Make the Mediterranean Diet Low Carb Friendly
Ways to make the Mediterranean diet low carb friendly can seem like a culinary puzzle, but it’s a delicious one! The Mediterranean diet, known for its abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, is often praised for its heart-healthy benefits.
However, if you’re looking to reduce your carbohydrate intake, you might wonder how to adapt this beloved dietary approach.
The good news is that you can enjoy the delicious flavors and health benefits of the Mediterranean diet while adhering to a low-carb lifestyle. This means making some strategic swaps, embracing low-carb alternatives, and understanding the nuances of this dietary combination.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of low-carb Mediterranean eating, uncovering tips, tricks, and recipes to make it work for you.
Understanding the Mediterranean Diet and Low-Carb Principles
The Mediterranean diet and low-carb diets are both popular approaches to healthy eating, each with its own set of principles and benefits. Understanding their key components can help you decide which approach might be best for your health goals.
So you want to enjoy the delicious flavors of the Mediterranean diet but keep your carb intake low? It’s definitely doable! Focus on plenty of healthy fats like olive oil and avocados, and load up on protein from fish, seafood, and lean meats.
Remember, though, that even on a low-carb diet, why quality of carbs matters – choose whole grains like quinoa and brown rice in moderation, and opt for plenty of fiber-rich veggies. You can even enjoy a small portion of fruit for a sweet treat! With a little planning, you can enjoy the benefits of the Mediterranean diet while staying low-carb.
Mediterranean Diet Components
The Mediterranean diet is a way of eating inspired by the traditional dietary patterns of people living in the Mediterranean region, particularly in Greece, Italy, and Spain. It emphasizes consuming whole, unprocessed foods, with a focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Here are some key components of the Mediterranean diet:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Consumed in abundance, providing vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Include whole wheat bread, pasta, brown rice, and quinoa, providing fiber and complex carbohydrates.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and other nutrients.
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil is the primary fat source, providing monounsaturated fatty acids beneficial for heart health.
- Nuts and Seeds: Provide healthy fats, protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals.
- Fish and Seafood: Consumed at least twice a week, providing omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and other essential nutrients.
- Poultry and Eggs: Consumed in moderation, offering lean protein and other nutrients.
- Dairy Products: Consumed in moderation, primarily in the form of yogurt and cheese.
- Red Meat and Sweets: Consumed sparingly, as they are considered less healthy options.
Low-Carb Diet Principles
Low-carb diets focus on significantly reducing carbohydrate intake, often replacing it with increased protein and fat consumption. The primary goal is to induce a metabolic state called ketosis, where the body starts burning fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. Key principles of a low-carb diet include:
- Limited Carbohydrate Intake: Typically restricts carbohydrates to 20-50 grams per day, depending on the specific diet plan.
- Increased Protein Consumption: Emphasizes lean protein sources like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
- Healthy Fat Sources: Includes avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, providing essential fatty acids and energy.
- Focus on Non-Starchy Vegetables: Promotes consumption of leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, and other low-carb vegetables.
- Limited Processed Foods and Sugars: Avoids refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, and processed foods high in carbohydrates.
Macronutrient Profiles
The Mediterranean diet and low-carb diets differ significantly in their macronutrient profiles:
| Macronutrient | Mediterranean Diet | Low-Carb Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 45-65% | 5-20% |
| Protein | 15-20% | 20-35% |
| Fat | 20-35% | 50-75% |
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes a balanced intake of all macronutrients, while low-carb diets prioritize protein and fat, significantly reducing carbohydrates.
Identifying High-Carb Foods in the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is known for its abundance of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are naturally high in carbohydrates. While these foods are nutritious, a low-carb approach might require adjustments to the traditional Mediterranean diet.
Identifying High-Carb Foods
Here’s a table listing common Mediterranean diet foods and their carbohydrate content per serving:
| Food | Serving Size | Carbohydrates (grams) |
|---|---|---|
| Whole Wheat Bread | 1 slice | 15 |
| Rice | 1/2 cup cooked | 22 |
| Pasta | 1 cup cooked | 45 |
| Couscous | 1/2 cup cooked | 20 |
| Fruit (e.g., Apples, Bananas, Grapes) | 1 medium | 15-25 |
| Legumes (e.g., Chickpeas, Lentils, Beans) | 1/2 cup cooked | 15-20 |
| Potatoes | 1 medium | 20 |
Foods like bread, rice, pasta, couscous, and fruit are typically high in carbohydrates. While they offer valuable nutrients, limiting their intake is crucial for a low-carb approach.
Low-Carb Substitutes
Here are some low-carb substitutes for high-carb Mediterranean foods:* Bread:Swap white bread for low-carb alternatives like cauliflower bread, almond flour bread, or flaxseed bread.
Making the Mediterranean diet low carb friendly is all about focusing on protein and healthy fats while limiting carbs. This can be a great way to manage your weight and feel energized, but it’s important to be mindful of how dietary changes can impact your mental well-being.
For example, common types of anxiety and how to cope with stress and anxiety can be more effectively addressed with a holistic approach, which includes a balanced diet. So, while limiting carbs can be beneficial, it’s crucial to ensure you’re still getting the nutrients your body needs to thrive, both physically and mentally.
Rice Opt for cauliflower rice, zucchini noodles, or shirataki noodles.
Pasta Use zucchini noodles, spaghetti squash, or kelp noodles instead of traditional pasta.
Couscous Explore alternatives like quinoa or cauliflower couscous.
Fruit Choose low-carb fruits like berries or avocados.
Legumes Limit the intake of legumes, or choose low-carb alternatives like edamame or green beans.
Potatoes Substitute with sweet potatoes, turnips, or rutabagas.
By making these substitutions, you can enjoy the flavors of the Mediterranean diet while keeping your carbohydrate intake in check.
Incorporating Low-Carb Alternatives
The beauty of the Mediterranean diet lies in its flexibility. You can easily adapt it to fit your dietary needs, including a low-carb approach. This involves making smart substitutions and prioritizing protein and healthy fats.
Low-Carb Mediterranean Recipes
Here are some low-carb versions of popular Mediterranean dishes, focusing on substituting high-carb ingredients with low-carb alternatives:* Greek Salad with Zucchini Noodles:Replace traditional pasta with zucchini noodles for a lighter, lower-carb option. Combine zucchini noodles with chopped cucumbers, tomatoes, red onion, olives, and feta cheese.
Dress it with a simple lemon vinaigrette.
Cauliflower Rice Paella Swap traditional rice with cauliflower rice for a lower-carb version of this classic Spanish dish. Sauté onions, garlic, and bell peppers, then add cauliflower rice, chicken or seafood, and saffron. Season with salt, pepper, and paprika.
Lentil Soup with Spinach Lentils are a great source of protein and fiber. Make a hearty soup by simmering lentils with vegetable broth, chopped onions, carrots, and celery. Add spinach at the end for a boost of nutrients.
Baked Salmon with Roasted Vegetables A simple and satisfying dish. Roast salmon with broccoli, asparagus, and bell peppers. Season with herbs like rosemary, thyme, and oregano.
One of the best ways to make the Mediterranean diet low-carb friendly is by focusing on protein and healthy fats. This is where soups come in! You can find some delicious and satisfying recipes in this article on 9 hearty winter soups under 360 calories.
And remember, even though you’re limiting carbs, make sure to include plenty of vegetables in your diet to get all the essential vitamins and minerals.
Chicken Skewers with Lemon-Herb Marinade Marinate chicken cubes in a blend of lemon juice, olive oil, garlic, oregano, and salt. Thread the marinated chicken onto skewers and grill or bake.
Increasing Protein and Healthy Fats
To maintain a balanced low-carb Mediterranean diet, it’s essential to increase protein and healthy fat intake. * Prioritize Protein:Include lean protein sources like chicken, fish, seafood, eggs, and legumes (in moderation) in your meals.
Healthy Fat Sources Incorporate olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds. These sources provide essential fatty acids and contribute to satiety.
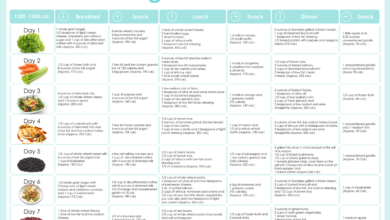
Sample Low-Carb Mediterranean Meal Plan, Ways to make the mediterranean diet low carb friendly
Here’s a sample meal plan that demonstrates a balanced low-carb Mediterranean diet for a day:* Breakfast:Scrambled eggs with spinach and feta cheese.
Lunch Greek salad with zucchini noodles and grilled chicken breast.
Dinner Baked salmon with roasted vegetables and a side of quinoa (in moderation).
Snacks A handful of almonds, sliced avocado with lemon juice and salt, or a hard-boiled egg.
Addressing Potential Nutrient Deficiencies
While the Mediterranean diet is generally considered a healthy and balanced eating plan, transitioning to a low-carb version might lead to potential nutrient deficiencies. It’s crucial to understand these potential shortcomings and adopt strategies to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients.
Fiber Intake
Fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet, contributing to digestive health, blood sugar control, and overall well-being. However, the low-carb Mediterranean diet may limit fiber intake due to the restriction of high-fiber carbohydrates like whole grains and legumes.
To address this, prioritize consuming plenty of low-carb vegetables like broccoli, spinach, Brussels sprouts, and asparagus, which are rich in fiber. Additionally, incorporating nuts, seeds, and avocado can further boost your fiber intake.
Benefits and Considerations: Ways To Make The Mediterranean Diet Low Carb Friendly
Adopting a low-carb Mediterranean diet offers a unique approach to reaping the benefits of the traditional Mediterranean diet while potentially enhancing weight management and blood sugar control. This approach can also potentially reduce the risk of chronic diseases. However, like any dietary approach, it’s crucial to understand the potential drawbacks and considerations before embarking on this journey.
Potential Health Benefits
A low-carb Mediterranean diet can offer numerous health benefits due to its emphasis on nutrient-rich foods and its lower carbohydrate content.
- Weight Management:By reducing carbohydrate intake, this dietary approach can lead to a decrease in insulin levels, potentially promoting fat burning and weight loss. Studies have shown that low-carb diets can be effective for weight management, particularly in the short term.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control:The lower carbohydrate content of this diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels, potentially benefiting individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk. This can lead to better insulin sensitivity and improved blood sugar control.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:The abundance of fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats in the Mediterranean diet can contribute to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and some types of cancer.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While a low-carb Mediterranean diet offers potential benefits, it’s essential to consider its potential drawbacks:
- Nutrient Deficiencies:Restricting carbohydrates can limit the intake of essential nutrients, such as fiber, certain vitamins (B vitamins, vitamin E), and minerals (magnesium, potassium). Careful planning and supplementation may be necessary to ensure adequate intake of these nutrients.
- Potential Side Effects:Some individuals may experience side effects when initially transitioning to a low-carb diet, such as fatigue, headaches, and constipation. These effects typically subside as the body adapts. It’s important to listen to your body and adjust the diet as needed.
- Sustainability:Maintaining a low-carb Mediterranean diet can be challenging in the long term, especially if social gatherings or travel involve foods that don’t align with the dietary approach. Planning ahead and finding ways to incorporate the diet into social settings can improve sustainability.
Tips for a Sustainable Low-Carb Mediterranean Lifestyle
- Focus on Whole Foods:Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This foundation ensures a balanced intake of nutrients.
- Choose Low-Carb Alternatives:Explore low-carb substitutes for high-carb foods, such as cauliflower rice for white rice or zucchini noodles for pasta. This allows you to enjoy familiar flavors and textures while staying within your dietary guidelines.
- Plan Ahead:Prepare meals and snacks in advance to avoid impulsive choices and ensure you have healthy options readily available. This can help maintain consistency and prevent cravings.
- Listen to Your Body:Pay attention to your body’s signals and adjust your diet as needed. If you experience any adverse effects, consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for guidance.
Closure
By making conscious choices and embracing low-carb alternatives, you can enjoy the benefits of a Mediterranean diet while managing your carbohydrate intake. It’s a delicious journey that prioritizes your health and well-being, allowing you to savor the flavors of the Mediterranean region while staying true to your dietary goals.
Remember, a low-carb Mediterranean diet is a personalized approach, so listen to your body, consult with a healthcare professional, and enjoy the journey of creating a healthier and happier you.