Need to Know: The Latest Nutrition Label Explained
Need know latest nutrition label – Need to know the latest nutrition label? You’re not alone. The FDA recently updated the nutrition label on food packaging, making it easier to understand and use. This new label provides valuable information about the nutrients in the food you eat, helping you make healthier choices.
The updated label features a more prominent emphasis on added sugars, which can help consumers become more aware of their intake. It also includes a clearer presentation of serving sizes, which can be particularly helpful for understanding how much you are actually consuming.
Understanding the New Nutrition Label
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has revamped the Nutrition Facts label to provide consumers with a clearer and more comprehensive understanding of the nutritional content of food products. This update reflects the evolving understanding of nutrition and the importance of making informed food choices.
Key Changes to the Nutrition Label
The new label features several key changes that aim to make nutritional information more accessible and relevant to consumers. These changes include:
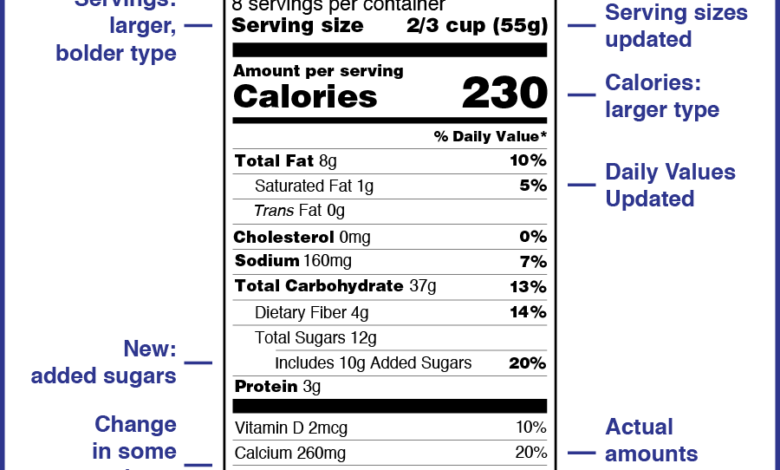
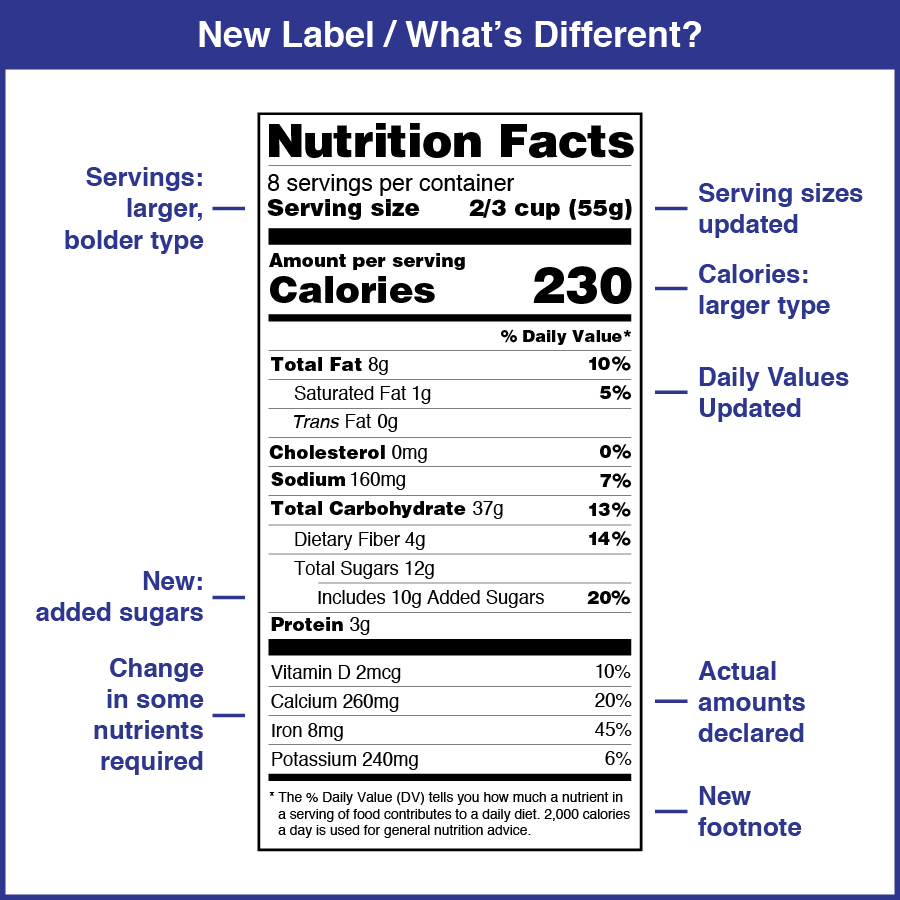
- Larger Type for Calories and Serving Size:The calorie count and serving size are now displayed in larger, bolder type to emphasize their importance in dietary planning.
- Updated Daily Values (DV):The daily values for nutrients have been revised to reflect current dietary recommendations, providing a more accurate guide for consumers.
- Added Sugars:The label now includes a separate line for “Added Sugars” to highlight the amount of sugar added to food products during processing. This information helps consumers make more informed choices about added sugars in their diets.
- Updated Vitamin D and Potassium:The label now requires the declaration of vitamin D and potassium, reflecting their importance for overall health.
- New “Percent Daily Value” (DV):The label now uses the term “Percent Daily Value” (DV) instead of “Percent Daily Value” (DV) to better reflect the meaning of this information. The DV represents the percentage of a nutrient that a serving of food contributes to a daily diet.
Sections of the New Nutrition Label
The new nutrition label is divided into several sections, each providing valuable information about the nutritional content of the food product:
- Serving Size:This section specifies the amount of food that constitutes a single serving. It’s important to note that serving sizes can vary significantly across different food products, so it’s essential to pay close attention to this information.
- Calories:This section displays the total number of calories in a single serving of the food product. Calories are the units of energy that our bodies derive from food.
- Nutrients:This section lists the amounts of various nutrients per serving, including:
- Total Fat:This includes saturated and unsaturated fats, which play different roles in health. Saturated fat is generally considered less healthy than unsaturated fat.
- Cholesterol:This nutrient is found in animal products and can contribute to heart disease.
- Sodium:This mineral is essential for bodily functions but excessive sodium intake can increase blood pressure.
- Total Carbohydrates:This includes sugars, starches, and fiber. Fiber is essential for digestive health and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Dietary Fiber:This is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest, but it plays an important role in digestion and overall health.
- Total Sugars:This includes naturally occurring sugars and added sugars. Added sugars are sugars that are added to food products during processing.
- Protein:This is an essential nutrient that helps build and repair tissues, and it plays a role in many bodily functions.
- Vitamin D:This vitamin is important for bone health and calcium absorption.
- Potassium:This mineral is essential for maintaining blood pressure and muscle function.
- Percent Daily Value (%DV):This section shows the percentage of each nutrient in a serving of the food product that contributes to a daily diet. The DV is based on a 2,000-calorie diet.
Understanding the New Nutrition Label: A Closer Look
The new nutrition label provides consumers with a wealth of information about the nutritional content of food products. By understanding the key changes and the various sections of the label, consumers can make more informed food choices that support their overall health and well-being.
Key Components of the Nutrition Label
The new Nutrition Label is designed to be more user-friendly and informative, helping you make healthier food choices. It features several key components that provide valuable insights into the nutritional content of packaged foods. Understanding these components empowers you to make informed decisions about what you eat.
Serving Sizes
Serving sizes are the foundation of understanding the nutritional information on a food label. They represent the amount of food that is typically consumed in one sitting. The serving size listed on the label is not always the amount you actually eat, so it’s crucial to pay attention to the number of servings per container.
For example, a bag of chips may have 10 servings, but you might eat more than that in one sitting. In this case, you’ll need to multiply the nutritional values on the label by the number of servings you consume to get an accurate picture of your total intake.
Calories
Calories represent the energy provided by food. The new label prominently displays the total calories per serving, making it easy to track your daily calorie intake. This is especially helpful for managing weight or following a specific diet plan.
Nutrients
The Nutrition Label lists a variety of nutrients, categorized as either “required” or “added.” Required nutrients are those that are naturally present in the food, while added nutrients are those that have been added during processing. Understanding the different types of nutrients listed on the label is essential for making informed choices.
- Macronutrients: These are the nutrients that your body needs in large amounts, including carbohydrates, protein, and fats. They provide energy and support various bodily functions.
- Micronutrients: These are nutrients that your body needs in smaller amounts, including vitamins and minerals. They play crucial roles in maintaining overall health and well-being.
- Added Sugars: The new label highlights added sugars, which are sugars that have been added to food during processing. Consuming too much added sugar can contribute to weight gain and other health problems.
- Dietary Fiber: Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that your body cannot digest. It plays a vital role in digestive health and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Daily Values (DV)
Daily Values (DV) are a reference standard that helps you understand the nutritional content of a food in relation to your overall daily intake. The updated DV for essential nutrients are listed on the new Nutrition Label, providing a more accurate and relevant guide for making healthy choices.
| Nutrient | Updated DV |
|---|---|
| Total Fat | 78g |
| Saturated Fat | 20g |
| Cholesterol | 300mg |
| Sodium | 2,300mg |
| Total Carbohydrates | 275g |
| Dietary Fiber | 28g |
| Total Sugars | 50g |
| Added Sugars | 36g |
| Protein | 50g |
| Vitamin D | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
| Calcium | 1,000mg |
| Iron | 18mg |
| Potassium | 4,700mg |
DV are based on a 2,000-calorie diet. Your individual needs may vary.
Decoding the Label’s Information
Now that you understand the basic components of the new nutrition label, let’s dive into how to effectively use this information to make informed choices about your food. The nutrition label is designed to be user-friendly, with key information presented in a clear and concise manner.
Identifying Key Nutritional Information
The new nutrition label highlights key nutrients that contribute to overall health. To quickly identify this information, focus on the following:
- Calories:This is the amount of energy you get from a serving of food.
- Serving Size:This is the amount of food that the nutrition information is based on. It’s crucial to note the serving size as many packaged foods contain multiple servings.
- Total Fat:This includes all types of fat, including saturated and unsaturated fats.
- Sodium:This is the amount of salt in a serving of food.
- Total Carbohydrates:This includes all types of carbohydrates, including sugars, starches, and fiber.
- Sugars:This includes added sugars, which are sugars that are added to foods during processing.
- Protein:This is the amount of protein in a serving of food.
Understanding Added Sugars
Added sugars are a significant concern for public health. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting added sugar intake to less than 10% of your daily calories.
Excessive intake of added sugars can lead to weight gain, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other health problems.
- Examples of added sugars:High-fructose corn syrup, sucrose, glucose, fructose, dextrose, maltose, and lactose.
- Hidden Sugars:Added sugars are often hidden in processed foods, such as breakfast cereals, baked goods, and sweetened beverages.
- Reading the Label:The nutrition label clearly indicates the amount of added sugars per serving.
Making Informed Food Choices
The nutrition label empowers you to make informed food choices based on your individual dietary needs.
- Compare Products:Use the nutrition label to compare different brands and products within the same category.
- Set Dietary Goals:Set realistic dietary goals based on your health and nutritional needs.
- Limit Added Sugars:Choose foods with lower added sugars, particularly if you are trying to manage your weight or reduce your risk of chronic diseases.
- Prioritize Whole Foods:Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that are naturally rich in nutrients.
Benefits of the New Nutrition Label
The updated Nutrition Facts label, implemented by the FDA in 2018, offers several benefits for consumers, helping them make informed decisions about their food choices and potentially contributing to improved public health. This new label presents information in a clearer and more user-friendly way, making it easier for individuals to understand the nutritional content of packaged foods.
Improved Understanding of Serving Sizes
The updated label clearly defines serving sizes, which are often more realistic and closer to what people actually consume. Previously, serving sizes could be misleading, leading consumers to underestimate the total calories and nutrients they were ingesting. The new label provides a more accurate representation of the amount of food people typically eat, making it easier for them to track their calorie and nutrient intake.
Navigating the ever-changing world of nutrition labels can feel overwhelming, but it’s essential for making informed choices about what we put in our bodies. It’s amazing how much information is packed into those tiny boxes, and sometimes, you just need a little extra guidance.
That’s where registered dietitians come in. You might be surprised to learn that their role extends far beyond just telling you what to eat. Check out these 3 surprising takeaways about being a registered dietitian and see how they can help you make sense of the latest nutrition label updates.
Emphasis on Added Sugars
The new label prominently displays the amount of added sugars in a product, making it easier for consumers to identify foods that are high in added sugars. This is crucial because excessive added sugar intake has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
By highlighting added sugars, the label encourages consumers to choose foods with lower amounts of added sugars, promoting healthier dietary choices.
Enhanced Information on Vitamins and Minerals
The updated label provides more detailed information on vitamins and minerals, including the percentage of Daily Value (%DV) for Vitamin D, potassium, and calcium. This information helps consumers understand the nutritional value of foods and make informed decisions about their dietary intake.
It’s so important to be mindful of what’s in our food, especially when we’re trying to make healthy choices. That’s why I always take a close look at the nutrition label, especially when I’m craving pizza! If you’re looking for some guilt-free pizza options, check out this list of 11 healthy pizzas under 400 calories.
After all, knowing what’s in your food helps you make informed choices and enjoy your favorite foods in moderation!
For example, the label may indicate that a product provides a significant percentage of the daily recommended intake of calcium, highlighting its potential contribution to bone health.
It’s super important to stay on top of the latest nutrition label changes, especially when you’re whipping up delicious meals. And speaking of delicious meals, have you explored the world of possibilities with a Dutch oven? From hearty stews to crusty bread, you can find some truly amazing things to do with a Dutch oven right here.
But back to those nutrition labels, knowing what’s in your food is key to making informed choices about what you eat, and that’s something we can all get behind!
Potential Impact on Public Health
The new Nutrition Facts label has the potential to positively impact public health by encouraging healthier food choices. By providing clearer and more comprehensive information about the nutritional content of foods, the label empowers consumers to make informed decisions that can contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Challenges and Limitations
While the new label offers significant benefits, it also presents some challenges and limitations. One limitation is that it does not provide information about the source of the nutrients, such as whether the protein comes from plant-based or animal-based sources.
Another limitation is that the label does not address the potential health risks associated with specific ingredients, such as artificial sweeteners or trans fats. Additionally, the label does not provide guidance on portion sizes or the overall dietary context in which a particular food should be consumed.
Practical Applications: Need Know Latest Nutrition Label
The new nutrition label is more than just a list of numbers; it’s a powerful tool for making informed food choices. By understanding the information presented, you can compare different products, plan healthy meals, and make adjustments to your diet based on your individual needs.
Comparing Food Products
The nutrition label provides a standardized way to compare similar food products. This allows you to choose the option that best fits your dietary goals.
- For example, when choosing between two brands of cereal, you can compare the serving size, calories, and amount of sugar per serving. This will help you determine which cereal is lower in calories and added sugars, aligning with a healthier choice.
- Similarly, when comparing different types of yogurt, you can compare the amount of protein, fat, and calcium per serving. This can help you choose a yogurt that meets your specific nutritional needs.
Planning Healthy Meals and Snacks
The nutrition label can be used to plan healthy meals and snacks by ensuring you’re consuming the right amount of calories, nutrients, and added sugars.
- You can use the label to estimate how much of a particular food you need to eat to meet your daily nutrient needs. For example, if you’re looking to increase your intake of fiber, you can choose foods that are high in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- The label can also help you identify foods that are high in added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium. These are nutrients that should be limited in a healthy diet. By making informed choices based on the nutrition label, you can create a balanced and nutritious meal plan.
Tips for Reading and Interpreting the Label Effectively, Need know latest nutrition label
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Pay attention to serving size. | The nutrition information is provided per serving, so make sure you understand how many servings are in the entire package. |
| Look at the % Daily Value. | The % Daily Value tells you how much of a nutrient a serving provides compared to a 2,000 calorie diet. This can help you determine if a food is high or low in a particular nutrient. |
| Focus on the nutrients you want to increase or decrease. | If you’re trying to eat more fiber, look for foods that are high in fiber. If you’re trying to reduce your intake of saturated fat, choose foods that are low in saturated fat. |
| Don’t be afraid to ask questions. | If you’re unsure about something on the nutrition label, don’t hesitate to ask a nutritionist, registered dietitian, or healthcare provider for clarification. |
Final Thoughts
By understanding the latest nutrition label, you can become a more informed consumer, making healthier choices for yourself and your family. The new label empowers you to take control of your dietary habits, promoting a healthier lifestyle overall.






