily functions. While some minerals are relatively stable during cooking, others can be lost due to leaching into cooking water or through chemical reactions. For example, potassium, magnesium, and calcium can be lost during prolonged boiling or steaming.
- Antioxidants:Antioxidants are compounds that protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Many fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants, but these compounds can be degraded during cooking. For instance, vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, is easily lost during cooking, especially when exposed to air or high temperatures.
Chemical Reactions Involved in Nutrient Loss
The degradation of nutrients during cooking is often due to chemical reactions triggered by heat and moisture.
- Oxidation:Oxidation is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of electrons. Many nutrients, particularly vitamins, are susceptible to oxidation. Exposure to air, heat, and light can accelerate oxidation, leading to nutrient loss. For example, vitamin C is easily oxidized, which contributes to its loss during cooking.
- Hydrolysis:Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction that involves the breakdown of molecules by the addition of water. Some nutrients, like starch, can be hydrolyzed during cooking, resulting in changes in their structure and digestibility.
- Maillard Reaction:The Maillard reaction is a complex chemical reaction that occurs between amino acids and sugars, resulting in the formation of brown pigments and flavor compounds. While the Maillard reaction contributes to the desirable flavors and colors of cooked food, it can also lead to the degradation of some nutrients, including lysine, an essential amino acid.
Examples of Nutrient Loss in Specific Foods
- Broccoli:Broccoli is a rich source of vitamin C, but it can lose a significant amount of this vitamin during cooking. Boiling broccoli for a long time can result in the loss of up to 50% of its vitamin C content.
Steaming or stir-frying broccoli for shorter periods can help preserve more of its vitamin C.
- Spinach:Spinach is a good source of vitamin A, but its vitamin A content can be reduced by cooking. Boiling spinach can lead to the loss of up to 75% of its vitamin A content. Steaming or microwaving spinach can help preserve more of its vitamin A.
- Carrots:Carrots are a good source of beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. Boiling carrots can result in the loss of some beta-carotene. Steaming or roasting carrots can help preserve more of their beta-carotene content.
- Potatoes:Potatoes are a good source of potassium and vitamin C. Boiling potatoes can lead to the loss of some potassium and vitamin C. Microwaving or baking potatoes can help preserve more of their potassium and vitamin C content.
Cooking and Food Safety
Cooking is a vital step in food preparation, not only for enhancing flavor and texture but also for ensuring food safety. The heat generated during cooking effectively eliminates harmful bacteria and pathogens that can cause foodborne illnesses.
Cooking can significantly impact a food’s nutritional value. For example, steaming vegetables preserves more vitamins than boiling them. And while we’re on the topic of maximizing nutrition, have you ever considered turning last night’s leftovers into a delicious breakfast?
Check out these 5 ways to turn last night’s leftovers into a morning’s breakfast for a quick and healthy start to your day. The same principles of preserving nutrients through mindful cooking apply to leftovers, so you can enjoy a nutritious and flavorful breakfast without sacrificing any of the goodness from the previous night’s meal.
The Importance of Cooking to Kill Harmful Bacteria and Pathogens
Foodborne illnesses, commonly known as food poisoning, are caused by consuming food contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins. These microorganisms can thrive in raw or undercooked foods, posing a serious threat to human health. Proper cooking plays a crucial role in eliminating these pathogens and preventing foodborne illnesses.
You know how cooking can really change the nutritional value of food, right? Like, steaming veggies is better than frying them. And speaking of pushing your limits, have you ever considered ultra walking? It’s like a marathon, but on foot! You can find everything you need to know about ultra walking on this amazing website: everything you need to know about ultra walking.
Anyway, back to food. It’s all about making smart choices in the kitchen to get the most out of your meals, just like you’d strategize for an ultra walk!
Cooking Temperature and Food Safety
Cooking food to the appropriate internal temperature is essential for killing harmful microorganisms. Different types of food require different temperatures and cooking times to ensure safety. The minimum internal temperature for safe cooking varies depending on the food type. For instance, poultry should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C), while ground meat should reach 160°F (71°C).
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) provides detailed guidelines on safe cooking temperatures for various food types.
Examples of Foodborne Illnesses Prevented by Proper Cooking
Numerous foodborne illnesses can be prevented by proper cooking. Some common examples include:
- Salmonella:This bacteria is often found in raw poultry, eggs, and meat. Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps. Proper cooking, especially to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) for poultry, effectively eliminates Salmonella.
- E. coli:This bacteria can be found in undercooked ground beef and contaminated produce. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and vomiting. Cooking ground beef to an internal temperature of 160°F (71°C) helps prevent E. coli infection.
- Campylobacter:This bacteria is commonly found in raw poultry and unpasteurized milk. Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps. Cooking poultry to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) eliminates Campylobacter.
- Listeria:This bacteria can be found in soft cheeses, deli meats, and raw sprouts. Symptoms include fever, muscle aches, and headache. Cooking foods that may contain Listeria to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) can help prevent infection.
Cooking Techniques for Nutrient Preservation

Choosing the right cooking method can significantly impact the nutritional value of your food. While cooking transforms raw ingredients into palatable meals, it can also lead to the loss of essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Understanding the effects of different cooking techniques on nutrient retention is crucial for maximizing the nutritional benefits of your meals.
Cooking can significantly affect the nutritional content of food, sometimes for the better and sometimes for the worse. While grilling can lock in nutrients, boiling can leach them out. To ensure you’re getting the most out of your meals, it’s essential to choose cooking methods that preserve nutrients.
And, to fuel your healthy cooking endeavors, try this quick and effective 9-minute total body bodyweight workout – it’s a great way to boost your energy levels and get ready to whip up a nutritious feast!
Cooking Techniques and Nutrient Retention
The following table Artikels various cooking methods and their impact on nutrient retention, highlighting advantages and disadvantages:
| Cooking Method | Nutrient Retention | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steaming | High | Preserves vitamins, minerals, and flavor; requires minimal fat; gentle cooking method suitable for delicate foods | Can take longer than other methods; may not be suitable for all foods |
| Boiling | Moderate | Simple and quick; suitable for vegetables, legumes, and grains; can be used to prepare soups and stews | Can leach water-soluble vitamins and minerals into the cooking water; may result in overcooked food |
| Stir-frying | Moderate to High | Quick cooking time; preserves texture and flavor; requires minimal oil | May require higher heat, which can lead to nutrient loss if not done correctly; not suitable for all foods |
| Microwaving | Moderate | Fast and convenient; uses minimal energy; can preserve some nutrients | Can lead to uneven cooking; may result in nutrient loss, especially for water-soluble vitamins |
| Baking | Moderate | Produces even cooking; suitable for meat, poultry, and vegetables; can be used to create baked goods | Can lead to nutrient loss, especially for water-soluble vitamins; may require longer cooking times |
| Roasting | Moderate | Produces flavorful and tender results; suitable for meat, poultry, and vegetables; can be used to create roasts and casseroles | Can lead to nutrient loss, especially for water-soluble vitamins; may require longer cooking times |
| Grilling | Moderate | Adds flavor and char; suitable for meat, poultry, and vegetables; can be used to create kebabs and burgers | Can lead to nutrient loss, especially for water-soluble vitamins; may produce harmful compounds at high temperatures |
| Deep-frying | Low | Produces crispy texture; suitable for various foods; can be used to create fried chicken, fries, and onion rings | High in fat and calories; can lead to significant nutrient loss; may produce harmful compounds at high temperatures |
Cooking and Dietary Guidelines
Cooking plays a crucial role in our health and well-being by influencing the nutritional value of food. It is a key factor in maintaining a healthy diet and meeting our daily nutritional needs. Understanding how cooking impacts nutrient content and adhering to dietary guidelines can significantly contribute to our overall health.
Cooking Recommendations for a Healthy Diet, How cooking impacts foods nutrition levels
Dietary guidelines emphasize the importance of consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods prepared using methods that preserve their nutritional value. They recommend limiting processed foods, saturated and trans fats, added sugars, and sodium. Cooking at home allows for greater control over ingredients and cooking methods, enabling us to make healthier choices.
The Role of Cooking in Meeting Daily Nutritional Needs
Cooking is essential for meeting our daily nutritional needs. By preparing meals at home, we can incorporate a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats. Cooking allows us to control portion sizes, adjust seasonings, and experiment with different recipes to create meals that are both nutritious and enjoyable.
Cooking Practices Aligned with Dietary Guidelines
- Prioritize Whole Foods:Focus on incorporating whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and legumes into your diet.
- Minimize Processing:Choose minimally processed foods and avoid highly processed foods, such as packaged snacks, fast food, and sugary drinks.
- Limit Added Sugars:Reduce the consumption of added sugars found in processed foods, sweetened beverages, and desserts.
- Control Sodium Intake:Reduce the use of salt in cooking and choose low-sodium options when available.
- Embrace Healthy Fats:Include healthy fats like those found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds in your diet.
- Cook with Flavor:Use herbs, spices, and citrus fruits to add flavor to your dishes without relying on excessive salt or sugar.
- Practice Portion Control:Pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating.
Last Point

By understanding the impact of cooking on nutrition, we can make informed choices in the kitchen to maximize the nutritional value of our food. Whether you’re a seasoned chef or a beginner in the culinary world, this knowledge empowers you to cook meals that are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients.
From choosing the right cooking methods to selecting ingredients wisely, we can all take steps to enhance the nutritional quality of our diets and promote overall well-being.






